Abstract
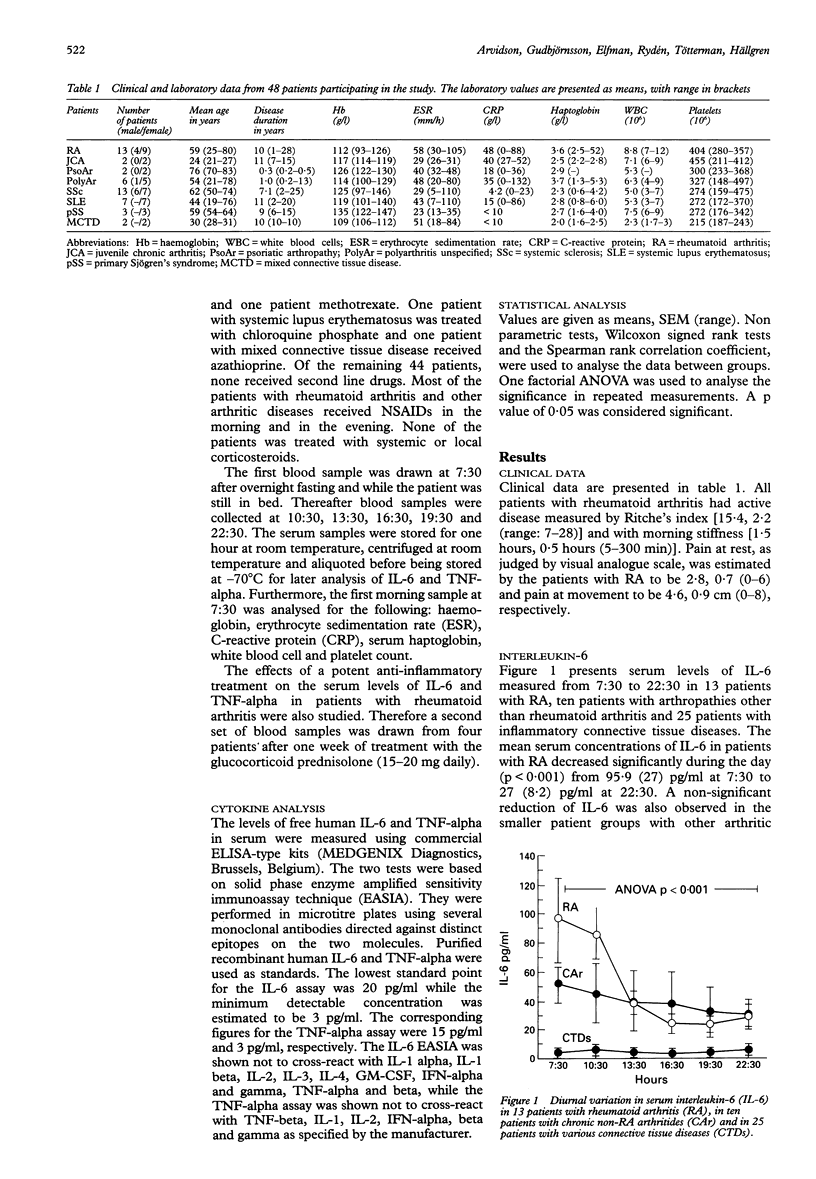
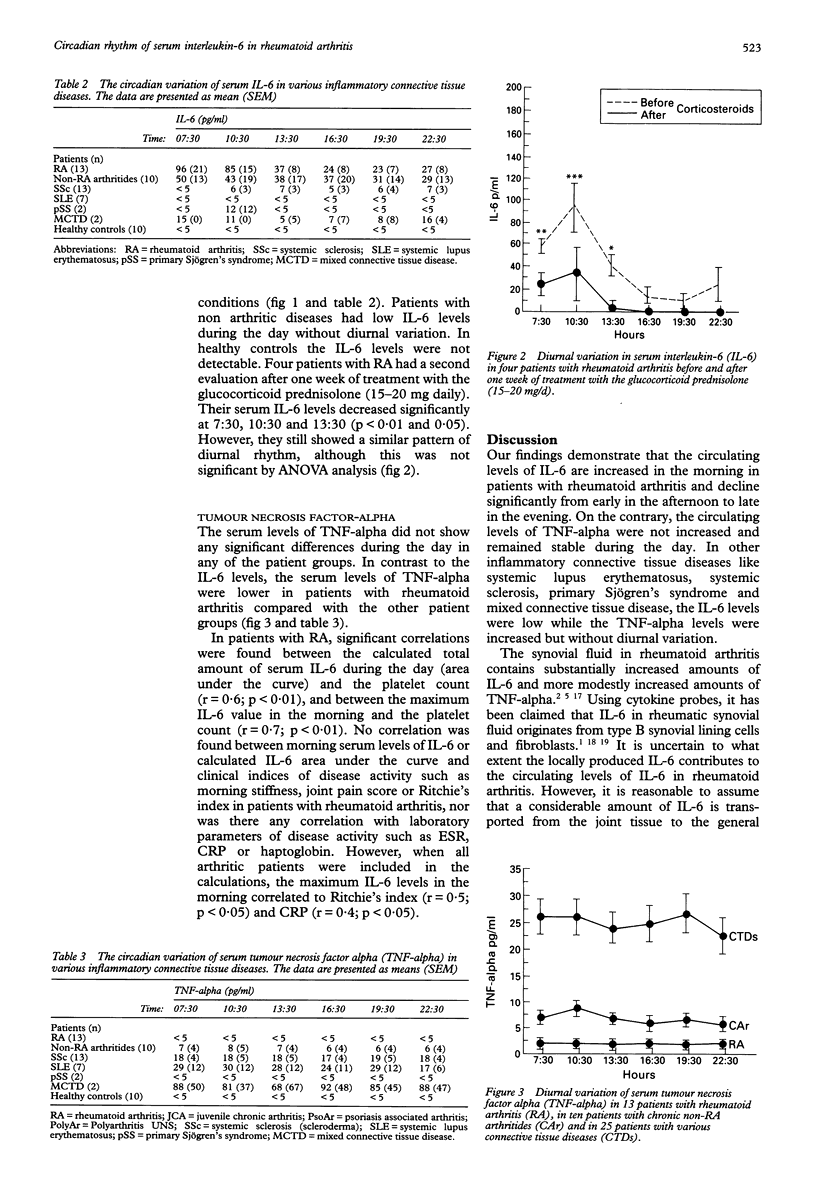
OBJECTIVES--To test the hypothesis of a diurnal variation in circulating levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and/or tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory connective tissue diseases. METHODS--Serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha were measured at three hour intervals from 7:30 to 22:30 in 48 patients with different rheumatic diseases as well as ten healthy controls. In four of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis, serum IL-6 levels were measured before and after one week of treatment with prednisolone 15-20 mg daily. RESULTS--IL-6 and TNF-alpha could not be detected in serum from healthy controls. However, serum IL-6 levels were substantially increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Furthermore, patients with rheumatoid arthritis showed a statistically significant circadian variation in levels of IL-6. Peak values appeared in the morning and low values in the afternoon and evening. In contrast, levels were low and stable in other connective tissue diseases. Levels of TNF-alpha were low in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and high in patients with other connective tissue diseases, but without circadian rhythm. After treatment with prednisolone, levels of serum IL-6 decreased significantly, but the circadian rhythm remained. CONCLUSIONS--The circadian rhythm of circulating IL-6 might correspond to the circadian rhythm of symptoms in rheumatoid arthritis. The diurnal variation of IL-6, and possibly other cytokines, might explain the conflicting results previously reported on the inter-relationship between circulating IL-6 levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj N., Santhanam U., Lau L. L., Tatter S. B., Ghrayeb J., Rivelis M., Steinman R. M., Sehgal P. B., May L. T. IL-6/IFN-beta 2 in synovial effusions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthritides. Identification of several isoforms and studies of cellular sources. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2153–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Petrou P., Kingsley G., Chrousos G., Panayi G. S. Defective hypothalamic response to immune and inflammatory stimuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1281–1288. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Hällgren R. Circulating hyaluronic acid levels vary with physical activity in healthy subjects and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Relationship to synovitis mass and morning stiffness. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Dec;30(12):1333–1338. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerne P. A., Zuraw B. L., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Synovium as a source of interleukin 6 in vitro. Contribution to local and systemic manifestations of arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):585–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI113921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. J., Warren M. K., Levin J. Stimulation of thrombopoiesis in mice by human recombinant interleukin 6. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1242–1247. doi: 10.1172/JCI114559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Turner M., Miyasaka N., Buchan G., Tang B., Sato K., Shimizu M., Maini R., Feldmann M. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I., Cooper R. G., Denton J., Meager A., Hopkins S. J. Cytokine inter-relationships and their association with disease activity in arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;31(11):725–733. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.11.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Yokoi T., Takano N., Kanegane H., Yachie A., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. Detection by in situ hybridization and phenotypic characterization of cells expressing IL-6 mRNA in human stimulated blood. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1317–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.2457950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhok R., Crilly A., Watson J., Capell H. A. Serum interleukin 6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis: correlations with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Mar;52(3):232–234. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.3.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicourt D. H., Triki R., Fukuda K., Devogelaer J. P., Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C., Thonar E. J. Levels of circulating tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Relationship to serum levels of hyaluronan and antigenic keratan sulfate. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Apr;36(4):490–499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa T., Orita T., Matsushita J., Tsuchiya M., Neichi T., Imazeki I., Imai N., Ochi N., Kanma H., Abe T. Thrombopoietic activity of human interleukin-6. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 29;260(2):176–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale M. L., Williams B. D., Matthews N. Tumour necrosis factor activity in joint fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Apr;28(2):104–108. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., DeForge L. E., Sullivan J. F., Showell H. J. Profile of cytokines in synovial fluid specimens from patients with arthritis. Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and IL-6 correlate with inflammatory arthritides. Immunol Invest. 1992 Jul;21(4):321–327. doi: 10.3109/08820139209069371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Cugnini R., Tara D. C., Hefeneider S., Ansel J. C. Production and modulation of interleukin 6 synthesis by synoviocytes derived from patients with arthritic disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Feb;51(2):198–202. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., van Rooyen A., Nieuwenhuis E., Aarden L. A. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatic diseases. Scand J Rheumatol. 1988;17(6):469–474. doi: 10.3109/03009748809098809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Kaufmann C., Espevik T., Husby G. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid from patients with arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):394–398. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Benedetti F., Massa M., Robbioni P., Ravelli A., Burgio G. R., Martini A. Correlation of serum interleukin-6 levels with joint involvement and thrombocytosis in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1158–1163. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


