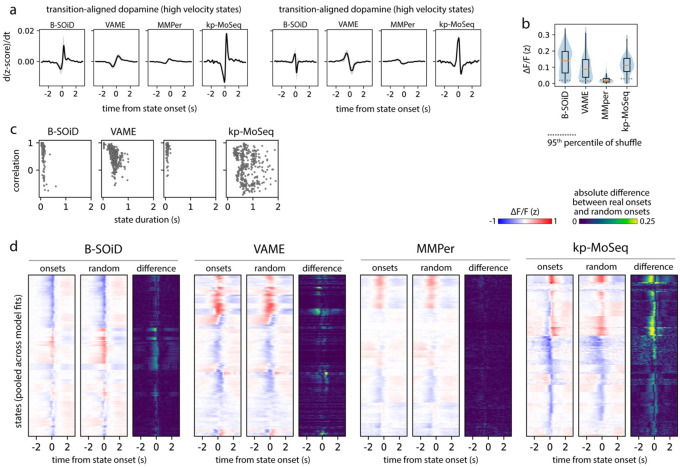
Extended Data Figure 6: Striatal dopamine fluctuations are enriched at keypoint-MoSeq syllable onsets.
a) Keypoint-MoSeq best captures dopamine fluctuations for both high- and low-velocity behaviors. Derivative of the dopamine signal aligned to the onsets of high velocity or low velocity behavior states. States from each method were classified evenly as high or low velocity based on the mean centroid velocity during their respective frames. b) Distributions capturing the average of the dopamine signal across states from each method. c-d) Keypoint-MoSeq syllable onsets are meaningful landmarks for neural data analysis. c) Relationship between state durations and correlations from Fig 5f, showing that the impact of randomization is not a simple function of state duration. d) Average dopamine fluctuations aligned to state onsets (left) or aligned to random frames throughout the execution of each state (middle), as well as the absolute difference between the two alignment approaches (right), shown for each unsupervised behavior segmentation approach.