Abstract
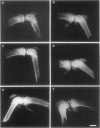
OBJECTIVES--To investigate the time course of a monoarthritis induced with the purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD) or a recombinant 65 kDa heat shock protein (rhsp65) in two different strains of sensitised rats. METHODS--Wistar and Lewis rats, sensitised with heat killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis in oil, were challenged intraarticularly with PPD or rhsp65 and monitored for six weeks. Inflammation was assessed by joint swelling, histology, and radiographic studies. RESULTS--Sensitised Lewis rats injected with PPD or rhsp65 showed a chronic response with recurrent spontaneous flares, while Wistar rats showed one inflammatory episode. CONCLUSIONS--The Wistar strain response to PPD resembles a transient reactive arthritis, while the response of the Lewis strain mimics the relapsing nature of rheumatoid synovitis, providing an interesting model to determine dominant immunopathogenic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderton S. M., van der Zee R., Goodacre J. A. Inflammation activates self hsp60-specific T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham M. E., Carney S., Butler R., Colston M. J. A mycobacterial 65-kD heat shock protein induces antigen-specific suppression of adjuvant arthritis, but is not itself arthritogenic. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):339–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Petrou P., Kingsley G., Chrousos G., Panayi G. S. Defective hypothalamic response to immune and inflammatory stimuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1281–1288. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. L., Cuttino J. T., Jr, Anderle S. K., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Radiologic analysis of arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cell walls. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jan;22(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Holoshitz J., van Eden W., Frenkel A. T lymphocyte clones illuminate pathogenesis and affect therapy of experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):841–845. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daynes R. A., Araneo B. A. Contrasting effects of glucocorticoids on the capacity of T cells to produce the growth factors interleukin 2 and interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2319–2325. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice G., Gervaix A., Costantino P., Wyler C. A., Tougne C., de Graeff-Meeder E. R., van Embden J., van der Zee R., Nencioni L., Rappuoli R. Priming to heat shock proteins in infants vaccinated against pertussis. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):2025–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Sercarz E. How some T cells escape tolerance induction. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):183–185. doi: 10.1038/342183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Bailey L. C., Bacon P. A. In vitro responses to a 65-kilodalton mycobacterial protein by synovial T cells from inflammatory arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2494–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Granfors K., Merilahti-Palo R., Bailey L., Consalvey S., Toivanen A., Bacon P. A. Synovial T lymphocyte recognition of organisms that trigger reactive arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jun;76(3):348–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Jenner P. J., Colston M. J., Bacon P. A. Recognition of a mycobacteria-specific epitope in the 65-kD heat-shock protein by synovial fluid-derived T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):831–841. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L. What can we learn about rheumatoid arthritis from animal models? Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(3):315–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00197310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijsen M. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Sequential alterations of periarticular structures in antigen-induced arthritis in mice. Histological observations on fibrous capsule, ligaments, bone and muscles, using whole joint sections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1983 Jun;64(3):298–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. I., Kingston A. E., Estrada I., Colston M. J. Heterologous expression of the 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium leprae and murine T-cell responses to the gene product. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1237–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1237-1241.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., van den Bersselaar L. Flare-up of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after challenge with oral antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):364–371. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Bachmann S., Munoz S. R., Schwab J. H., Bender D. E., Sartor R. B., Lemasters J. J. Bacterial cell wall polymers (peptidoglycan-polysaccharide) cause reactivation of arthritis. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4645–4653. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4645-4653.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lussow A. R., Barrios C., van Embden J., Van der Zee R., Verdini A. S., Pessi A., Louis J. A., Lambert P. H., Del Giudice G. Mycobacterial heat-shock proteins as carrier molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2297–2302. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch J., Lydyard P. M., Rook G. A. Rheumatoid arthritis: how well do the theories fit the evidence? Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Apr;92(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. E. Infectious agents in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;16(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(86)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P. C., Schaar C. G., Breedveld F. C., van Eden W., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R., de Vries R. R. Synovial fluid T cell reactivity against 65 kD heat shock protein of mycobacteria in early chronic arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Lydyard P. M., Stanford J. L. A reappraisal of the evidence that rheumatoid arthritis and several other idiopathic diseases are slow bacterial infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Mar;52 (Suppl 1):S30–S38. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.suppl_1.s30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J., Wu P., Kingsley G. T cells are responsible for the enhanced synovial cellular immune response to triggering antigen in reactive arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):96–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Hill J. M., Chrousos G. P., Kamilaris T., Listwak S. J., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. Inflammatory mediator-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation is defective in streptococcal cell wall arthritis-susceptible Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symmons D. P., Chakravarty K. Can immunisation trigger rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Dec;52(12):843–844. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.12.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Dauwerse H. G., Das P. K., Groothuis D. G., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D. Cloning of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA and expression of antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):800–806. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.800-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfa G., Rook G. A., Bahr G. M., Sattar M. A., Behbehani K., Young D. B., Mehlert A., Van-Embden J. D., Hay F. C., Isenberg D. A. Elevated IgG antibody levels to the mycobacterial 65-kDa heat shock protein are characteristic of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Nov;30(5):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyakarnam A., Lachmann P. J., Sia D. Y. The killing of tumour cell targets coupled to tuberculin (PPD) by human and murine PPD-reactive T helper clones. I. PPD specificity of killing. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Mar;27(3):337–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winrow V. R., Ragno S., Morris C. J., Colston M. J., Mascagni P., Leoni F., Gromo G., Coates A. R., Blake D. R. Arthritogenic potential of the 65 kDa stress protein--an experimental model. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Mar;53(3):197–201. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.3.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., Gasser J., Feige U. Prevention of adjuvant arthritis in rats by a nonapeptide from the 65-kD mycobacterial heat shock protein: specificity and mechanism. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jan;87(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graeff-Meeder E. R., Voorhorst M., van Eden W., Schuurman H. J., Huber J., Barkley D., Maini R. N., Kuis W., Rijkers G. T., Zegers B. J. Antibodies to the mycobacterial 65-kd heat-shock protein are reactive with synovial tissue of adjuvant arthritic rats and patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1013–1017. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte L. B., Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W. Exacerbation of antigen-induced arthritis after challenge with intravenous antigen. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., Hogervorst E. J., Van Bruggen M. C., Van Eden W., van der Zee R., van den Berg W. B. Protection against streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis by pretreatment with the 65-kD mycobacterial heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):449–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]