Abstract
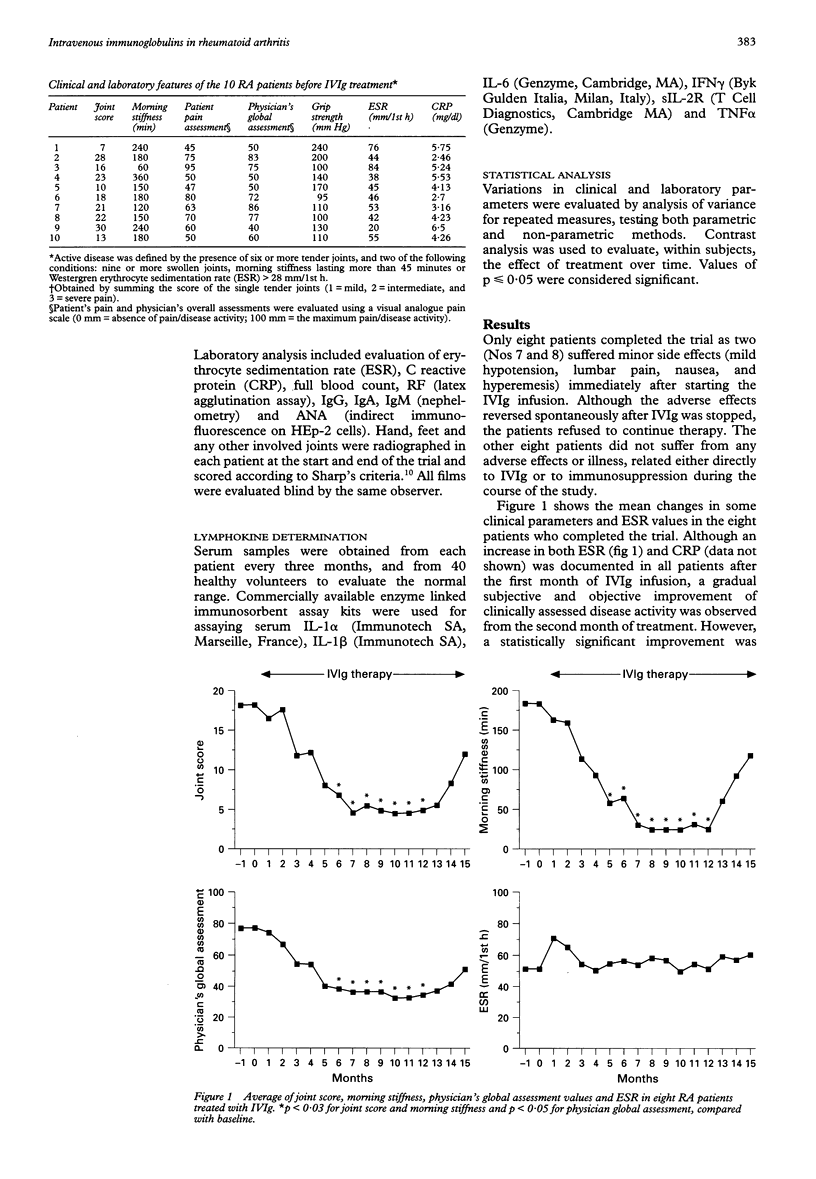
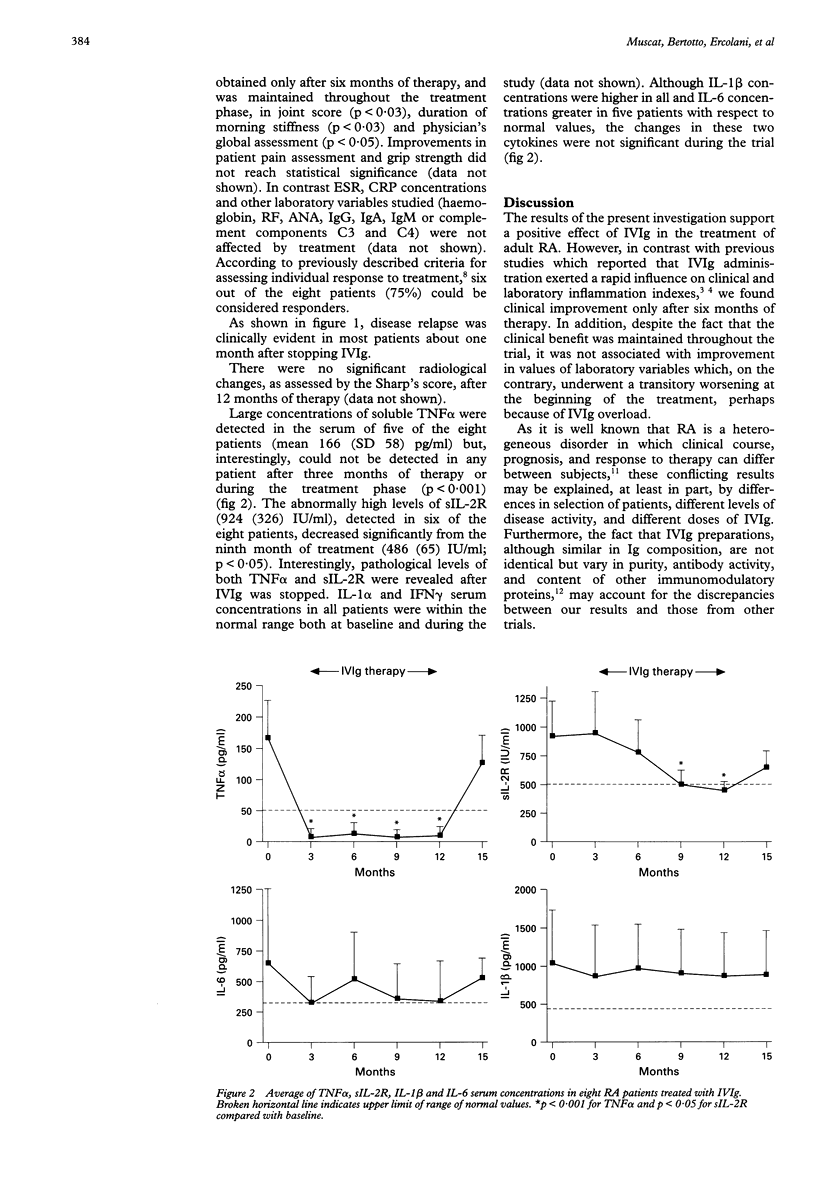
OBJECTIVE--To evaluate the effects of long term treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with high doses of intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg). METHODS--Ten patients with active RA and prior unsuccessful treatment with at least one slow acting antirheumatic drug were treated with 400 mg/kg of IVIg for the first three days and then once a month for 12 months. Clinical evaluation and laboratory analysis were performed every month. Serum levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6 and interferon gamma (IFN gamma) were measured at baseline and at three monthly intervals for 15 months. RESULTS--Although laboratory parameters were not influenced by the treatment, a late but significant clinical improvement was observed after six months. Serial measurement of cytokines revealed a rapid and persistent decrease in serum TNF alpha and a late and significant reduction in sIL-2R concentrations. CONCLUSION--This study suggests that IVIg can ameliorate the symptoms and improve the functional capability of RA patients. This effect is associated with a partial modulation of serum concentrations of inflammatory cytokines and, more interestingly, with a late decrease in sIL-2R which correlated with the late reduction in disease activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achiron A., Margalit R., Hershkoviz R., Markovits D., Reshef T., Melamed E., Cohen I. R., Lider O. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of experimental T cell-mediated autoimmune disease. Upregulation of T cell proliferation and downregulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):600–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI117012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera P., Boerbooms A. M., Janssen E. M., Sauerwein R. W., Gallati H., Mulder J., de Boo T., Demacker P. N., van de Putte L. B., van der Meer J. W. Circulating soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors, interleukin-2 receptors, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Longitudinal evaluation during methotrexate and azathioprine therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1070–1079. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combe B., Cosso B., Clot J., Bonneau M., Sany J. Human placenta-eluted gammaglobulins in immunomodulating treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1985 Jun;78(6 Pt 1):920–928. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danis V. A., Franic G. M., Rathjen D. A., Laurent R. M., Brooks P. M. Circulating cytokine levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results of a double blind trial with sulphasalazine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Aug;51(8):946–950. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.8.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M. Manipulating the immune system with immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 9;326(2):107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201093260206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam L., Whitsett C. F., McNicholl J. M., Hodge T. W., Hooper J. Immunologically active proteins in intravenous immunoglobulin. Lancet. 1993 Sep 11;342(8872):678–678. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91784-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus H. E., Egger M. J., Ward J. R., Williams H. J. Analysis of improvement in individual rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, based on the findings in patients treated with placebo. The Cooperative Systematic Studies of Rheumatic Diseases Group. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Apr;33(4):477–484. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Levison H., Gelfand E. W. High-dose versus low-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in hypogammaglobulinaemia and chronic lung disease. Lancet. 1987 May 9;1(8541):1075–1077. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Young D. Y., Bluhm G. B., Brook A., Brower A. C., Corbett M., Decker J. L., Genant H. K., Gofton J. P., Goodman N. How many joints in the hands and wrists should be included in a score of radiologic abnormalities used to assess rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1326–1335. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman E. D., Laxer R. M., Greenwald M., Gelfand E., Shore A., Stein L. D., Roifman C. M. Intravenous gamma globulin therapy in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jul;33(7):1015–1022. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Bombardier C., Gent M., Bennett K. J., Bensen W. G., Carette S., Chalmers A., Esdaile J. M., Klinkhoff A. V., Kraag G. R. Low-dose cyclosporin versus placebo in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1990 May 5;335(8697):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92630-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumiati B., Casoli P., Veneziani M., Rinaldi G. High-dose immunoglobulin therapy as an immunomodulatory treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1126–1133. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


