Abstract
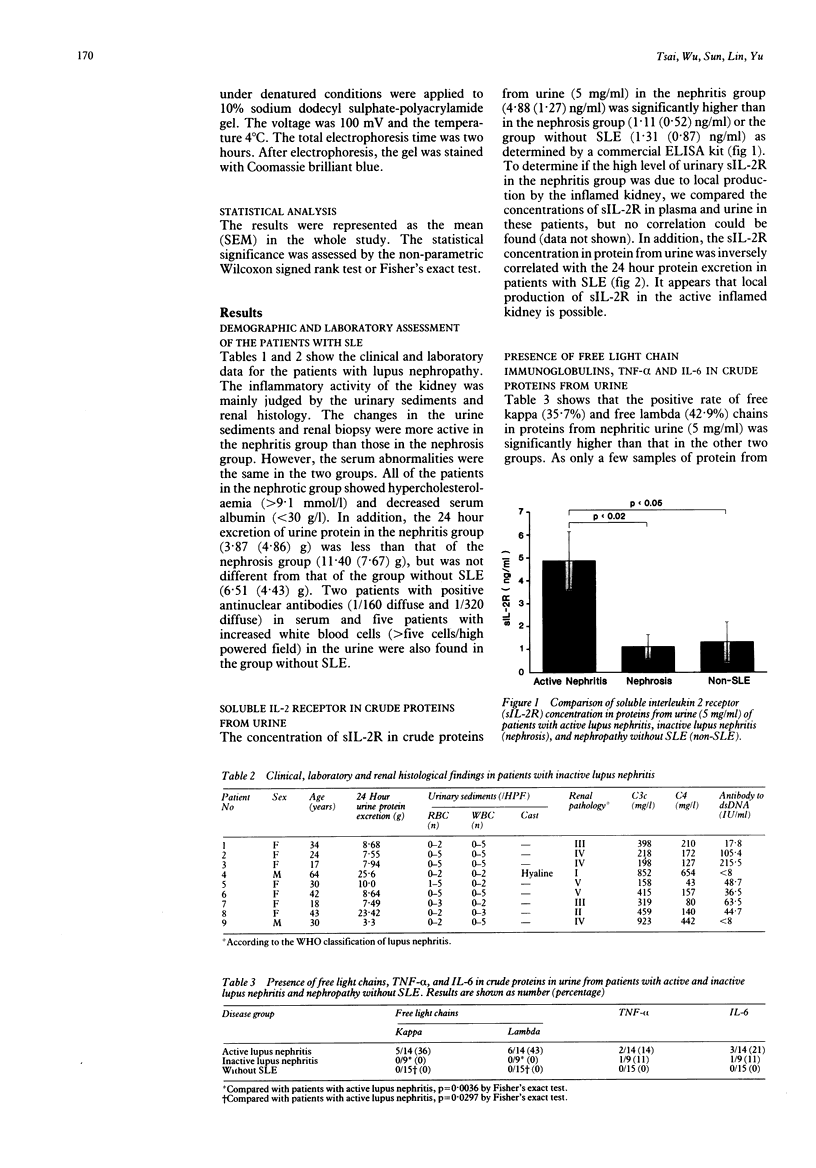
Samples of protein from the urine of 23 patients with lupus nephropathy and 15 patients with proteinuria who did not have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) were studied for the presence of cytokines, soluble interleukin 2 receptors (sIL-2R), and free light chain immunoglobulins. The patients with lupus nephropathy were divided into two groups with active (nephritis) and inactive inflammation (nephrosis) based on the results of the analysis of urine samples and renal histology. The crude urine proteins (5 mg/ml) after precipitation by 80% ammonium sulphate from 14 patients with lupus nephritis contained higher concentrations of sIL-2R (4.88 (SEM 1.27 ng/ml) than those from nine patients with nephrosis (1.11 (0.52) ng/ml) or 15 patients without SLE (1.31 (0.87) ng/ml). The concentration of sIL-2R in protein from urine samples was not correlated with the concentration in plasma and was inversely correlated with the excretion of protein in urine over 24 hours in patients with SLE. It is suggested that, in addition to leakage from the circulation, the local production of sIL-2R by inflamed kidneys is possible. The crude proteins in urine were further fractionated by gel filtration on Sephacryl S-200. Arbitrarily, four fractions could be obtained from urine from patients with SLE but only three fractions were found in the urine of patients without SLE. Fraction IV derived from patients with nephritis or nephrosis augmented the pokeweed mitogen induced [3H]thymidine uptake of mononuclear cells. In addition, the positive rates of free kappa (kappa) (35.7%) and lambda (lambda) (42.9%) chains in proteins in urine from nephritic patients were higher than those in the other two groups. These results suggest that the severity of inflammation in the kidneys of patients with lupus can be reflected by the increased excretion of sIL-2R, free light chain immunoglobulins, and cytokine-like molecules in urine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker G. J., Hancock W. W., Stow J. L., Glasgow E. F., Atkins R. C., Thomson N. M. Involvement of the macrophage in experimental chronic immune complex glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1982;32(3):227–233. doi: 10.1159/000182850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell J. M., Yui M. A., Burt D. W., Kelley V. E. Increased tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 beta gene expression in the kidneys of mice with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3050–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell J. M., Yui M. A., Endres S., Burt D. W., Kelley V. E. Novel and enhanced IL-1 gene expression in autoimmune mice with lupus. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V. Immunologic events preceding clinical exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1973 May;54(5):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke D. H., Hancock W. W., Gee D. C., Kraft N., Atkins R. C. Monoclonal antibody analysis of glomerular hypercellularity in human glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1984 Oct;22(4):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Papagiannes E. Evidence by radioimmunoassay that mitogen-activated human blood mononuclear cells secrete significant amounts of light chain Ig unassociated with heavy chain. Cell Immunol. 1986 Aug;101(1):122–131. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. A thymocyte-activating factor derived from glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1796–1801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Sterzel R. B., Ryan J. L., Atkins E. Production of an endogenous pyrogen by glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):670–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcon L., Fritz M. E., Kurman C. C., Jensen J. C., Nelson D. L. Soluble Tac peptide is present in the urine of normal individuals and at elevated levels in patients with adult T cell leukaemia (ATL). Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):29–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Ren K., Taverne J., Dipirro J., Van Liew J., Dijkstra C., Janossy G., Poulter L. W. Mononuclear cells in glomeruli and cytokines in urine reflect the severity of experimental proliferative immune complex glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):281–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolasco F. E., Cameron J. S., Hartley B., Coelho A., Hildreth G., Reuben R. Intraglomerular T cells and monocytes in nephritis: study with monoclonal antibodies. Kidney Int. 1987 May;31(5):1160–1166. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Engelmann H., Wallach D., Rubinstein M. Soluble cytokine receptors are present in normal human urine. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1409–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Williamson K., Balavoine J. F., Mach B., Mazzei G., Shaw A., Dayer J. M. A urine inhibitor of interleukin 1 activity affects both interleukin 1 alpha and 1 beta but not tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1541–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl R. A., Thaiss F., Kahf S., Schoeppe W., Helmchen U. M. Immune-mediated mesangial cell injury--biosynthesis and function of prostanoids. Kidney Int. 1990 Aug;38(2):273–281. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokano Y., Murashima A., Takasaki Y., Hashimoto H., Okumura K., Hirose S. Relation between soluble interleukin 2 receptor and clinical findings in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Oct;48(10):803–809. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.10.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oers M. H., Van der Heyden A. A., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in serum and urine of renal transplant recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):314–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W., Mogielnicki R. P. The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome, or uremia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2162–2174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werber H. I., Emancipator S. N., Tykocinski M. L., Sedor J. R. The interleukin 1 gene is expressed by rat glomerular mesangial cells and is augmented in immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3207–3212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Brelsford W. G. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]