Abstract
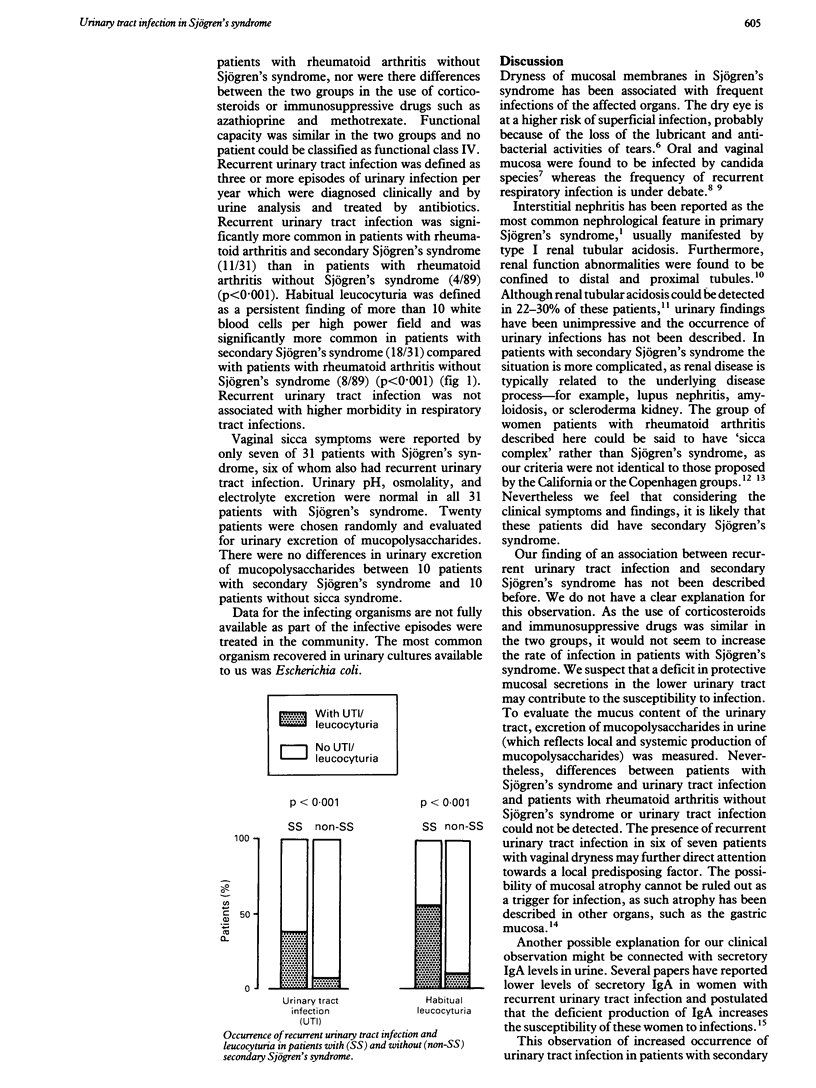
The incidence of lower urinary tract infection in 120 women with rheumatoid arthritis and secondary Sjögren's syndrome was evaluated retrospectively. Thirty one patients (26%) had secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Recurrent urinary tract infection was significantly more common in these patients (11/31) than in patients without Sjögren's syndrome (4/89). Habitual leucocyturia was also more common in patients with secondary Sjögren's syndrome (18/31) than in patients with rheumatoid arthritis without Sjögren's syndrome (8/89). Of seven patients with vaginal sicca symptoms, six had recurrent urinary tract infection. Urinary 24 hour mucopolysaccharide excretion in 20 patients with Sjögren's syndrome was similar to the excretion in 10 patients without Sjögren's syndrome. These results show that recurrent urinary tract infection is significantly more common in women with rheumatoid arthritis and secondary Sjögren's syndrome. A local deficit in protective urinary mucosal secretion or other immune mechanisms may be responsible for this susceptibility.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON A. J., MACLAGAN N. F. The isolation and estimation of urinary mucoproteins. Biochem J. 1955 Apr;59(4):638–644. doi: 10.1042/bj0590638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Robinson C. A., Curd J. G., Kozin F., Howell F. V. Sjögren's syndrome. Proposed criteria for classification. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):577–585. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmstrup P., Bessermann M. Clinical, therapeutic, and pathogenic aspects of chronic oral multifocal candidiasis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983 Oct;56(4):388–395. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(83)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpi A., Bergroth V., Konttinen Y. T., Maury C. P., Reitamo S., Wegelius O. Lymphocyte infiltrations of the gastric mucosa in Sjögren's syndrome. An immunoperoxidase study using monoclonal antibodies in the avidin-biotin-peroxidase method. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1196–1200. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemp M. A., Gold J. B. An in vivo study of the corneal surface in keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1985;104(Pt 4):436–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou M. P., Constantopoulos S. H., Tsampoulas C., Drosos A. A., Moutsopoulos H. M. Reappraisal of respiratory abnormalities in primary and secondary Sjögren's syndrome. A controlled study. Chest. 1986 Sep;90(3):370–374. doi: 10.1378/chest.90.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEARN M. A., TU W. H. NEPHROGENIC DIABETIC INSIPIDUS AND OTHER DEFECTS OF RENAL TUBULAR FUNCTION IN SJOERGREN'S SYNDROME. Am J Med. 1965 Aug;39:312–318. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearn M. A. Sjögren's syndrome. Med Clin North Am. 1977 Mar;61(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Shiozawa K., Shimizu S., Nakada M., Isobe T., Fujita T. Clinical studies of renal disease in Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Oct;46(10):768–772. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.10.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



