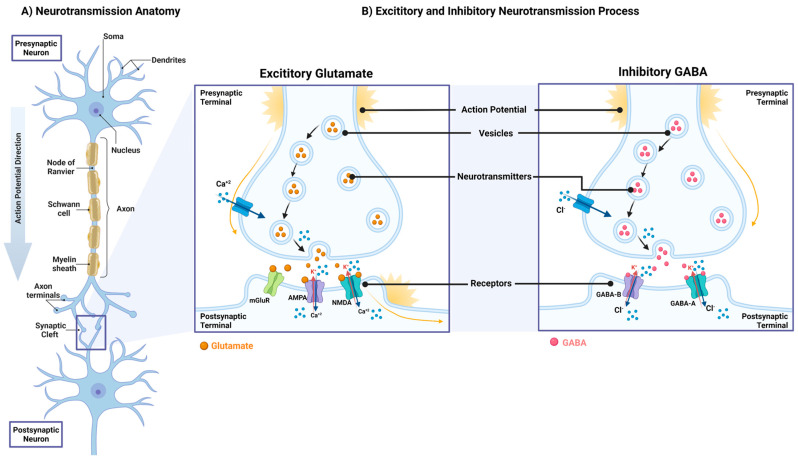
Figure 1.
Neurotransmission anatomy and process. (A) Neurotransmission anatomy: An action potential moves along the axon of the presynaptic neuron to interact with the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron creating a synaptic cleft in which the neurotransmission process occurs. (B) Excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission process: Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles in the presynaptic terminal and are released upon the receipt of an action potential that triggers the release of different ions (i.e., Ca2+, Cl−, K+) and neurotransmitters (i.e., excitatory glutamate and inhibitory GABA) which activates different receptors depending on the synaptic activity. Abbreviations: Ca2+: calcium ions; K+: potassium ions; mGluR: metabotropic glutamate receptor; AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; Cl−: Chloride ions; GABAA and GABAb: γ-Aminobutyric acid receptors (A,B), respectively. Created with BioRender.com.