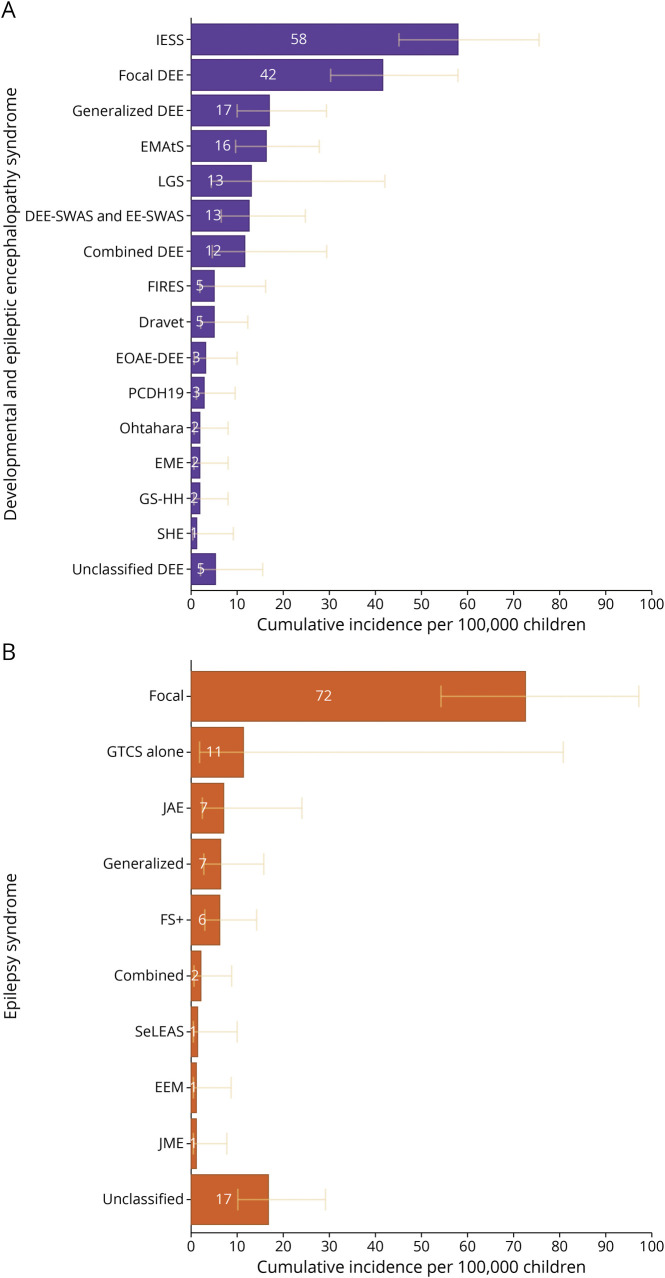
Figure 3. Cumulative Incidence of Epilepsy Syndromes.
The cumulative incidence for each epilepsy syndrome in children to age 16 years is provided per 100,000 children with the 95% CIs in yellow. (A) Epilepsy syndromes in individuals with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy epilepsy syndromes. (B) Epilepsy syndromes in individuals with intellectual disability and epilepsy. DEE-SWAS & EE-SWAS = developmental and epileptic encephalopathy with spike-and-wave activation in sleep and epileptic encephalopathy with spike-and-wave activation in sleep; Dravet = Dravet syndrome; EME = early myoclonic encephalopathy; EEM = epilepsy with eyelid myoclonia; EOAE-DEE: early-onset absence epilepsy with DEE; FIRES = febrile infection–related epilepsy syndrome; GS-HH = gelastic seizures with hypothalamic hamartoma; FS+ = febrile seizures plus; GTCS = generalized tonic-clonic seizures; JAE = juvenile absence epilepsy; JME = juvenile myoclonic epilepsy; IESS = infantile epileptic spasms syndrome; LGS = Lennox-Gastaut syndrome; EMAtS = epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures; Ohtahara = Ohtahara syndrome; PCDH19 = PCDH19 clustering epilepsy; SeLEAS = self-limited epilepsy with autonomic seizures; SHE = sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy.