Abstract
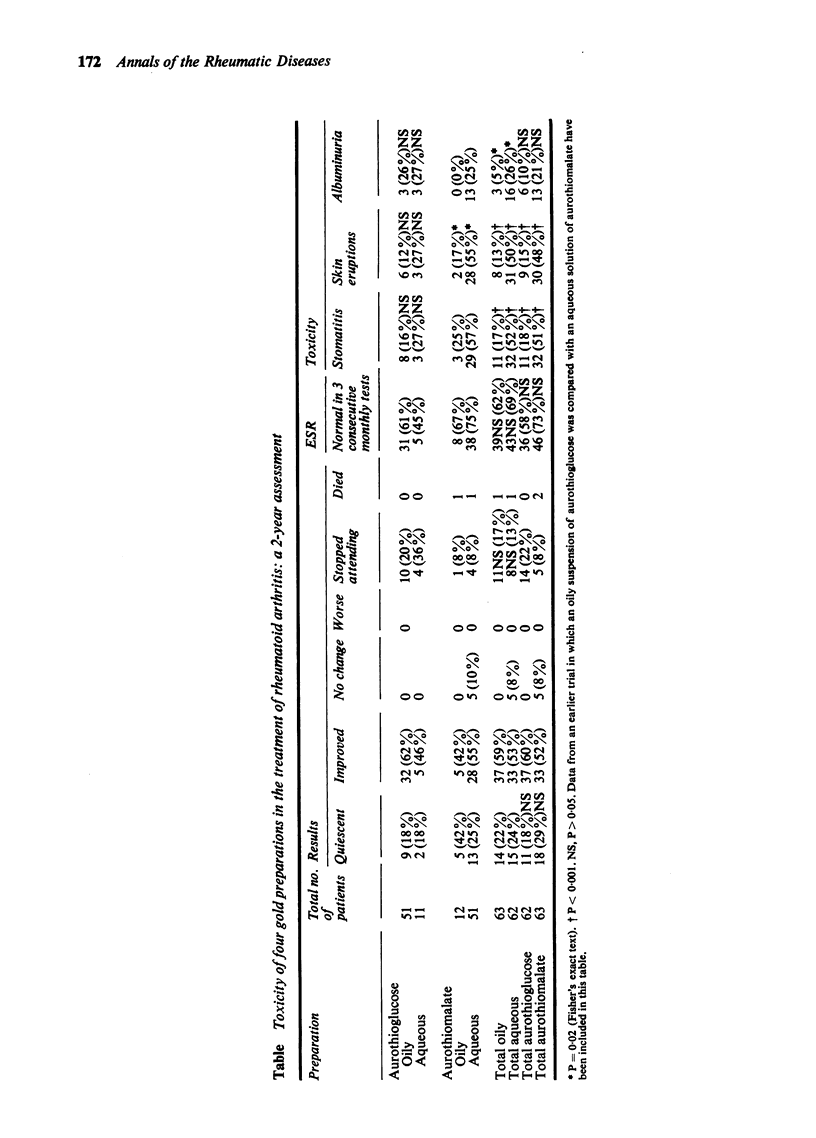
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis have been treated alternately with aurothioglucose and aurothiomalate. In the earlier part of the study an oily suspension of aurothioglucose and an aqueous solution of aurothiomalate were used, but later an aqueous solution of aurothioglucose was alternated with the oily suspension and an oily suspension of aurothiomalate with the aqueous solution. Skin eruptions, stomatitis, and albuminuria were significantly more common in patients treated with the aqueous solution than with the oily suspension.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gottlieb N. L., Smith P. M., Smith E. M. Gold excretion correlated with clinical course during chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Nov-Dec;15(6):582–592. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE J. S. Factors in gold dosage and toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1953 Jun;12(2):129–135. doi: 10.1136/ard.12.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


