Abstract
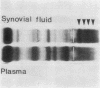
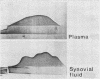
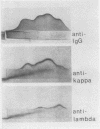
In order to see if the complement (C) consumption and conversion, which are typical of rheumatoid joints, continue after synovectomy, 23 knee joints in which synovectomy had been performed from 4-5 to 6-5 years previously, were studied. The mean ratio of the concentration of C3, C4, and C5 in synovial fluid to that in palsma of the same patient was significantly lower than the corresponding ratio for the total protein content. This was found both in joints with active arthritis and in joints without clinical signs of arthritis, and in both seropositive and seronegative patients. Conversion products of C3 were found in 7 of the synovial fluids. The study thus indicated that the complement alterations in synovectomized joints are very similar to those in nonsynovectomized rheumatoid joints. In one synovial fluid agarose electrophoresis showed multiple sharp bands in the gamma region. By crossed immunoelectrophoresis some bands seemed to contain IgG with one type of light chains only. In plasma of the same patients the bands were much weaker, indicating local production of oligoclonal IgG in the joint.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Alper CA, Rosen FS: Studies of the in vivo behavior of human C'3 in normal subjects and patients. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2021–2034. doi: 10.1172/JCI105691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cracchiolo A., 3rd, Barnett E. V. Immunologic changes in synovial fluid following synovectomy of the knee for rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969 Apr;51(3):475–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD R. A., ROTSTEIN J. Rheumatoid arthritis and agammaglobulinemia. Bull Rheum Dis. 1960 Jan;10:203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay R., Micheli A., Fallet G. H. Behaviour of synovial complement C3 and C4 components in inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases, before and after synoviorthesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Apr;34(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEDBERG H. STUDIES ON THE DEPRESSED HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT ACTIVITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID IN ADULT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:165–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K., Mellbye O. J. Rheumatoid factor in synovial effusions: local production and consumption. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):501–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H., Lundh B., Laurell A. B. Studies of the third component of complement in synovial fluid from arthritic patients. II. Conversion and its relation to total complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):707–712. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh B., Hedberg H., Laurell A. B. Studies of the third component of complement in synovial fluid from arthritic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):407–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Experimentally produced antibodies to the pepsin site of IgG due to untreated autologous IgG in immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):257–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of IgG complexes in eluates from rheumatoid tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):249–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Winchester R. J. Complement in rheumatoid inflammation. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1969;15(3):161–168. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1969.15.issue-1-4.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEKIN T. J., Jr, ZVAIFLER N. J. HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT IN SYNOVIAL FLUID. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1372–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI105013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. D., Sachs C., Ziff M. In vitro synthesis of immunoglobulin by rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):624–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI105758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B., Norrby E. Oligoclonal IgG antibody response in the central nervous system to different measles virus antigens in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1060–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versey J. M., Hobbs J. R., Holt P. J. Complement metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. I. Longitudinal studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Nov;32(6):557–564. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid synovitis. An extravascular immune complex disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):297–305. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]