Abstract
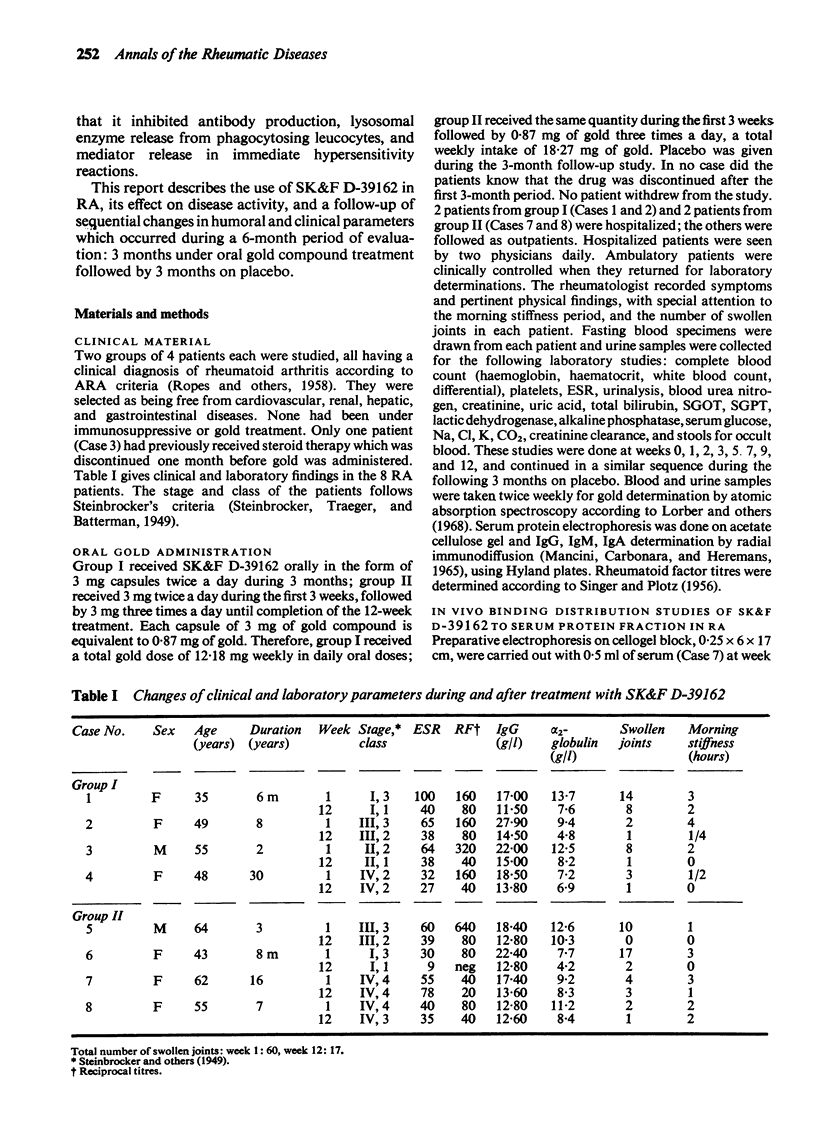
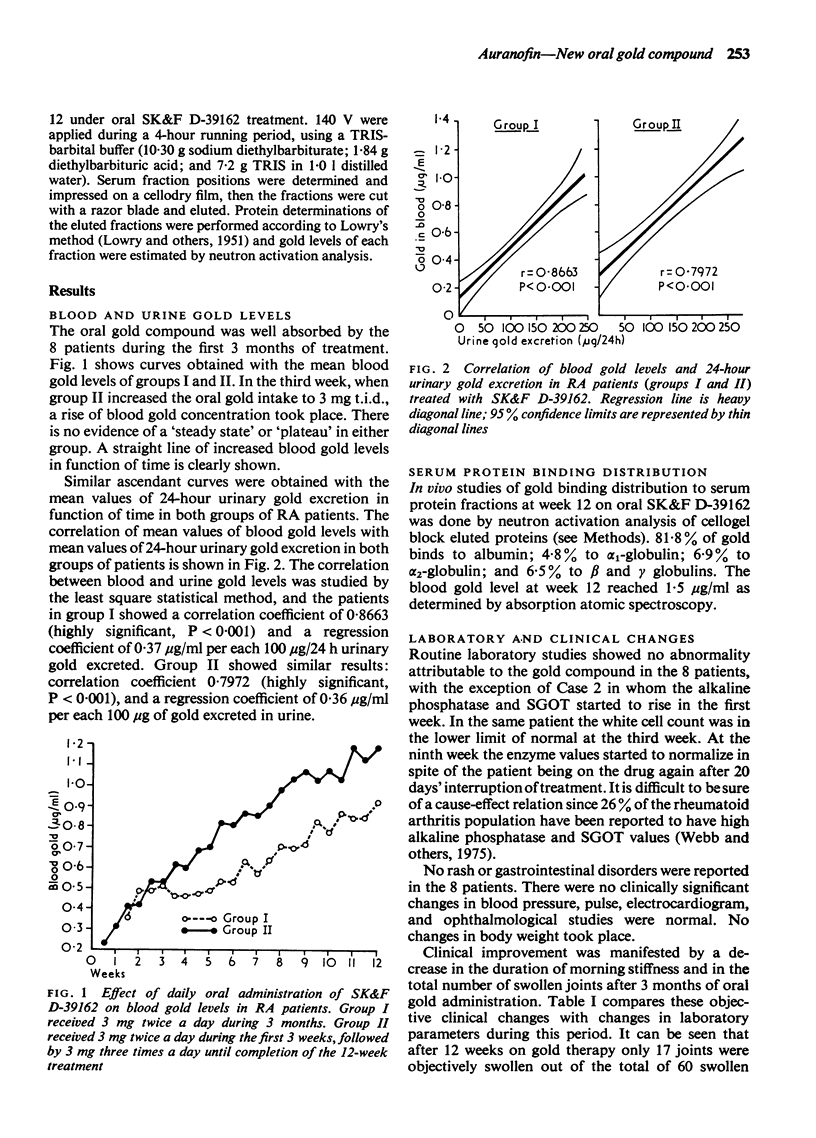
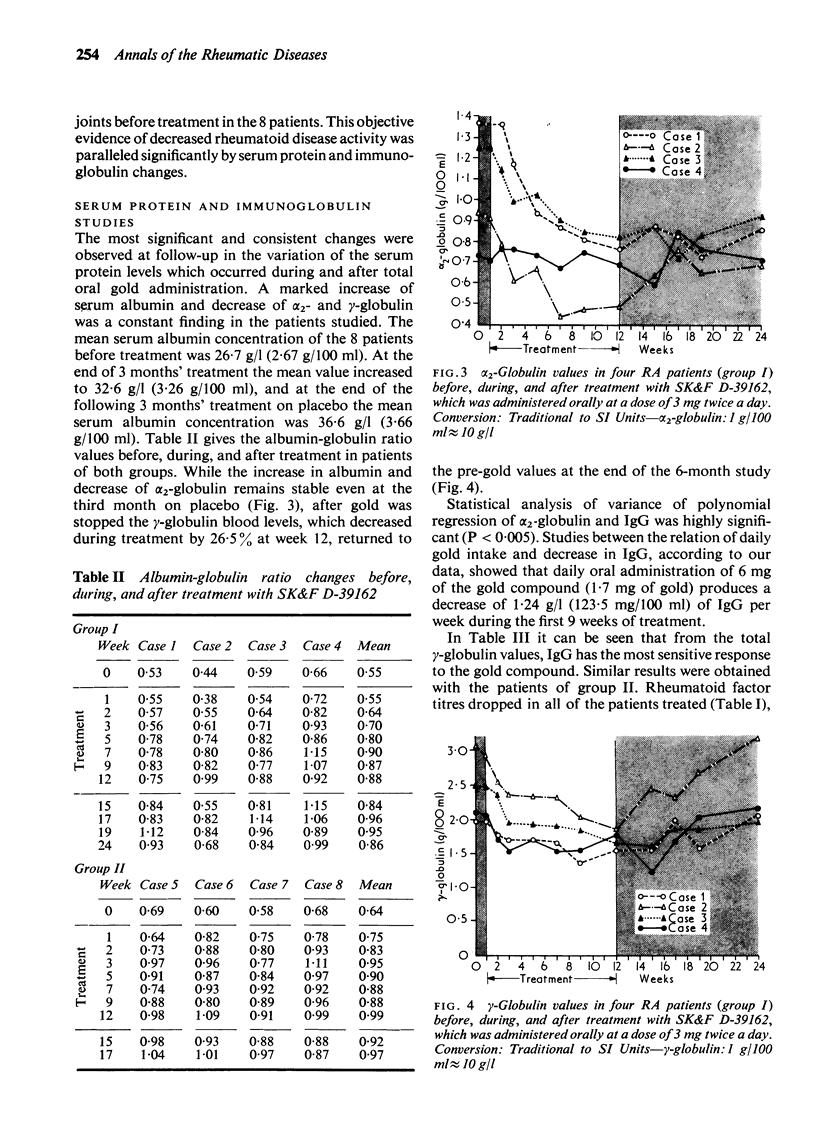
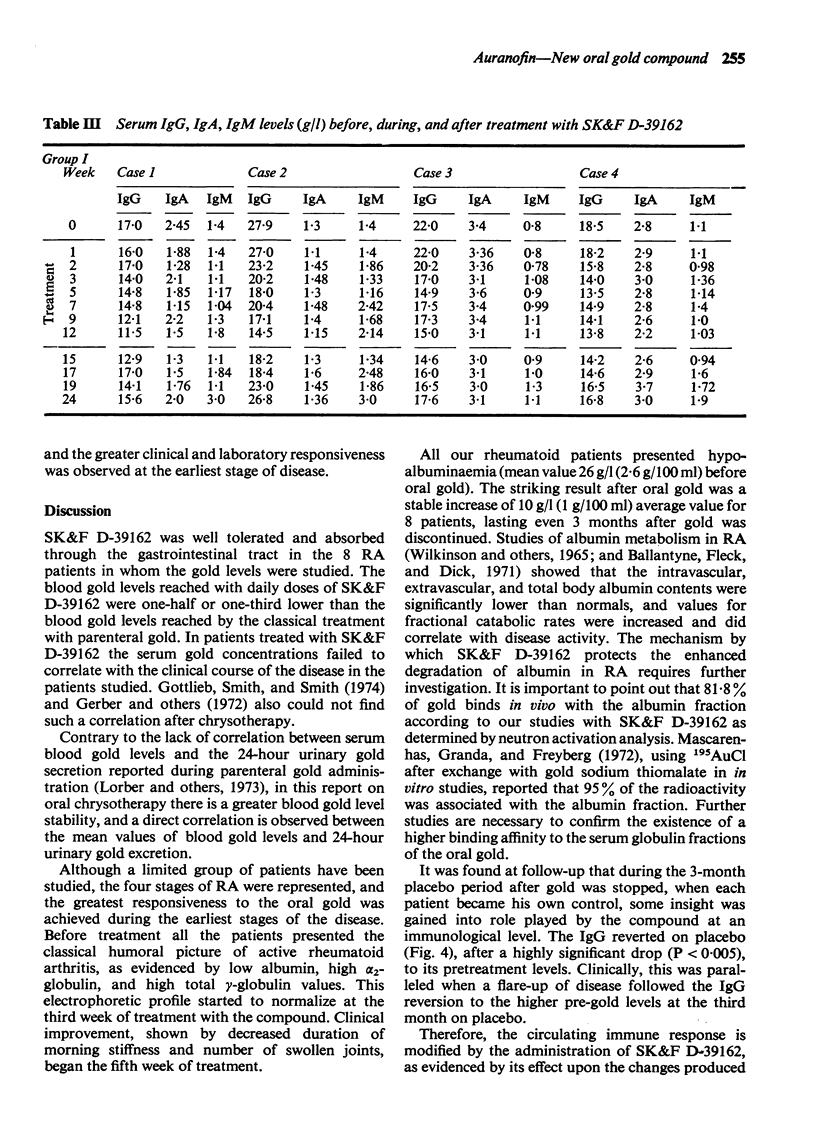
Eight patients with rheumatoid arthritis were treated with SK & F D-39162 (auranofin), a new oral gold compound which was effective in suppressing adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Clinical and humoral parameters were studied during a 3-month period of drug administration followed by a 3-month period under placebo. The drug was absorbed, well tolerated, and its action was manifested by a drop in the mean IgG blood levels in the third week of treatment accompanied by clinical improvement after 5 weeks of oral gold intake. Together with IgG changes, an increase of the albumin ratio was observed, as well as a decrease of alpha2-globulin and rheumatoid factor titres. From a total number of 60 swollen joints found initially in the 8 patients only 17 were swollen at week 12 and 9 at week 15. Although the number of patients treated was too small to allow definite conclusions, a follow-up study under placebo of clinical and laboratory changes in the same patients during another 3-month period showed that IgG serum levels rapidly reverted preceding a flare up of disease activity after withdrawal of the drug. This confirmed a direct role in cause-effect relation played by the new oral gold compound.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne F. C., Fleck A., Dick W. C. Albumin metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):265–270. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHODIRKER W. B., TOMASI T. B., Jr Low-molecular-weight rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jun;42:876–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI104780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN A. E., KWOK G., HALL A. P., BAYLES T. B. The erythrocyte in rheumatoid arthritis. I. A method for the detection of an abnormal globulin coating. N Engl J Med. 1961 Feb 9;264:270–273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196102092640603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber R. C., Paulus H. E., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. Clinical response and serum gold levels in chrysotherapy. Lack of correlation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):308–310. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. A., Koehler B. E., Russell M. L., Urowitz M. B., Broder I. The clinical significance of immune complexes in rheumatoid disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:338–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb N. L., Smith P. M., Smith E. M. Pharmacodynamics of 197Au and 195Au labeled aurothiomalate in blood. Correlation with course of rheumatoid arthritis, gold toxicity and gold excretion. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):171–183. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Atkins C. J., Chang C. C., Lee Y. B., Starrs J., Bovy R. A. Monitoring serum gold values to improve chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Mar;32(2):133–139. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Cohen R. L., Chang C. C., Anderson H. E. Gold determination in biological fluids by atomic absorption spectrophotometry: application to chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):170–177. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarenhas B. R., Granda J. L., Freyberg R. H. Gold metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with gold compounds--reinvestigated. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):391–402. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of IgG complexes in eluates from rheumatoid tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):249–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Mannik M., Gilliland B. C., Teller D. C. The hyperviscosity syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis due to intermediate complexes formed by self-association of IgG-rheumatoid factors. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):97–106. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E. Characterization of the gamma-globulin complexes present in certain sera having high titers of anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):501–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI105364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler J. W., Bluhm G. B., Duncan H., Sharp J. T., Ensign D. C., McCrum W. R. Gold salts in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):21–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton B. M., McGusty E., Walz D. T., DiMartino M. J. Oral gold. Antiarthritic properties of alkylphosphinegold coordination complexes. J Med Chem. 1972 Nov;15(11):1095–1098. doi: 10.1021/jm00281a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON P., JEREMY R., BROOKS F. P., HOLLANDER J. L. THE MECHANISM OF HYPOALBUMINEMIA IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Jul;63:109–114. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz D. T., DiMartino M. J., Chakrin L. W., Sutton B. M., MISHER A. Antiarthritic properties and unique pharmacologic profile of a potential chrysotherapeutic agent: S K & F D-30162. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Apr;197(1):142–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


