Abstract
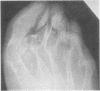
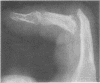
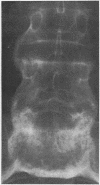
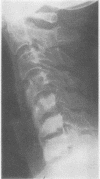
Histocompatibility typing was carried out in 74 patients with psoriasis and an inflammatory arthropathy. In 40 patients with peripheral arthropathy characterized by distal interphalangeal joint involvement, 13 (32-5%) were HLA-B27 positive, significantly higher than the control frequency (P = 5-8 X 10 (-6). 26 of the 40 patients did not have ankylosing spondylitis or radiological sacroiliitis and 7 were HLA-B27 positive, also significantly higher than in controls (P = 0-0049). All 7 patients with psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis without peripheral arthropathy were HLA-B27 positive. The 10 patients with ankylosing spindylitis or radiological sacroliitis who were HLA-B27 negative all had peripheral arthropathy. It is suggested that being HLA-B27 positive increases the risk of a psoriatic patient developing both peripheral arthropathy and ankylosing spondylitis. In addition, some of the genes involved in susceptibility to psoriasis also have a role in the pathogenesis of both types of arthropathy. A hypothesis is put forward that some of the genes for psoriasis may be aetiologically important in some HLA-B27 negative patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYWATERS E. G. Heel lesions of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1954 Mar;13(1):42–51. doi: 10.1136/ard.13.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Caffrey M., Nicholls A., Walters D., James D. C. HL-A 27 and arthropathies associated with ulcerative colitis and psoriasis. Lancet. 1974 May 18;1(7864):956–958. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karvonen J. HL-A antigens in psoriasis with special reference to the clinical type, age of onset, exacerbations after respiratory infections and occurrence of arthritis. Ann Clin Res. 1975 Oct;7(5):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger A. L., Morris R. I., Bluestone R., Terasaki P. I. HL-A W27 in psoriatic arthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):111–115. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. M., Wright V. Familial occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 May;32(3):181–201. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. M., Wright V. Psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1973;3(1):55–78. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(73)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sany J., Seignalet J., Guilhou J. J., Serre H. HL-A et rhumatisme psoriasique. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1975 Jul-Sep;42(7-9):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Newcomer V. D., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Disturbance of HL-A antigen frequency in Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 12;287(15):740–743. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210122871504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow J. C., Dave V. K., Usher N., Anderson J. The HL-A system and psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Apr;92(4):427–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb03104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]