Abstract
The adoption of omnichannel interaction services in health care can bring significant benefits to both health care institutions and their patients. The ongoing health pandemic caused by coronavirus disease has further emphasized the need for health care providers to implement an omnichannel strategy to provide seamless personalized experiences to their patients through multiple access channels. This study aimed to examine the current state of research on omnichannel interaction services in health care with a focus on the benefits, challenges, and issues that health care institutions may encounter when adopting this strategy. A systematic literature review was conducted to synthesize the current state of research and provide a comprehensive overview of the field. The results of the review were used to perform a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis of omnichannel services in health care and identify 5 key criteria that health care institutions should consider when implementing an omnichannel strategy. This study contributes to the field by offering an updated and comprehensive understanding of omnichannel interaction services in health care and provides valuable insights for health care providers considering this strategy. The ultimate goal of an omnichannel strategy in health care is to improve patient engagement, increase access to care, and reduce costs while improving communication and collaboration among health care providers. The successful implementation of this strategy requires a well-defined plan, robust technology, infrastructure, data analytics, capabilities, trained professionals, and a basic understanding of the communication channels among patients. The adoption of an omnichannel strategy in health care can lead to new business growth and increased patient engagement, but health care institutions must be properly aligned and patients must be prepared for its implementation.
Article Highlights.
-
•
Omnichannel strategy in health care services aims to provide a seamless, personalized service and patient care experience.
-
•
It improves patient engagement, satisfaction, and access to care, especially for underserved populations.
-
•
Other advantages include cost saving, improved patient satisfaction, and adherence to treatment plans.
-
•
It enhances communication and coordination among health care providers.
-
•
However, it requires robust technology infrastructure, data analytics, and trained professionals.
The current pace and evolution of digital transformation in e-commerce and marketing have increasingly motivated certain health care businesses to adopt an omnichannel interaction strategy in their daily activities and in the way they interact with their existing and potential new customers.1 The evolution of this strategy has presented significant advances in the omnichannel environment and has demonstrated the potential that this approach has in the long term for organizations that adopt it. Besides, it should be noted that in recent years, this practice has been adopted with great success in the areas of marketing and e-commerce.2 , 3
The way marketing and e-commerce organizations interact with their customers through different channels motivated us to perform this study regarding omnichannel interaction and apply the same principle to the health care business.4 These organizations have made a tremendous effort to improve the quality of service offered to their customers. Omnichannel services aim to leverage available technologies to ensure that organizations’ target audiences receive the correct information across multiple channels.4 , 5
Thus, this article is based on the studies and research conducted by e-commerce and marketing organizations and on the reports from organizations that somehow managed to successfully implement the omnichannel strategy. In addition to these, several academic studies addressing the topic were also considered. It should be noted that this work follows a strategic management approach, whose main objective was to identify its status and apply the lessons learned with these strategies to the health care services that are provided to patients through different interaction channels.
Currently, there has been a growing interest in the use of omnichannel interaction in health care services. Omnichannel interaction refers to the use of multiple channels to communicate with patients to provide them with seamless and smooth care services. The adoption of omnichannel interaction in health care has the potential to improve patient satisfaction and outcomes, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. However, there is limited research on the use of omnichannel interaction in health care, and it is not clear how it compares with traditional channels of communication. In this systematic literature review, we aimed to address the following research questions (RQs):
-
•
Research question 1—To what extent can the omnichannel strategies that marketing and e-commerce organizations have implemented be adopted in health care organizations?
-
•
Research question 2—What are the best practices for implementing omnichannel interaction in health care services based on the available evidence?
-
•
Research question 3—What are the challenges and limitations of using omnichannel interaction in health care services, and how can they be addressed?
-
•
Research question 4—What are the potential future directions for the use of omnichannel interaction in health care services based on the current state of evidence?
Owing to the RQs raised and following studies from other areas, it is intended to establish a very linear path that follows a strategic approach to adopting the practice of omnichannel strategies in the health care field.
Background
Over the years, the concept of omnichannel interaction has evolved as technology and customer expectations have changed. Historically, businesses primarily interacted with customers through a single channel (phone or in person). However, as technology advanced and customers became more accustomed to interacting with businesses through multiple channels, such as email, social media, and online chat, businesses began to adopt new strategies to meet these changing expectations.6 First, the business introduced the concept of cross channels,7 in which they started to target customers across different channels of interactions. Later, they started to combine some channels to provide a better user experience (UX) to customers and to meet customers’ expectations through a multichannel interaction.8 As the last step of evolution, omnichannel interaction involved using multiple channels to interact with customers in a coordinated and seamless way, allowing for a more personalized and convenient UX. Now, many businesses are using omnichannel approaches that include a combination of online and offline channels, such as mobile applications, voice assistants, and in-store kiosks, to provide customers with a consistent and cohesive experience across all touch points.9
Multichannel Interaction
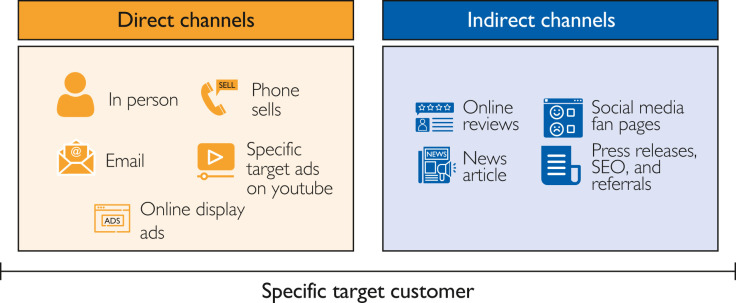
When approaching a multichannel interaction, it essentially addresses the use of multiple channels to reach users at some point in the consumer journey. In this type of interaction, the existing approach consists of a variety of channels that work separately from each other and that do not communicate with each other, with their interaction being indirect.8 , 10 In this sense, each channel has its benefits, but none of them work together to create a perfect customer journey in all interaction processes, which is one of the major drawbacks of multichannel interaction. The customer simply cannot switch between a different channel and have seamless continuity and interaction on their journey, which means that if the customer is switching from one channel to another channel, they must start the journey again at a new touch point. Organizations today leverage a huge variety of channels that can be direct channels, such as in person, phone sales, email, specific target advertisements on YouTube, and online display advertisements, and indirect channels, such as online reviews, social media fan pages, news articles, press releases, search engine optimization, and referrals, as shown in Figure 1 . Through these channels, they can create a specific type of interaction with a specific target customer.5 , 11, 12, 13
Figure 1.
Multichannel channels. SEO, search engine optimization.
Cross-Channel Interaction
Cross-channel interaction is quite similar to multichannel interaction but with 1 exception—that the interaction channels are connected. This enables customer interaction to be stored and provides the necessary means for channels to communicate and share information about the customers among them. Additionally, cross-channel interaction allows the customer to move almost effortlessly between the channels during their interaction journey.5 , 11 , 13 In short, the advantage for the consumer is that he/she can switch from one channel to another without major problems or difficulties.
Omnichannel Interaction
Omnichannel interaction is the most sophisticated of all types of interactions. At its core, it includes multiple channels such as multichannel and cross-channel interaction but in a much better way. The channels are all connected similar to that in a cross-channel interaction, but they are at the same time all interconnected and interactive, which allows for the highest level of engagement with the customers during their journey.13 In omnichannel interaction, the channels simultaneously exchange information about the customer and work seamlessly together to create an environment with a comprehensive UX across multiple interaction channels. The main objective of omnichannel interaction is to remove all barriers between the online and offline customer journey, which happens in other types of interactions.5 , 10, 11, 12 An omnichannel strategy is a process of designing, implementing, coordinating, integrating, and evaluating different channels to increase customer value through effective customer acquisition, retention, and development.11 Thus, the multichannel strategy is presented as a set of channels that intend to provide a service or sell products to consumers in multiple interaction channels.8 , 13
In summary, multichannel interaction refers to the use of multiple channels, such as phone, email, and social media, to complete transactions with customers.8 Cross-channel interaction is similar to multichannel interaction but includes the added element of connectivity and information sharing between channels. Omnichannel interaction is the most comprehensive type of interaction, involving the seamless integration and management of the customer experience across all channels.8 , 11, 12, 13 Several studies have been conducted on multichannel interaction services in health care services.14, 15, 16, 17 Despite these efforts, there is a notable dearth of literature regarding the development and implementation of omnichannel interaction services. Further research is required to fill this gap and fully understand the potential impact of omnichannel interaction services in health care.
Research Methodology
This systematic literature review aimed to provide an overview of the current state of evidence on omnichannel interaction in general and to apply the lessons learned to health care services. In addition, this review aimed to examine the benefits and challenges of using omnichannel interaction, and the best practices for its implementation. Moreover, it also considered the potential future directions for the use of omnichannel interaction in health care.
For the realization of this review, the methodology used was Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis18 because it provides a systematic and transparent approach to identify, evaluate, and synthesize the available evidence on the topic. This systematic literature review follows an accepted scientific methodology in the fields of information systems and computer science, followed by a checklist and a flow diagram.18 The focus of the review was on research published in the past decade, as there is a large body of literature on omnichannel strategy and its recent impact on the retail sector. The review included articles from bibliographic databases, such as the Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus, as well as white papers and other secondary sources, such as books, magazines, and opinion articles. The inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to select the studies for this review. This study also included some internet research to provide additional context and understanding of the various concepts. The scope of the review included research in the areas of management, retail, information systems, and health care, with a particular focus on the retail sector and the implementation of omnichannel strategies. Finally, the data extracted from the selected studies were analyzed and synthesized to answer the aforementioned RQs.
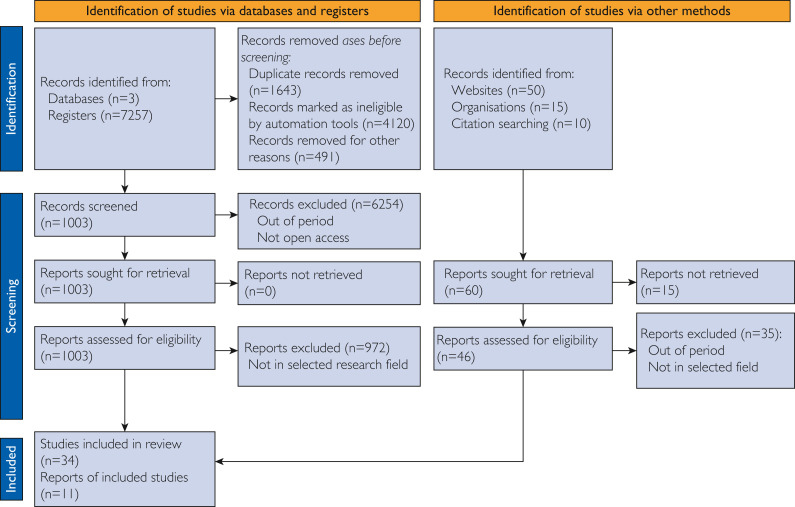
To search for these publications in the repositories, the following keywords were used: omnichannel strategy, multichannel strategy, omnichannel retail, multichannel/omnichannel challenges and benefits, channel integration, multichannel services, omnichannel services, multichannel care services, and omnichannel in health care. The combination of these keywords resulted in a diverse set of scientific articles, most of which were unrelated to the topic. Thus, the articles were chosen by year, with only publications published in the recent 10 years being considered. However, extra selection criteria were required to minimize and choose only the publications relevant to the study in question. More than 1003 publications were analyzed, and only open-access articles published in indexed journals were chosen (Figure 2 ). There were some deviations in the selection of articles because they had a large number of citations and the author had previously published in the field (2 articles were added through an exception). Regarding the white papers and opinion articles, they were chosen on the basis of the omnichannel strategy used by retail companies, in which various issues related to the omnichannel strategy were addressed.
Figure 2.
Applied Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis methodology.
(TITLE-ABS-KEY(omnichannel retail)
OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(omnichannel strategy) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(omnichannel challenges) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(omnichannel benefits) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(omnichannel healthcare)
OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(multichannel interaction) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(multichannel services) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(multichannel benefits) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(multichannel challenges OR
TITLE-ABS-KEY(multichannel healthcare))
AND PUBYEAR > 2011 AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBSTAGE, “final”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (OA, “all”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”) OR LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “cp”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, “ENGI”)
OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,” “COMP”) OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,” “MEDI”) OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,” “BUSI”) OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,” “MULT”) OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,” “DECI”)
OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, “HEAL”) OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA, “ECON”))
Results
Through the selection of relevant studies, information was extracted from these studies and analyzed to generate a set of outcomes regarding the omnichannel interaction strategy.
Study Selection
Study selections were performed through the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis statement18 using a checklist and a flow diagram, as represented in Figure 2. The use of these criteria for inclusion and exclusion of articles resulted in a significant reduction in the number of articles chosen for this review: 34 articles and 11 white papers/web pages. It is also noteworthy that the application of these criteria resulted in the creation of a base of publications in renowned scientific journals in their fields, which will ensure the scientific rigor of this article. A systematic literature review of omnichannel interaction in health care services would involve searching for and analyzing various research articles on the topic. The primary articles used are those that have been published in reputable journals have a general focus on the use of omnichannel strategies and are somehow related to health care services. The main findings of each study would most likely differ, but they could include findings on the effectiveness of different omnichannel strategy approaches, the benefits and challenges of implementing omnichannel in health care, and patients’ perspectives on omnichannel interaction. The main contributions of this literature review would be to provide an overview of the current state of research on omnichannel interaction in health care services and to identify key themes and gaps in the literature. Each selected article provided specific information and insights into the topic that have contributed to a better understanding of this approach and drawn some conclusions about this work. The result of this study can be applied in the health care field by providing a better understanding of the opportunities and challenges to implementing omnichannel strategies in health care services provided to patients. Comparisons can also be made between different studies and health care settings to identify best practices and areas for improvement. The following section will present the main characteristics and outcomes of each study selected.
Study Characteristics
The examination of omnichannel customer engagement via selected research studies holds significant importance in the acquisition and evaluation of relevant information. This subsection provides an exhaustive analysis of the essential attributes of these studies. The focal point of the selected studies is to comprehend the manner in which customers engage with a brand through multiple channels. The sample size of these studies is typically small, with participants selected on the basis of factors such as their level of interaction with the brand across multiple channels. These studies emphasize the examination of customer behavior and preferences and employ both quantitative and qualitative methods for data collection. Additionally, they assess the effects of omnichannel interactions on customer loyalty, satisfaction, and conversion rates. It is crucial to note that the sample size and population selection are contingent upon the RQ and objectives of the study; thus, the results may not be generalizable to other populations or settings. Furthermore, the validity of the results may be influenced by participant homogeneity and the degree of bias introduced by the selection criteria. The essential characteristics of the selected studies are outlined in Table 1 .1 , 3, 4, 5 , 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 , 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49
Table 1.
Studies Characteristics
| Characteristics | Studies | Total (n) | Values (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of publication | |||
| Journal articles | 1, 3, 4, 7, 9-13, 19-37 | 28 | 62.22 |
| Conference proceedings | 15-17, 38-40 | 6 | 13.33 |
| Others | 5, 8, 14, 41-48 | 11 | 24.44 |
| Study type | |||
| Research article | 3, 10, 12, 25, 27, 30, 33, 36, 37 | 9 | 18 |
| Review article | 11, 19, 21-23, 28, 29, 32 | 8 | 16 |
| Case study | 21, 35, 36, 38, 40 | 5 | 10 |
| Original article | 1, 4, 7, 9, 10, 13, 15-17, 20, 24, 26, 31, 34 | 14 | 28 |
| Book chapter | 4, 39 | 2 | 4 |
| Short communications | 5, 8, 14, 41-49 | 12 | 24 |
| Research type | |||
| Interviews | 19, 21 | 2 | 5.26 |
| Survey | 10, 26, 28 | 3 | 7.89 |
| Quantitative research | 3, 24, 26, 28, 40 | 5 | 13.16 |
| Qualitative research | 1, 4, 7, 9-13, 15-17, 19-23, 25, 27, 29-38 | 28 | 73.68 |
| Research field | |||
| E-commerce | 1, 10, 13, 20, 30, 37 | 6 | 12 |
| Marketing | 3, 4, 13, 22, 30, 33, 36 | 7 | 14 |
| Retails | 7, 11, 12, 20, 21, 23, 26-30, 32, 35 | 13 | 26 |
| Health care | 14-17, 19, 22-25, 31, 38, 40 | 12 | 24 |
| Others | 9, 34 | 12 | 24 |
Study Outcomes
Upon the curation of studies deemed relevant for this review, a comprehensive set of results was generated through the characterization of omnichannel interaction. Table 2 displays the selected studies and the principal outcomes delivered from these studies in relation to the implementation of omnichannel interaction.1 , 2 , 4 , 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 , 15 , 17 , 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 , 26, 27, 28, 29 , 32 , 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 , 44 , 49 , 50 A succinct explanation of the correlation between these outlined outcomes and the omnichannel interaction strategy is also presented.
Table 2.
Studies Outcomes
| Studies | Main outcomes | Total (n) | Values (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4, 9-11, 20, 22, 24, 27, 29, 35, 36, 44, 49 | Omnichannel strategy | 13 | 35.14 |
| 17, 23, 32, 34, 37 | Decision support systems | 5 | 13.51 |
| 1, 2, 9, 12, 15, 21, 26, 28, 29, 50 | Digital transformation | 10 | 27.03 |
| 1, 13, 21, 35, 38, 50 | Technology adoption | 6 | 16.22 |
| 2, 34, 37 | User experience | 3 | 8.11 |
Omnichannel Strategy
The studies analyzed in this systematic review elucidated that an omnichannel strategy represents a method for businesses to engage with customers across multiple channels in a harmonious and seamless manner. The objective of this strategy is to elevate customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty through the provision of a consistent and coherent experience across all customer touch points. The analyzed studies indicated that the implementation of an omnichannel strategy can yield several benefits, including improved access to information, optimized communication, and personalization of customer services. However, challenges such as the lack of integration and coordination between channels and the difficulty in quantifying and evaluating the impact of the omnichannel strategy were also identified.
Decision Support Systems
The utilization of decision support systems is pivotal in the decision-making process within an omnichannel environment. Decision support systems are computer systems designed to support informed decisions by providing decision makers with relevant information, tools, and models. In an omnichannel context, these systems can help organizations better understand customer data from multiple channels, spot patterns, and trends and make more informed and timely decisions, such as how to best engage with customers, choose the right channels, and allocate resources. Furthermore, decision support systems can play a role in personalizing customer interactions and delivering targeted and timely information to customers via multiple touch points.
Digital Transformation
Studies suggest that digital transformation plays a vital role in setting up an omnichannel interaction atmosphere. This provides customers with multiple channels to engage with a brand, resulting in an improved customer experience through consistent and uninterrupted communication across all touch points. Companies can use digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics, to gain a better understanding of customer needs and preferences, thereby allowing them to personalize and optimize their interactions. Furthermore, digital transformation empowers organizations to streamline and automate their processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. In summary, digital transformation is a crucial factor in creating an omnichannel environment that enhances customer experience and drives business growth.
Technology Adoption
The incorporation of innovative technological solutions is indispensable for the effective implementation of an omnichannel interaction strategy. This strategy involves the harmonious integration of several technological advancements, including cloud computing, big data analytics, AI, and mobile technology. These advances enable organizations to gather and analyze a wealth of customer data from multiple sources, including online and offline channels, mobile devices, and social media platforms. By doing so, businesses can attain a more nuanced understanding of their customer’s needs and preferences, thereby allowing them to personalize their interactions with greater precision.
Furthermore, incorporating technology into the interaction process streamlines operations, increases efficiency, and reduces costs. Additionally, it enables the seamless integration of multiple communication channels, such as chatbots, voice assistants, and messaging platforms, into the customer service process. This in turn leads to a marked improvement in customer experience and engagement. Thus, it is evident that the adoption of technology plays a vital role in the successful execution of an omnichannel interaction strategy.
User Experience
User experience holds paramount significance in an omnichannel interaction ecosystem. The aim of the omnichannel strategy is to provide a consistent and uninterrupted customer experience across all touch points. A positive UX is critical in achieving this objective because it significantly affects customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement. Hence, organizations must design their omnichannel interactions strategy with a user-centered approach, which prioritizes comprehending and catering to the needs and preferences of customers. Organizations should undertake user research, such as usability testing and user interviews, to gather feedback and make data-driven design decisions. They should also employ customer experience analytic tools to collect and analyze data from various touch points, thereby enabling them to recognize patterns and trends and make informed decisions on how to enhance the customer experience. A user-centric approach and a focus on UX are crucial for creating an omnichannel environment that not only improves customer experience but also drives business growth.
The next section presents an analysis of the findings gathered from the selected studies and valuable insights into the knowledge gained regarding the use of omnichannel interaction strategies that can be applied in health care services to improve patient care.
Discussion
This section highlights the most important contributions gathered about omnichannel interaction in general and in health care services in particular. First, some general omnichannel strategy insights are presented, followed by some findings gathered that can be applied in omnichannel interaction in health care services provided to patients. Finally, some limitations are identified as well as future research to be addressed in an omnichannel environment.
Omnichannel Strategy
Omnichannel interaction is considered a source of great competitive advantage and is completely transforming the e-commerce and marketing industries. This is achieved because of the digital transformation that is currently being adopted and which is driving omnichannel interaction, where consumers expect an easy and seamless UX across multiple interaction channels, both digital and physical.4 , 27 The main objective of omnichannel interaction strategy is to create a fully integrated and interconnected environment in which consumers can interact with organizations to acquire products or services through different interaction channels continuously and without interruption in the transition of different channels.49 Despite the huge benefits of omnichannel strategy adoption, there are some issues and challenges that organizations have to address first to achieve the full potential of an omnichannel strategy. Such issues and challenges regarding the omnichannel strategy were identified and are presented further.
Key Issues and Challenges
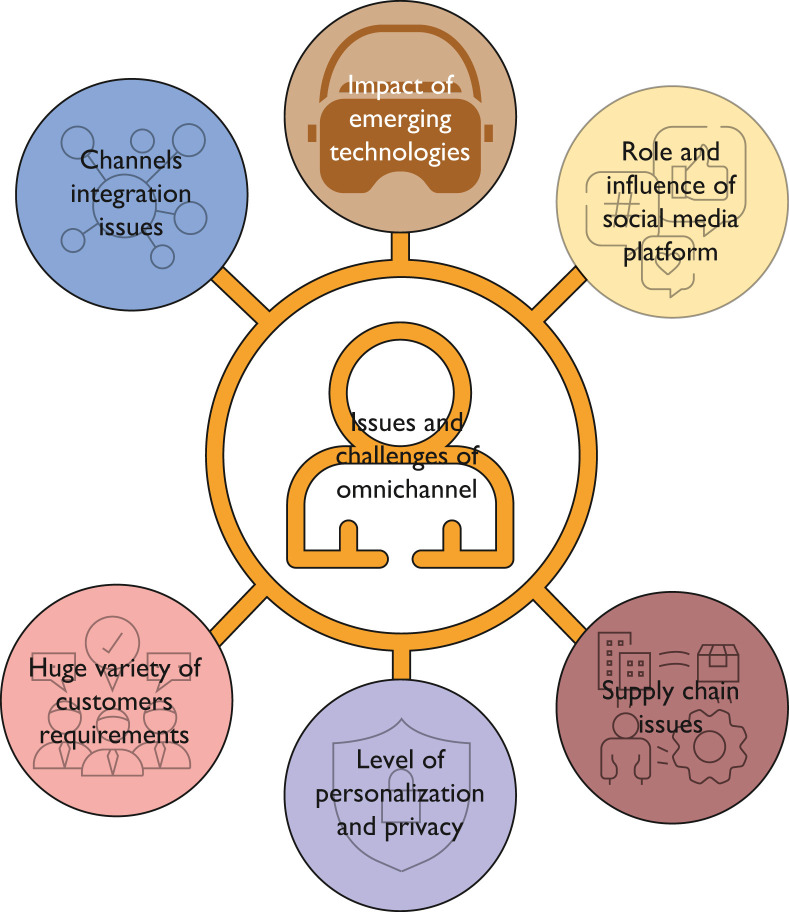
Based on the studies from academia and retail industries conducted by different groups currently, there are still numerous issues, challenges, and barriers that organizations must overcome to successfully implement the omnichannel interaction strategy.1 The most common issues identified are presented in Figure 3 .
Figure 3.
Issues and challenges of omnichannel interaction.
Channel Integration Issues
Customer channel integration is one of the challenges that customers perceive most in the omnichannel interaction environment because they expect the organization to provide consistent, continuous, integrated, and standardized service and experience across the different channels they use to interact with the organization. Customers expect to be able to interact effortlessly, switch from one channel to another, and continue where they were on the previous channel on any device anywhere. However, in many cases, organizations are still unable to provide this full integration between the different interaction channels available to their customers.4 , 12 , 21
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies and devices are constantly evolving daily and bring more innovations with these devices. Customers want to take advantage of these technologies in their interactions with organizations, which is why there is increasingly a need for organizations to include new technologies and devices in the omnichannel interaction strategy. Many organizations are not yet properly prepared to deal with the emerging technologies and devices that are being introduced to the market. The great challenge that organizations face at this level is to identify how they can properly respond and keep up with new trends in the evolution of technologies to delight and create even more of an environment of engagement with their customers.11 , 21 , 33
Role and Influence of Social Media Platform
Emerging technologies on mobile devices bring a new window of opportunity for creating social media platforms. Customers desire to interact with the organization through their preferred social media platform; to visit the business’s store to view, buy, rate, and promote a product or service; to get in touch with the business itself; and to share their thoughts regarding the product or service, even their satisfaction or disappointment with the product or service. The big challenge regarding social media is that an organization has a powerful influence on any customer’s social media platform. The organization must leverage social media platforms to create a strong presence and create close relationships with their existing and potential new customers to leverage their services and products.1 , 4 , 22
Huge Variety of Customer Requirements
Customers have different needs for different services or products or even different needs for the same product or service. The organization must overcome this variety of customer requirements in omnichannel interaction by adopting a clear strategy for each channel and product/service that they provide in a specific channel of interaction with their customers and adapting these products/services to customers’ needs. However, this can lead to a great level of customization and personalization of products and services provided to customers in a certain channel.9 , 4 , 22
Level of Personalization and Privacy
Customers expect to receive personalized information across different channels on the basis of their preferences and needs. However, there is an important factor that organizations must consider when targeting their customers with personalized information, which is customer privacy. The organization can obtain customers’ data through web browser cookies and loyalty cards to better understand customers’ needs and target them with the right offers at the right time. However, this can have a big effect on customer relationships if there is any breach of customer privacy, especially if customers are receiving too many marketing advertisements. Organizations must define a clear strategy about how they will handle and control customers’ data to provide them with personalized targeted information and to prevent all chances of leaking their customers’ data.1 , 35
Supply Chain Issues
In an omnichannel environment, managing the supply chain has a direct impact on customers’ experiences. Organizations need to create a single integrated point of contact where they can manage the stock of their products or availability of their services across all channels available to their customers to avoid future issues regarding lack of inventory or service in a specific channel, that is, as it is managed separately from other channels (lack of integration of channels inventory).21 , 22
There are many more issues and challenges that organizations must overcome when adopting omnichannel interaction in their business, but the aforementioned issues are the ones most referred to by different authors. In the end, omnichannel experiences are about how organizations choose to fulfill their customers’ expectations across multiple channels of interaction, and organizations that have not been able to do this right can be severely limited in their growth. With the issues and challenges of omnichannel strategy adoption, the next section will present the main benefits identified with the adoption of this approach.
Benefits of Omnichannel Strategy
The adoption of omnichannel interaction strategies in the areas of e-commerce and marketing has had a huge impact on these organizations, both from the point of view of business growth and the significant improvement that these organizations have had with their customers.21 There are countless advantages and benefits that the omnichannel interaction strategy has for organizations that decide to implement it and manage to implement it successfully. Several benefits were identified by different authors, but the most common is an information system that effectively and seamlessly engages customers across all channels.
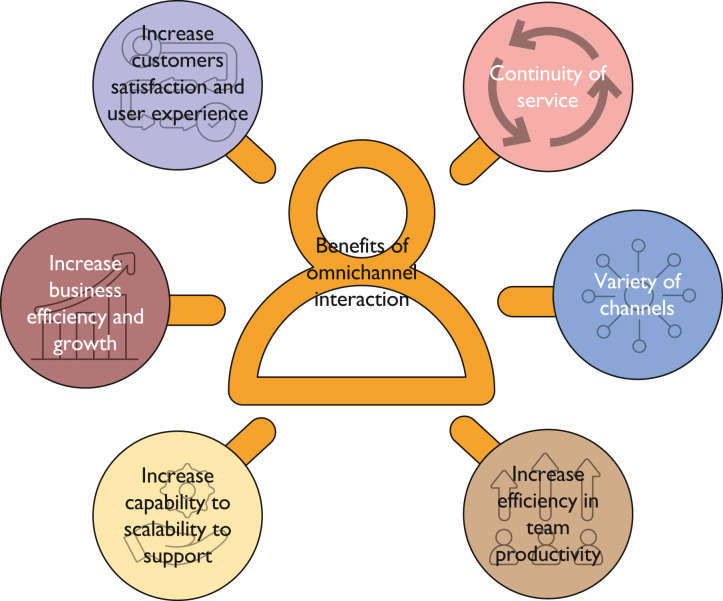
The adoption of an omnichannel strategy brings many benefits to the organization that implements it and to the organization’s existing customers and new customers. The most commonly found benefits of omnichannel strategy are presented in Figure 4 .
Figure 4.
Benefits of omnichannel interaction.
Increase Customer Satisfaction and UX
From a customer’s standpoint, every interaction with the business organization should be part of a singular experience. This means that, unlike multichannel customer assistance, it should not be repetitive or isolated. Customers expect a seamless journey across all channels, both online and offline, which is key to providing a consistent omnichannel experience and increasing their satisfaction with the services or products that they are receiving. When brands engage across all online and offline customer service channels and deliver consistent support, there is an increase in customer experience and satisfaction.42 , 48
Continuity of Service
Customers can switch easily between multiple interaction channels without losing the previous interaction information when it suits them and from wherever they want to, depending on their preferences and the type of interaction.21 , 44
Variety of Channels
Customers have a huge variety of channels from which they can choose the one that better fits their preferences to interact with an organization’s service or product.48
Increase Efficiency in Team Productivity
The organization’s employees can be distributed across multiple channels and services on the basis of their expertise and knowledge. This can free up overloading and resource wasting and, therefore, increase team productivity.43
Increase Capability to Scalability
Owing to a variety of channels available, multiple channel customers can get insights regarding the business service or commercial product. This gives a huge advantage in scaling customer support where and when it is needed in the future to accomplish the desired growth in customers’ expectations.44
Increase Business Efficiency and Growth
One of the significant benefits of an omnichannel strategy is increased return on investment. This is one of the most important measures that organizations are looking for. With proper segmentation and personalization, an omnichannel strategy can be highly successful. Thus, greater customer engagement will lead to more interaction and a higher business revenue.21 , 48
Omnichannel Strategy in Health Care
According to several prior studies regarding multichannel and omnichannel interaction strategies, health care businesses must plan and adopt an omnichannel strategy.9 , 13 , 21 , 23 , 26 , 30 , 34 , 35 Studies performed during the past few years at Centro Hospitalar Universitário do Porto, Portugal, during the first wave of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic regarding multichannel interaction in health care services51 showed the potential and the impact that such an approach can have on a health care institution, health professionals, and patients.15 , 16 This adoption highlights the benefits that this paradigm has for the health care field itself. In a highly integrated health care system,50 omnichannel interaction has the potential to enable real-time and automatic data acquisition that releases health care practitioners from such responsibilities and enables them to devote their time to providing even better services to their patients. Currently, more health care organizations are trying to adopt or planning to adopt the omnichannel interaction approach in the many services they provide to their patients. The early adoption of the omnichannel approach is mainly used in triage, patient assessment, and medical discharge, which are some of the care services that do not rely on in-person care to be performed.41 , 45
The use of telemedicine and telehealth technology in care services is widespread and being adopted more by care providers. The pandemic has played an important role in this widespread adoption because many health care institutions have had their care capacity reduced in many services and relocated to coronavirus disease 2019 services, forcing them to find new, efficient, and secure ways to continue to provide their services to their patients.36 , 43 The focus of the adoption of the omnichannel interaction strategy is to deliver a health care services model that balances virtual care and in-person care as a unified system.
At its core, omnichannel interaction in health care services can be seen as the final level of aggregation and automatization of all available interaction channels to provide a better care service to patients and to enable the continuity of care services provided to patients across multiple channels of interaction, the systems and processes that make such interaction possible, and, finally, the care providers, who are focused on patients, processes, data, systems, services, and strategy.15 , 17 , 49
Omnichannel adoption in health care is still in its early infancy, and there are many challenges that health care organizations must address and overcome before successfully implementing the omnichannel strategy. However, when successfully implemented, it brings many benefits to a health care business that implements it. In this context, several brainstorming sessions were held with health professionals to discuss the challenges and benefits of omnichannel strategy adoption in health care services. This involves a collaborative process of identifying the best practices and strategies to implement an omnichannel approach in the delivery of health care services. Moreover, these sessions were used to cohort these health care professionals with the findings gathered from the literature review and to get their feedback regarding these findings. The discussions that ensued were comprehensive and exhaustive because various viewpoints were considered. The decisions made during the brainstorming process are reached on the basis of several factors, including the need to provide seamless and coordinated care services to patients, the growing demand for virtual care services, and the need to improve the patient UX. Additionally, the decisions are grounded in evidence-based research, expert opinions, and practical feasibility. Several challenges were identified in omnichannel strategy adoption in health care services but the ones that struck more are the urgent need for considerable investment in technology infrastructure, information systems, health care regulation, and personnel training. In addition to these challenges, there are many others that have been discussed, such as the privacy of the patient’s clinical data and channel integrations, among others, which are similar to the findings of the literature review.9 , 19 , 23 , 39 , 40 , 47
Despite these challenges, the advantages and benefits of implementing an omnichannel strategy in health care services are enormous. Providing personalized care services delivered to patients through a range of channels, such as online platforms, mobile applications, and telehealth, can result in augmenting patient engagement and satisfaction. Patients can receive treatment from a primary care provided by a physician, specialist, or pharmacist without the necessity of physical appointments, thus reducing wait times and improving overall patient outcomes and satisfaction. Additionally, it provides patients with seamless continuity of care services across multiple channels. Furthermore, the adoption of an omnichannel strategy has the potential to enhance efficiency and productivity because health care providers can grow their businesses; increase efficiency through sharing processes, technology, information, and clinical data; lower the cost of access; and improve the quality of care service provided to patients; and, in general, have a more integrated business process.25 , 39 , 42 , 44 , 46 In sum, the brainstorming process with health care professionals offered valuable insights into the benefits and challenges of adopting an omnichannel approach in the health care industry.
Although health care organizations are taking their first steps toward its adoption, it has already shown its potential for care providers and their patients. Now, a step forward will have to be taken to identify how omnichannel interaction in health care services is currently found and to analyze its benefits, advantages, and disadvantages. According to several prior studies regarding multichannel interaction in health care services,15 , 17 the finding gathered with this review was able to outline 5 key characteristics that are essential to be addressed by health care institutions when they are planning to adopt an omnichannel strategy (RQ 2). These key characteristics are as follows:
-
•
“Strategy” is the plan and focus that health care organizations have to carry out as a successful adoption of the omnichannel strategy.
-
•
“Processes” are all tasks and activities that are performed during the interaction (engagement) process.
-
•
“Systems” are all information technologies necessary to maintain and support all interactions between different actors in different channels.
-
•
“Data” are all clinical data and information that are exchanged between different channels in the interaction between patients and health practitioners.
-
•
“People” are all the actors involved in the interaction process, such as patients, health professionals, laboratory technicians, and administrative staff.
Based on these 5 key characteristics, there are several best practices identified that health care institutions should adopt when implementing an omnichannel strategy. The practices are related to a strategy definition and alignment, investment in technology infrastructure, health professionals training, focus on patient UX, and continuity of services across multiple channels and channels monitoring (RQ 2). These characteristics are crucial to the effective implementation of an omnichannel strategy in health care. More research is being conducted to shed light on these characteristics and other elements that could affect how the omnichannel interaction approach in health care is adopted.11 , 17
Currently, health care organizations have a lot to gain from the adoption of an omnichannel strategy, especially patients and health care practitioners. A strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis was performed to identify the main strengths, weaknesses, threats, and opportunities of the omnichannel strategy for health care organizations and to answer the identified RQ proposed in this article. Table 3 presents the SWOT analysis regarding the adoption of the omnichannel strategy in the health care area.4 , 9 , 16 , 19 , 23 , 25 , 30 , 38 , 40 , 47, 48, 49
Table 3.
Omnichannel Strategy in Health Care Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats Analysis
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| The health care organization focuses on providing continuous service to its patients and innovating new care services and making them available in an omnichannel environment, enabling health care organizations to maintain a strong market position and improve their patients’ relationships and desire fulfillment. The health care organization has a substantial gain in terms of geographical reach; it is not limited to providing only the patient in the same location that the organization is located and can increase its patient base and maintain a strong identity among its patients. The health care organization can reduce costs with in-person care services that usually are allocated to perform this activity as well to reduce health professional activities and allocate this resource to provide new care services or improve the existing ones. The health care organization will have the capability to provide continuity of care services across multiple channels of interaction. The patient has an active role in the interaction with health professionals. |
The health care organization’s inability to understand patients’ needs and expectations across multiple channels of interaction leads to an ineffective strategic decision-making process. This weakness may lead the organization to be unable to identify potential improvements in its services. In health care, several care providers still lack experience and understanding of the new approach to omnichannel strategy, which is a huge reason for low adoption and consequently low omnichannel adoption success. Poor quality of patient care service (inadequate handling of patient complaints) can trigger negative word of mouth toward the care provider and affect business growth. The health care organization may experience a lack of technical and financial resources when adopting this strategy, which can be a limiting factor to the health care organization’s growth. Poor omnichannel strategy definition, planning and goals, and metrics definition. The health care organization’s culture may become a big internal weakness when it is not properly aligned with the strategic business objectives. |
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| Increase the demand for care services provided to patients in an omnichannel environment. The emergence of new market segments and new niches provide health care organizations and their service a huge expansion opportunity. The development of new technologies to assist the care services provided to patients in an omnichannel environment can be exploited to embed innovation in business operations. |
Changes in regulatory laws and introducing new regulations impose a major threat to health care organizations. The increasing number of other health care businesses that somehow can be direct or indirect competitors affects the health care organization to maintain and sustain their patient base. The shortage of skilled health professionals with knowledge of omnichannel interaction can make it difficult for the health care organization to attract talent with the right set of skills. |
The SWOT analysis brings to the discussion that the health care organization should adopt the omnichannel strategy. They can take the lesson and learn from the omnichannel strategies being used by e-commerce and marketing companies and adapt them to suit their needs. Of course, in health care, there will be more challenges and restrictions in terms of patient privacy concerning the patient’s clinical data and laws on data protection and privacy, but a well-defined and planned strategy is essential to overcome these challenges and many others that may arise during the adoption of an omnichannel strategy. Providing patients with highly personalized and timely solutions also increases the health care organization’s brand value.22 , 25 , 31 , 44 , 49
Furthermore, the presented SWOT analysis helps to highlight the potential benefits of implementing such strategies within the health care context. To effectively do so, health care institutions must learn from the practices implemented in other areas (e-commerce and marketing) and adapt them to the specific context of health care services delivered to patients. However, it is crucial to note that solutions implemented in other fields may not be directly applicable to the health care sector. Therefore, it is essential for health care institutions to conduct thorough research and identify omnichannel interaction solutions that are particularly suited for the health care domain on the basis of on the insights gained from this literature review (RQ 1).
Limitations and Future Research
The implementation of an omnichannel strategy by health care providers is an area of ongoing research that presents a plethora of opportunities and obstacles to be addressed and overcome. The challenges faced in the implementation of an omnichannel strategy by health care providers are complex and multidimensional. One of the critical hurdles is the absence of standardization in the execution of the omnichannel strategy, making it difficult to conduct a comprehensive evaluation and comparison of different methodologies. Maintaining the confidentiality and security of patient information is a paramount consideration while implementing an omnichannel strategy because it requires the seamless integration of multiple health care information systems and platforms. The limited adoption of this strategy by health care providers may be due to factors such as cost, lack of awareness, or apprehension surrounding data protection and privacy. Finally, there is a scarcity of long-term research on the outcomes of the omnichannel strategy, hindering the comprehension of its effects on patient health and well-being (RQ 3).
To overcome these limitations, future research should prioritize the development of standard protocols for the omnichannel strategy to enhance the comparability and evaluation of different methods. There is also a requirement for additional research on the long-term outcomes of omnichannel interaction with a focus on understanding its effect on patient outcomes. An investigation of the impact of omnichannel interaction on the patient–provider relationship and its potential to enhance communication and continuity of care is critical. Moreover, exploring the influence of omnichannel interaction on health care costs and resource utilization is necessary to understand its role in improving the efficiency of health care systems. Finally, the use of AI and machine learning techniques to improve the personalization and efficacy of omnichannel interaction in health care services merits examination (RQ 4).
Conclusion
An omnichannel health care strategy can provide a seamless, personalized service and patient care experience that benefits not only patients but also the care provider and health professionals. Its adoption has the potential to enhance the patient user experience and improve overall health outcomes. Implementing an omnichannel interaction strategy in health care services can have a variety of positive outcomes. According to this systematic literature review, omnichannel interactions can improve patient engagement and satisfaction by providing patients with multiple channels of access to health care services. In addition, an omnichannel strategy can improve access to care, especially for underserved populations who may not have easy access to a physical health care facility. Moreover, implementing an omnichannel strategy can result in cost savings associated with unnecessary hospital visits. This, in turn, can lead to improved patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans.
Omnichannel interaction in health care services can improve patients’ lives and well-being by providing them with more convenient, efficient, and accessible health care services. This can be achieved by providing patients with multiple channels to access care services, enhancing communication and coordination among health care providers, improving patient engagement and empowerment, reducing waiting times to access the care services, and creating a full and integrated environment to offer continuity of care to the patient. Moreover, health care providers will have a more comprehensive view of patient needs, allowing for more personalized care. Moreover, an omnichannel strategy can improve health care provider communication and collaboration, resulting in more efficient and effective care coordination.
The health care institutions that implement the omnichannel approach will benefit from a new window of opportunity and business growth and patient engagement. However, health care institutions need to know that a well-defined strategy focused on omnichannel interaction is essential to their success and that patients are not yet properly prepared for the sudden adoption of these technologies in health care services.
Furthermore, for a health care institution to successfully implement an omnichannel strategy, all health care systems must be perfectly aligned with the strategy established and the patients must have a basic understanding of how to communicate with health care providers. Otherwise, the care provider will not be able to accomplish their goals with the adoption of an omnichannel strategy. Ultimately, the adoption of an omnichannel strategy will make the patient the true beneficiary of the health care system by providing them access to more practical effects and easily accessible health care services.
Finally, it is important to note that the successful implementation of an omnichannel strategy in health care services requires a robust technology infrastructure, data analytics, and trained professionals to handle the interactions. The integration of data from multiple channels can be challenging but can provide a more complete picture of the patient journey, which can be used for continuous improvement of health care services.
Potential Competing Interest
The authors report no competing interests.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nicolas Lori for his support during the review of the article.
Footnotes
Grant Support: This research was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, within the Projects Scope: UIDB/00319/2020. A.M. was supported by the grant 2022.10342.BD and C.A. was supported by the grant 2022.12629.BD.
References
- 1.Piotrowicz W., Cuthbertson R. Introduction to the special issue information technology in retail: toward omnichannel retailing. Int J Electron Commer. 2014;18(4):5–16. doi: 10.2753/JEC1086-4415180400. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alves C., Reis J.L. In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Symposium on Information Technology and Systems. Rocha A., Ferrás C., Marin C.E.M., García V.H.M., editors. Springer International Publishing; 2020. The intention to use e-commerce using augmented reality–the case of IKEA place; pp. 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fürst A., Leimbach M., Prigge J.K. Organizational multichannel differentiation: an analysis of its impact on channel relationships and company sales success. J Mark. 2017;81(1):59–82. doi: 10.1509/jm.14.0138. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rusanen O. In: Exploring Omnichannel Retailing. 1st ed. Piotrowicz W., Cuthbertson R., editors. Springer International Publishing; 2019. Crafting an omnichannel strategy: identifying sources of competitive advantage and implementation barriers; pp. 11–46. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Caldwell A. What is omnichannel? Benefits and strategies. NetSuite. https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/ecommerce/omnichannel.shtml
- 6.Krafft M., Goetz O., Mantrala M., Sotgiu F., Tillmanns S. The evolution of marketing channel research domains and methodologies: an integrative review and future directions. J. Retail. 2015;91(4):569–585. doi: 10.1016/jretai.2015.05.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yrjölä M., Saarijärvi H., Nummela H. The value propositions of multi-, cross-, and omni-channel retailing. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 2018;46(11/12):1133–1152. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-08-2017-0167. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lutkevich B. What is multichannel marketing? TechTarget. https://www.techtarget.com/searchcustomerexperience/definition/multichannel-marketing
- 9.Gerea C., Herskovic V. Transitioning from multichannel to omnichannel customer experience in service-based companies: challenges and coping strategies. J Theor Appl Electron Commer Res. 2022;17(2):394–413. doi: 10.3390/JTAER17020021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Silva S.C., Duarte P., Sundetova A. Multichannel versus omnichannel: a price-segmented comparison from the fashion industry. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 2020;48(4):417–430. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-07-2019-0232. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Asmare A., Zewdie S. Omnichannel retailing strategy: a systematic review. Int Rev Retail Distrib Consum Res. 2022;32(1):59–79. doi: 10.1080/09593969.2021.2024447. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Verhoef P.C., Kannan P.K., Inman J.J. From multi-channel retailing to omni-channel retailing: introduction to the special issue on multi-channel retailing. J Retail. 2015;91(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.jretai.2015.02.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Thaichon P., Phau I., Weaven S. Moving from multi-channel to omni-channel retailing: special issue introduction. J Retail Consum Serv. 2022;65 doi: 10.1016/J.jretconser.2020.102311. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brody J.E. A pandemic benefit: the expansion of telemedicine. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/05/11/well/live/coronavirus-telemedicine-telehealth.html?campaign_id=2&emc=edit_th_200512&instance_id=1840âĂę1/2https://nyti.ms/3bjGxmr
- 15.Moreira A., Guimarães T., Santos M.F. A conceptual model for multichannel interaction in healthcare services. Procedia Comput Sci. 2020;177:534–539. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.10.074. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moreira A., Miranda R., Santos M.F. Health professional’s decision-making based on multichannel interaction services. Procedia Comput Sci. 2021;184:899–904. doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2021.03.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moreira A., Santos M.F. Multichannel interaction for healthcare intelligent decision support. Procedia Comput Sci. 2020;170:1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.074. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Page M.J., McKenzie J.E., Bossuyt P.M., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2021;74(9):790–799. doi: 10.1016/J.REC.2021.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abdolkhani R., Gray K., Borda A., DeSouza R. Patient-generated health data management and quality challenges in remote patient monitoring. JAMIA Open. 2019;2(4):471–478. doi: 10.1093/JAMIAOPEN/OOZ036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ailawadi K.L., Farris P.W. Managing multi- and omni-channel distribution: metrics and research directions. J Retail. 2017;93(1):120–135. doi: 10.1016/j.jretai.2016.12.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barbosa J., Casais B. The transformative and evolutionary approach of omnichannel in retail companies: insights from multi-case studies in Portugal. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 2022;50(7):799–815. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-12-2020-0498. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Berman B, Thelen S. Planning and implementing an effective omnichannel marketing program. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 201846(7):598-614. doi:10.1108/IJRDM-08-2016-0131
- 23.Chen Y., Cheung C.M.K., Tan C.W. Omnichannel business research: opportunities and challenges. Decis Support Syst. 2018;109:1–4. doi: 10.1016/J.DSS.2018.03.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gutiérrez L.R., García R.S. Omnichannel strategy and consumer behavior in distribution channels: trends in the ophthalmology sector. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1142. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hjelm N.M. Benefits and drawbacks of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2005;11(2):60–70. doi: 10.1258/1357633053499886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hübner A., Wollenburg J., Holzapfel A. Retail logistics in the transition from multi-channel to omni-channel. Int J Phy Distrib Logist Manag. 2016;46(6-7):562–583. doi: 10.1108/IJPDLM-08-2015-0179. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ji G., Fu T., Chen J., Tan K.H. Optimal online service strategy and price decision in omnichannel retail. Math Probl Eng. 2022;2022(1):1–35. doi: 10.1155/2022/8698309. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ji J., Wang Y., Jia H., Hole Y., Pawar M.S., Khedkar E.B. Omni channel retailing: an opportunity and challenges in the Indian market. J Phys.: Conf Ser. 2019;1362(1) doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1362/1/012121. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jocevski M., Arvidsson N., Miragliotta G., Ghezzi A., Mangiaracina R. Transitions towards omni-channel retailing strategies: a business model perspective. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 2019;47(2):78–93. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-08-2018-0176. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Luiz J., De Carvalho G., Campomar M.C. Multichannel at retail and omni-channel: challenges for marketing and logistics. Bus Manag Revi. 2014;4(3):103–113. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mahajan V., Singh T., Azad C. Using telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. Indian Pediatr. 2020;57(7):658–661. doi: 10.1007/s13312-020-1895-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mishra R., Singh R.K., Koles B. Consumer decision-making in omnichannel retailing: literature review and future research agenda. Int J Consum Stud. 2021;45(2):147–174. doi: 10.1111/IJCS.12617. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rangaswamy A., Van Bruggen G.H. Opportunities and challenges in multichannel marketing: an introduction to the special issue. J Interact Market. 2005;19(2):5–11. doi: 10.1002/dir.20037. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shen X.L., Li Y.L., Sun Y., Wang N. Channel integration quality, perceived fluency and omnichannel service usage: the moderating roles of internal and external usage experience. Decis Support Syst. 2018;109:61–73. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2018.01.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sousa P.R., Barbosa M.W., de Oliveira L.K., et al. Challenges, opportunities, and lessons learned: sustainability in Brazilian omnichannel retail. Sustainability. 2021;13(2):666. doi: 10.3390/SU13020666. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang L., Wu L., Huang L., Zhang Y. Wield the power of Omni-channel retailing strategy: a capability and supply chain resilience perspective. J Strateg Mark. 2021:1–25. doi: 10.1080/0965254X.2021.1972440. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang M., Ren C., Wang G.A., He Z. The impact of channel integration on consumer responses in omni-channel retailing: the mediating effect of consumer empowerment. Electron Commer Res Appl. 2018;28:181–193. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2018.02.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Archip A, Botezatu N, Serban E, Herghelegiu PC, Zala A. An IoT based system for remote patient monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 2016 17th International Carpathian Control Conference. ICCC; 2016:1–6, 7. doi:10.1109/CarpathianCC.2016.7501056
- 39.Cunha C.R., Gomes J.P., Fernandes J., Morais E.P. Building smart rural regions: challenges and opportunities. Adv Intell Syst Comput. 2020;1161:579–589. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-45697-9_56. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.El-Mahalli A.A., El-Khafif S.H., Al-Qahtani M.F. Successes and challenges in the implementation and application of telemedicine in the eastern province of Saudi Arabia. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2012;9(Fall):1–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Multichannel vs. omnichannel: what’s the difference? Mercury Healthcare. Accessed November 9, 2022. https://www.mercuryhealthcare.com/blog/multi-channel-vs-omnichannel-whats-the-difference
- 42.5 benefits of omni-channel marketing. Maropost. https://www.maropost.com/5-benefits-of-omni-channel-marketing-for-smbs/
- 43.Mesibov M. 3 ways to improve your health care omnichannel strategy. Mad∗Pow. https://madpow.com/insights/2019/5/3-ways-improve-your-healthcare-omnichannel-strategy
- 44.O’Conneil M. How an omnichannel strategy benefits businesses and customers. Salesforce. https://www.salesforce.com/eu/blog/2020/12/omnichannel-strategy-benefits.html
- 45.Parmar A. How omnichannel engagement is bringing a paradigm shift to the healthcare system. Stefanini Group. Accessed October 5, 2022. https://stefanini.com/en/trends/articles/how-omnichannel-engagement-bringing-shift-to-healthcare-system
- 46.Patel S. Omnichannel benefits for businesses and customers. REVE Chat. https://www.revechat.com/blog/omnichannel-benefits/
- 47.Omnichannel Roi–how to get a quantifiable return on your omni-channel investment. Usan, Inc; 2015. https://www.usan.com/white-papers/omni-channel-roi/ [Google Scholar]
- 48.7 advantages of an omnichannel strategy. Vincle. https://www.vincle.com/seven-advantages-of-an-omnichannel-strategy/
- 49.Pietig M. Building an omnichannel healthcare strategy. Avtex. https://avtex.com/articles/building-an-omnichannel-healthcare-strategy
- 50.Cardoso L., Marins F., Portela F., Santos M., Abelha A., Machado J. The next generation of interoperability agents in healthcare. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(5):5349–5371. doi: 10.3390/ijerph110505349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moreira A., Duarte J., Santos M.F. Case study of multichannel interaction in healthcare services. Information. 2023;14(1):37. doi: 10.3390/info14010037. [DOI] [Google Scholar]