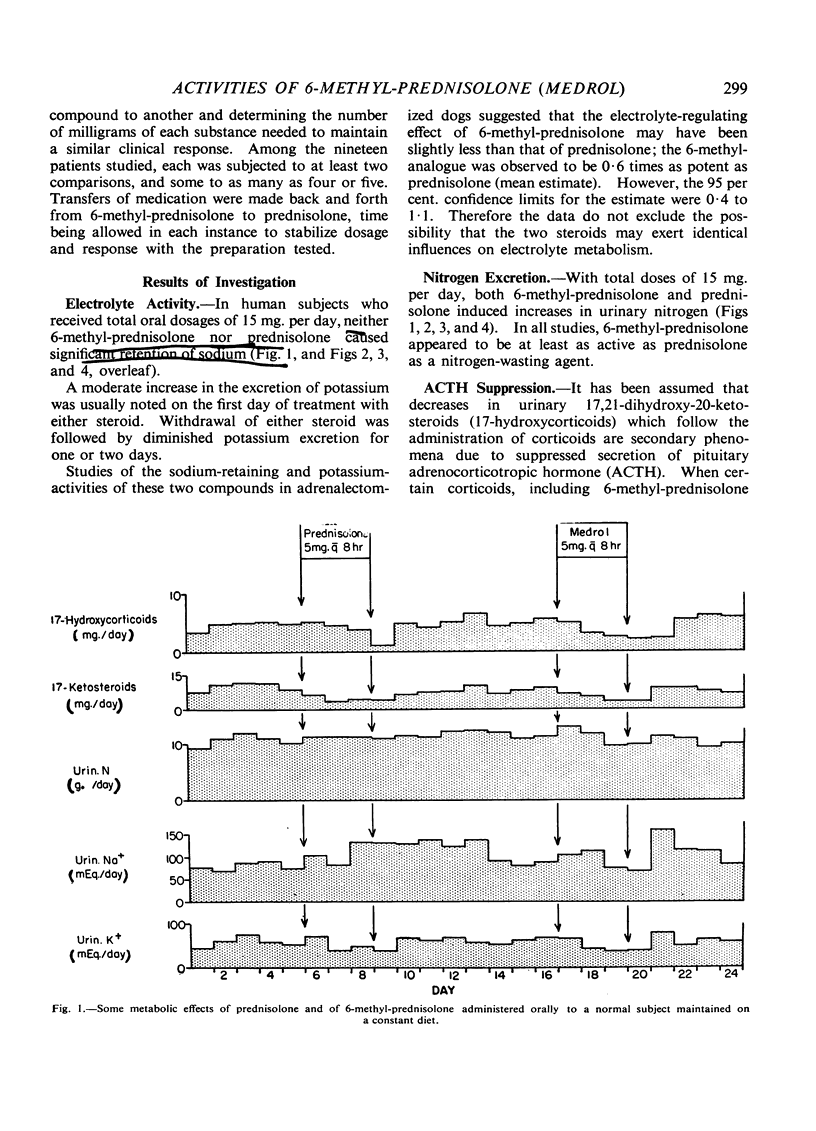
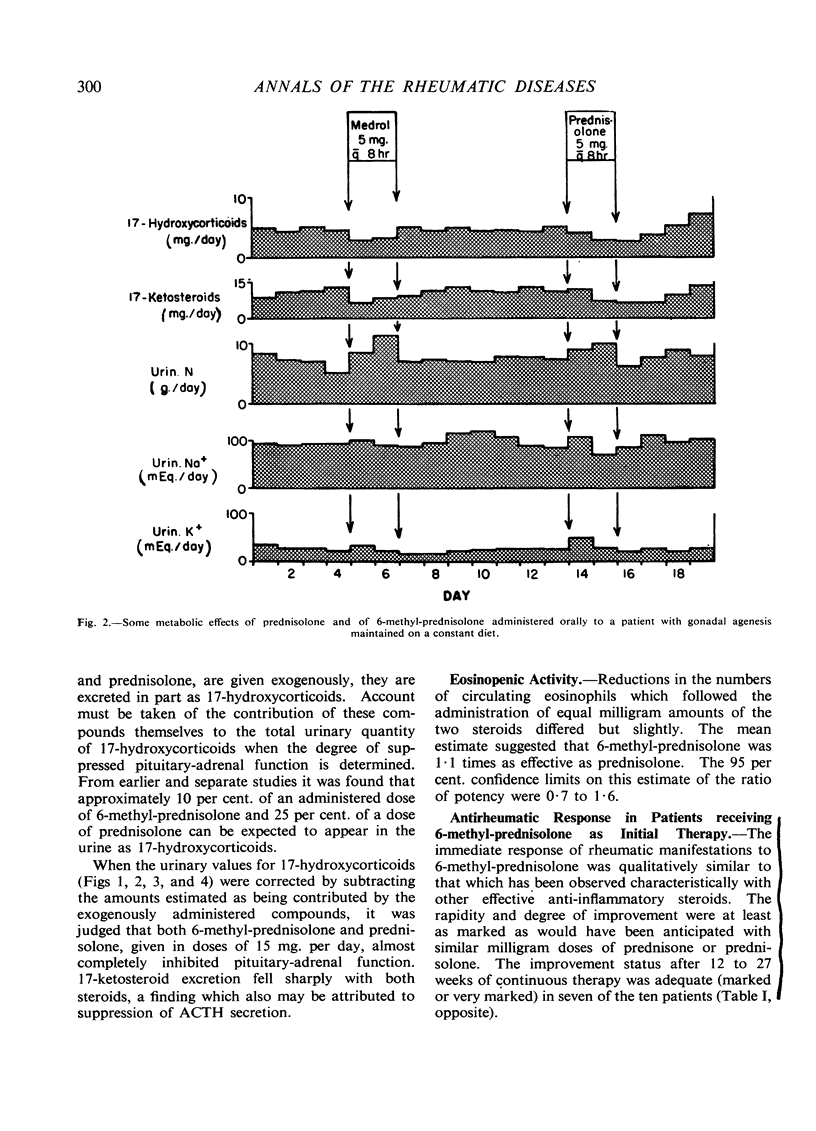
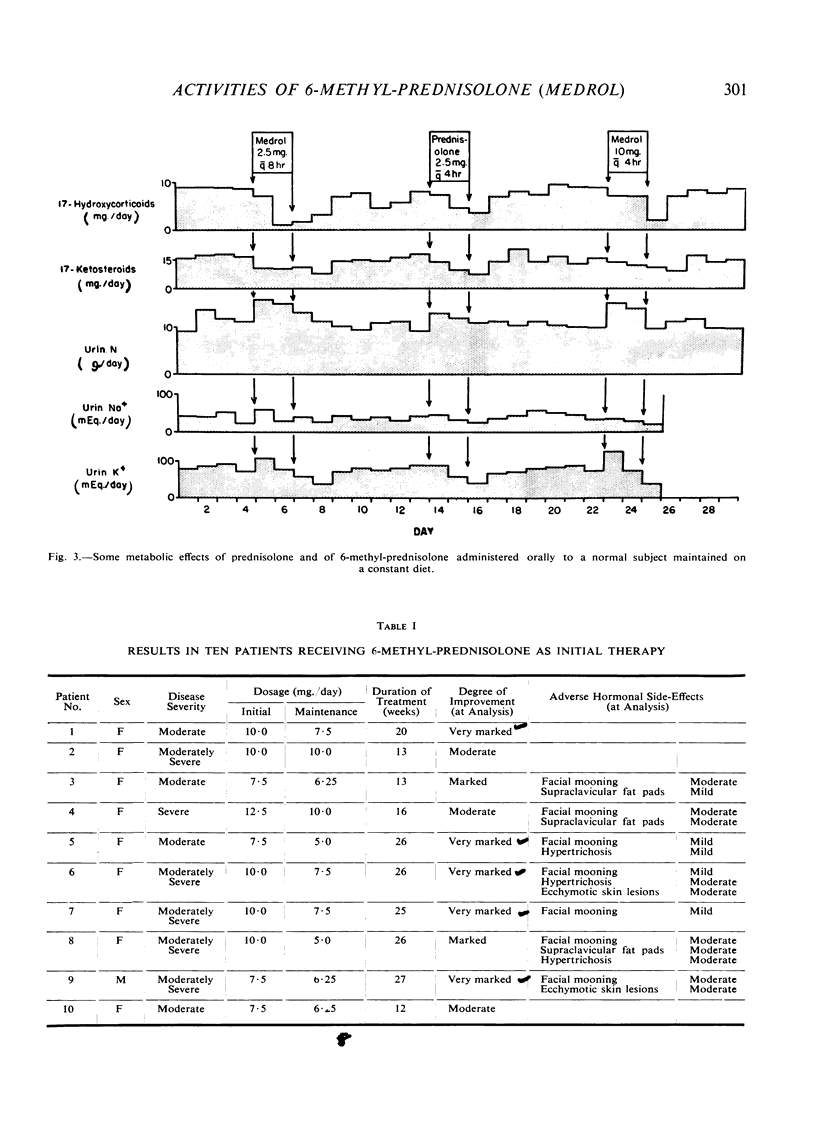
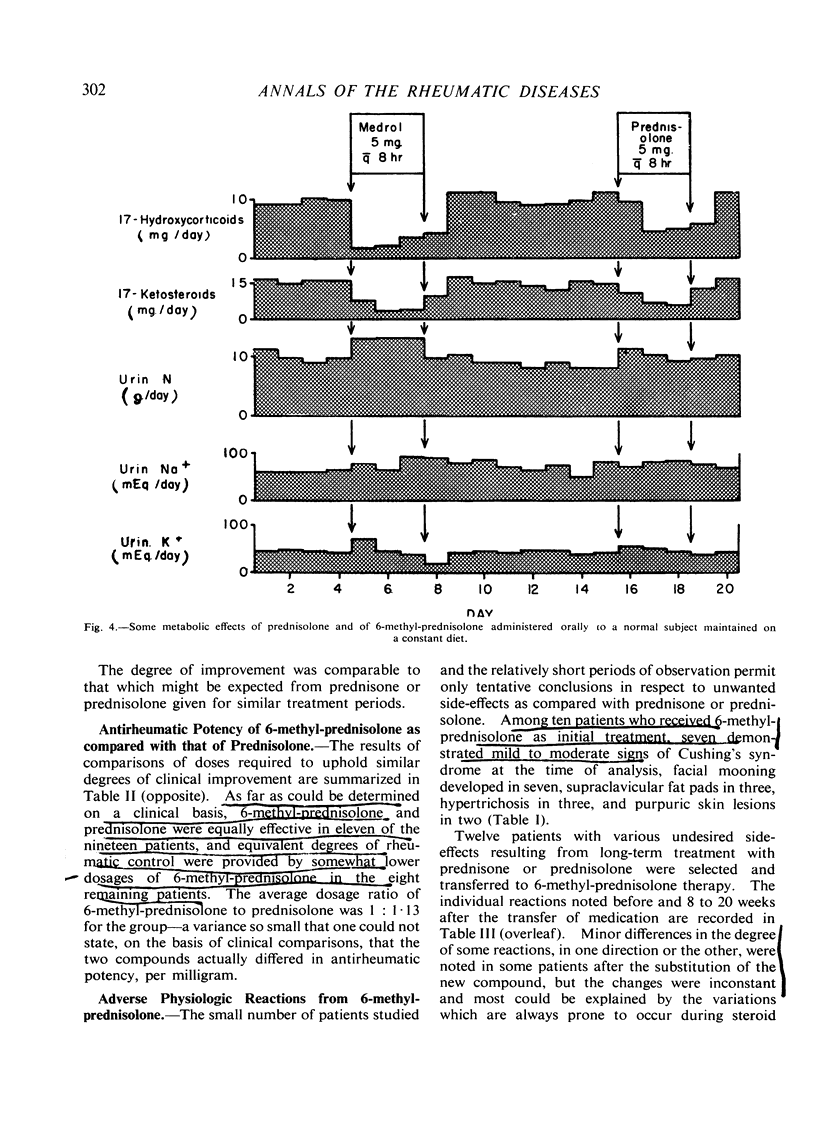
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES L. E., BYRNES W. W., LUND G. H., LYSTER S. C., MEINZINGER M. M. Adrenal corticoid activities of 6-methyl-delta-hydrocortisone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):159–162. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLAND E. W. Experiences with 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone acetate in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 May 27;61(2):591–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLET A. J., BLACK R., BUNIM J. J. Major undesirable side-effects resulting from prednisolone and prednisone. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Jun 11;158(6):459–463. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960060017005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUNIM J. J., PECHET M. M., BOLLET A. J. Studies on metacortandralone and metacortandracin in rheumatoid arthritis; antirheumatic potency, metabolic effects, and hormonal properties. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Jan 22;157(4):311–318. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02950210007003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callow N. H., Callow R. K., Emmens C. W. Colorimetric determination of substances containing the grouping -CH(2).CO- in urine extracts as an indication of androgen content. Biochem J. 1938 Aug;32(8):1312–1331. doi: 10.1042/bj0321312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREKTER I. J., HEISLER A., SCISM G. R., STERN S., PEARSON S., McGAVACK T. H. The determination of urinary steroids. I. The preparation of pigment-free extracts and a simplified procedure for the estimation of total 17-ketosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1952 Jan;12(1):55–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-12-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIED J. Biological effects of 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone and related halogenated steroids in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 May 27;61(2):573–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE G. W., CORNFIELD J., CASPER A. G., BARTTER F. C. The physiological basis for a method of assaying aldosterone in extracts of human urine. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1410–1416. doi: 10.1172/JCI103190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE G. W., RICHARD J. E., TOMKINS G. M. Studies of structure-function relationships of steroids: the 2-methyl-corticosteroids. Metabolism. 1956 Jul;5(4):384–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. E., WYNGAARDEN J. B., GUERRA S. L., BRODIE B. B., BUNIM J. J. The physiological disposition and metabolic fate of hydrocortisone in man. J Clin Invest. 1955 Dec;34(12):1779–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI103233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN E., KIRKWOOD S. Explanation of the effect of feeding desiccated thyroid on the incidence of dental caries in the rat. Science. 1955 Feb 4;121(3136):175–176. doi: 10.1126/science.121.3136.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILBER R. H., PORTER C. C. The determination of 17,21-dihydroxy-20-ketosteroids in urine and plasma. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):923–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


