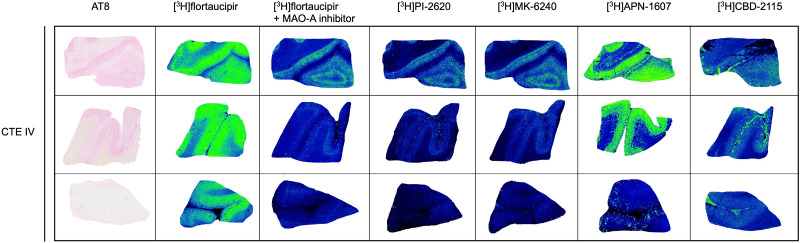
Visual Abstract
Keywords: CTE, PET, tau, autoradiography, chronic traumatic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurologic disorder associated with head injuries, diagnosed by the perivascular accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau protein (phospho-tau) identified at autopsy. Tau PET radiopharmaceuticals developed for imaging Alzheimer disease are under evaluation for brain injuries. The goal of this study was to conduct a head-to-head in vitro evaluation of 5 tau PET radiotracers in subjects pathologically diagnosed with CTE. Methods: Autoradiography was used to assess the specific binding and distribution of 3H-flortaucipir (also known as Tauvid, AV-1451, and T807), 3H-MK-6240 (also known as florquinitau), 3H-PI-2620, 3H-APN-1607 (also known as PM-PBB3 and florzolotau), and 3H-CBD-2115 (also known as 3H-OXD-2115) in fresh-frozen human postmortem CTE brain tissue (stages I–IV). Immunohistochemistry was performed for phospho-tau with AT8, 3R tau with RD3, 4R tau with RD4 and amyloid-β with 6F/3D antibodies. Tau target density (maximum specific binding) was quantified by saturation analysis with 3H-flortaucipir in tissue sections. Results: 3H-flortaucipir demonstrated a positive signal in all CTE cases examined, with varying degrees of specific binding (68.7% ± 10.5%; n = 12) defined by homologous blockade and to a lesser extent by heterologous blockade with MK-6240 (27.3% ± 13.6%; n = 12). The 3H-flortaucipir signal was also displaced by the monoamine oxidase (MAO)–A inhibitor clorgyline (43.9% ± 4.6%; n = 3), indicating off-target binding to MAO-A. 3H-APN-1607 was moderately displaced in homologous blocking studies and was not displaced by 3H-flortaucipir; however, substantial displacement was observed when blocking with the β-amyloid–targeting compound NAV-4694. 3H-MK-6240 and 3H-PI-2620 had negligible binding in all but 2 CTE IV cases, and binding may be attributed to pathology severity or mixed Alzheimer disease/CTE pathology. 3H-CBD-2115 showed moderate binding, displaced under homologous blockade, and aligned with 4R-tau immunostaining. Conclusion: In human CTE tissues, 3H-flortaucipir and 3H-APN-1607 revealed off-target binding to MAO-A and amyloid-β, respectively, and should be considered if these radiotracers are used in PET imaging studies of patients with brain injuries. 3H-MK-6240 and 3H-PI-2620 bind to CTE tau in severe- or mixed-pathology cases, and their respective 18F PET radiotracers warrant further evaluation in patients with severe suspected CTE.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to a history of head injuries, including traumatic brain injuries, repetitive concussive injuries, or subconcussive injuries. Individuals at risk for developing CTE include contact sport athletes, military veterans, and victims of intimate partner violence (1). The lasting implications of CTE have become more prevalent in recent years, with reported symptoms and comorbidities including memory loss, behavioral and mood changes, cognitive deficits, sleep disorders, and substance use disorders (1). Although neurodegeneration can be classified in the clinic on the basis of these cognitive or behavioral presentations, diagnosis of CTE is possible only on postmortem neuropathologic evaluation to identify the presence of perivascular hyperphosphorylated tau protein (phospho-tau) (2,3). CTE diagnosis is categorized into stages ranging from I to IV, where stage I consists of isolated perivascular centers at the depths of sulci in the frontal cortex. The pathology progresses in severity and spreads regionally, with widespread involvement of the neocortex, hippocampus, amygdala, cerebellum, and cervical spinal cord by stage IV (2). The traumatic encephalopathy syndrome criteria of 2014 were proposed for antemortem diagnosis of CTE but have been unable to effectively identify the disease (4). Revisions of these criteria have been proposed to include cognitive symptoms and biomarkers for Alzheimer disease (AD), as CTE and AD share characteristic tau pathology (2,3,5,6). Additionally, it has been suggested that moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury is also a risk factor for AD, emphasizing the need for differentiation between diagnoses (7).
PET shows promise for antemortem CTE diagnosis, and studies have been conducted on head injury patients using tau PET radiopharmaceuticals optimized for AD, including 18F-FDDNP, 18F-flortaucipir (also known as Tauvid [Eli Lilly and Co.], AV-1451, and T807), 11C-PBB3, and 18F-MK-6240 (also known as florquinitau), summarized in Table 1 (8–24).
TABLE 1.
Tau PET Studies in Head Injury Patients
| Radiotracer | Cohort | n | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18F-FDDNP | Retired NFL players | 14 | PET correlation with postmortem CTE pathology | (10,15,17) |
| 18F-flortaucipir | Single moderate-to-severe TBI patients | 21 | Elevated binding in right occipital cortex, white matter region, and whole brain of TBI subjects | (20) |
| Blast-exposed patients | 17 | Uptake associated with exposure to blast neurotrauma in several regions | (21) | |
| NFL player and severe-TBI patient | 1/1 | Increased nigral and striatal uptake in NFL patient; increased subcortical and hippocampal uptake in severe-TBI patient | (11) | |
| Former NFL players | 26 | Higher uptake in bilateral superior frontal, bilateral medial temporal, and left parietal regions in NFL players with cognitive/neuropsychiatric symptoms | (19) | |
| Former NFL player* | 1 | Uptake observed, but low tau burden quantified, in basal ganglia, thalamus, motor cortex, and calcarine cortex; insignificant correlation between uptake value ratio and tau burden | (9) | |
| Former NFL player | 1 | Retention at cortical gray matter–white matter junction; increased uptake bilaterally in cingulate, occipital, and orbitofrontal cortices and in temporal areas | (12) | |
| TBI patients | 2 | Significant uptake in occipital lobes | (8) | |
| Retired athletes, motor vehicle accident patient, and veterans | 5/1/2 | Heterogeneity in uptake between TBI patients; correlation of regions of higher uptake with decreased white matter integrity and greater functional connectivity | (22) | |
| Traumatic encephalopathy syndrome patients | 11 | Mildly elevated tau PET binding in subset of patients at risk for CTE, in distribution consistent with CTE pathology stages III and IV | (23) | |
| CTE brains | 5 | No signal in regions with tau aggregates; 2 cases indicating uptake in choroid plexus and meninges; off-target binding in leptomeningeal melanocytes | (14) | |
| 18F-THK-5317 | TBI and repeated sports-related concussions | 12/6 | Tau aggregation in corpus callosum in athletes with repeated sports-related concussions; tau aggregation in thalami, temporal white matter, and midbrain in TBI patients | (24) |
| 11C-PBB3 | Mild-repetitive or severe TBI patients | 27 | Increased binding capacity in neocortical gray matter associated with late-onset neuropsychiatric symptoms after TBI; close correlation between psychosis and binding capacity in white matter | (16) |
| 18F-MK-6240 | Australian Rules football player | 1 | Poor binding to tau aggregates in non-AD tauopathies; imaging findings of frontally predominant binding significantly different from pattern of prodromal AD | (13,18) |
In vivo imaging followed by postmortem neuropathologic examination.
NFL = National Football League; TBI = traumatic brain injury.
At present, there is no tau PET tracer optimized for CTE (mixed 3-repeat/4-repeat [3R/4R] tau), and considering the heterogeneity of pathology between tauopathies, designing radiotracers for CTE remains a challenge (25). Identifying appropriate radiotracers to successfully image CTE tau in vivo could enable antemortem diagnosis of CTE for the first time and provide opportunities for therapeutic intervention after brain injuries (19,26). The goal of the present study was to conduct a head-to-head in vitro evaluation of 5 tau PET radiotracers in 12 pathologically diagnosed subjects with CTE to determine the suitability of these tracers to image CTE-specific tau inclusions. Autoradiography was used to assess the specific binding and distribution of 3H-flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, 3H-PI-2620, 3H-APN-1607 (also known as PM-PBB3 and florzolotau), and 3H-CBD-2115 (also known as 3H-OXD-2115). Immunohistochemistry was validated for phospho-tau with AT8, 3R tau with RD3, 4R tau with RD4, and amyloid-β (Aβ) with 6F/3D antibodies. Tau target density (maximum specific binding [Bmax]) in postmortem tissue sections was quantified by saturation analysis with 3H-flortaucipir.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General
3H-flortaucipir (3.515 MBq/μmol, 37 MBq/mL), 3H-APN-1607 (1.998 MBq/μmol, 37 MBq/mL), 3H-MK-6240 (1.536 MBq/μmol, 37 MBq/mL), 3H-PI-2620 (1.554 MBq/μmol, 37 MBq/mL), and 3H-CBD-2115 (1.103 MBq/μmol, 37 MBq/mL) were prepared at Novandi Chemistry AB. Flortaucipir was purchased commercially (Med Chem Express). MK-6240 and NAV-4694 were generously provided by Cerveau Technologies. All other tritium labeling precursors and reference standards except CBD-2115 (Novandi AB and Oxiant Pharmaceuticals) were provided by MedChem Imaging, Inc. All other reagents were purchased from Millipore Sigma unless otherwise stated.
Human Postmortem Brain Tissue
Fresh-frozen human CTE brain tissues were obtained from the Understanding Neurologic Injury and Traumatic Encephalopathy (UNITE) Brain Bank. All AD and healthy control tissue was obtained from the Douglas Bell Canada Brain Bank, and Folio Biosciences, respectively, in accordance with the guidelines put forth by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Research Ethics Board (protocol 036-2019). Tissue demographics are summarized in Supplemental Table 1 (supplemental materials are available at http://jnm.snmjournals.org).
Detailed autoradiography and immunohistochemistry protocols can be found in the supplemental methods.
RESULTS
Specific Binding and Tau Target Density Quantification with 3H-Flortaucipir in CTE Tissue
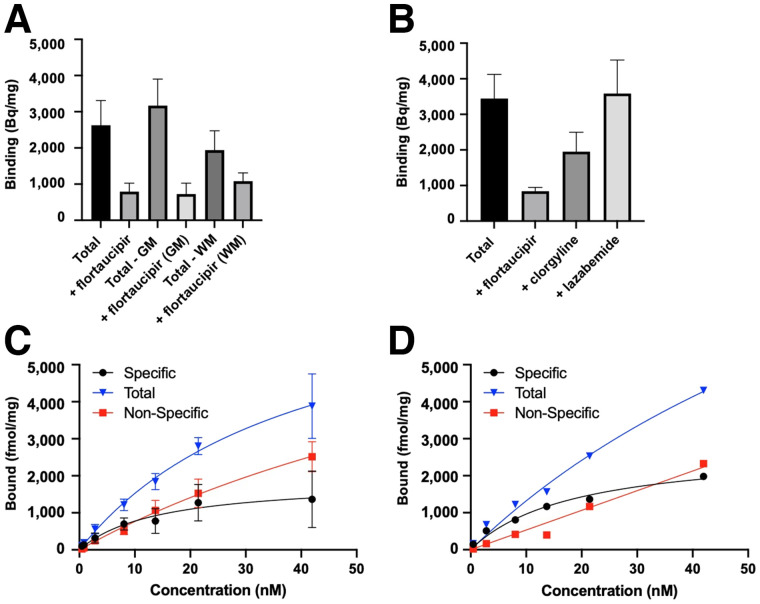
Specific binding of 3H-flortaucipir in CTE I, II, and IV tissues was evaluated under homologous blocking conditions. Specific binding in whole sections was 68.7% ± 10.5% (mean ± SD), compared with 76.0% ± 12.9% in gray matter and 42.1% ± 13.1% in white matter (n = 12; Fig. 1A). 3H-flortaucipir binding was also evaluated under heterologous blocking conditions with unlabeled MK-6240, and specific binding was 27.3% ± 13.6% (Supplemental Fig. 1; n = 12). Off-target binding of 3H-flortaucipir to monoamine oxidase (MAO)–A/B was investigated by heterologous blocking with clorgyline and lazabemide, inhibitors for MAO-A and MAO-B, respectively. Clorgyline inhibited 3H-flortaucipir binding by 43.9% ± 4.6% (n = 3), indicating off-target binding to MAO-A, whereas blocking for MAO-B did not inhibit 3H-flortaucipir binding (Fig. 1B).
FIGURE 1.
3H-flortaucipir binding in CTE IV and AD. (A) Quantification of 3H-flortaucipir (5 nM) total signal compared with homologous block signal in whole section, gray matter, and white matter of CTE cases. Binding is reported in Bq/mg (n = 12). (B) Quantification of 3H-flortaucipir (5 nM) total signal compared with blocking under homologous conditions (10 μM), clorgyline (10 μM) for MAO-A, or lazabemide (10 μM) for MAO-B (n = 3) of CTE cases. (C and D) Saturation analysis with increasing 3H-flortaucipir concentration in CTE (n = 4) (C) and AD (n = 1) (D) tissue sections to quantify Bmax and Kd. GM = gray matter; WM = white matter.
Saturation binding was assayed to quantify a tau Bmax for the first time (to our knowledge) in CTE. Increasing concentrations of 3H-flortaucipir allowed for saturability of the target and quantification of a Bmax, with nonspecific binding defined by homologous blockade, and off-target binding to MAO-A was displaced by clorgyline. Mean saturation curves displaying total, specific, and nonspecific binding are shown for quantification of tau protein in CTE IV (n = 4; Fig. 1C) and AD (n = 1; Fig. 1D). With 3H-flortaucipir in CTE IV, the experimentally determined Bmax was 99.8 ± 53.8 nM (n = 4) and target affinity (Kd) was 14.3 ± 6.6 nM (n = 4). Scatchard analysis of these saturation studies is shown in Supplemental Figure 2.
Comparative Binding of 3H-Flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 in CTE Tissues
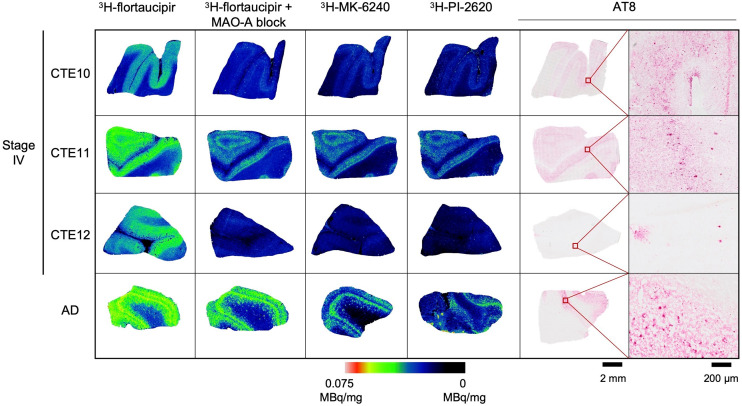
3H-flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 were evaluated for total radiotracer signal in CTE IV cases, compared with an AD-positive control (Fig. 2). The total signal of 3H-flortaucipir is shown, alongside the addition of clorgyline to eliminate the off-target binding contribution to MAO-A. 3H-flortaucipir with clorgyline aligned with 3H-MK-6240, 3H-PI-2620, and AT8 immunostaining for phospho-tau, with higher signal and antibody density localized to the gray matter. Additional CTE I, CTE II, and CTE IV cases were evaluated with 3H-MK-6240 and showed negligible binding (Supplemental Fig. 3).
FIGURE 2.
3H-flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 binding in CTE IV. Total 3H-flortaucipir signal (5 nM), displacement by 10 μM clorgyline to block off-target binding to MAO-A, total 3H-MK-6240 (5 nM) binding, and total 3H-PI-2620 (6 nM) binding are compared with AT8 immunostaining for phospho-tau at 2-mm and 200-μm scales in CTE IV and AD.
3H-APN-1607 Distribution in CTE and Off-Target Binding to Amyloid-β
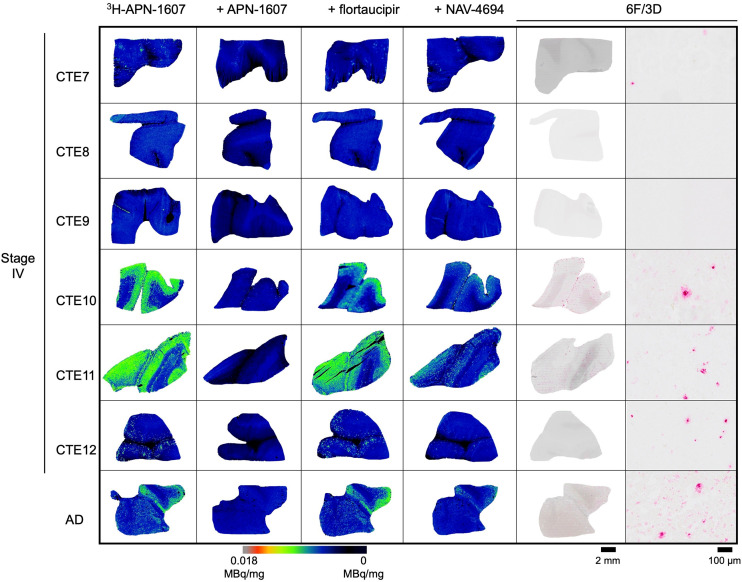
3H-APN-1607 was evaluated for total radiotracer signal and blocking with self, flortaucipir, or NAV-4694 (also known as flutafuranol and AZD-4694), an Aβ binding ligand (27), and compared with 6F/3D immunohistochemistry for Aβ in CTE IV and AD tissues (Fig. 3). 3H-APN-1607 binding was investigated in CTE I and II cases; however, no signal was observed (Supplemental Fig. 4). Positive 3H-APN-1607 binding was observed in a subset of CTE IV cases and a positive control AD case. Under homologous blocking conditions, specific binding was highly variable (52.9% ± 19.6%; n = 6). The 3H-APN-1607 binding when blocking with flortaucipir revealed increased radiotracer binding in 1 case, whereas the remaining 5 cases demonstrated variable radiotracer displacement (27.1% ± 14.0%). Variable displacement of 3H-APN-1607 binding by NAV-4694 was observed (31.7% ± 22.9%; n = 6), with higher displacement in samples with greater Aβ burden. In 1 case (CTE11) with the highest Aβ burden, 3H-APN-1607 binding was displaced by 61.4% with NAV-4694, compared with an Aβ-negative case (CTE9), which had a 10-fold lower displacement (6.3%).
FIGURE 3.
Binding of 3H-APN-1607 in CTE IV and AD. Total 3H-APN-1607 (5 nM) binding is shown along with displacement by unlabeled APN-1607 (10 μM), flortaucipir (10 μM), and NAV-4694 (10 μM) to indicate Aβ binding contribution compared with 6F/3D immunohistochemistry for Aβ shown at 2-mm and 200-μm scales in CTE IV and AD.
DISCUSSION
Specific Binding and Tau Target Density Quantification with 3H-Flortaucipir in CTE Tissue
We evaluated specific binding of 3H-flortaucipir in CTE stages I–IV (Fig. 1A). The highest percentage specific binding of 3H-flortaucipir was observed by homologous blockade in the gray matter; however, radiotracer signal was maximally displaced by 80%, indicating a degree of nondisplaceable binding with this tracer. The nonspecific binding observed in the white matter can confound PET imaging analysis with 3H-flortaucipir (14,28).
3H-flortaucipir binding to MAOs has been reported by in vitro assays, whereas in vivo studies have reported both the presence and the absence of off-target binding (29–32). The reported off-target binding of 3H-flortaucipir to MAO-A and MAO-B presents a challenge for interpretation of specific binding quantitation and distribution in vitro, as binding of 3H-flortaucipir to MAO-A/B has been reported with similar affinities to tau (31). MAO-B is considered a biomarker of reactive astrocytes (33), which are involved in the pathogenesis of CTE (34,35). We recently evaluated PET imaging biomarkers for neuroinflammation in pathologically diagnosed cases of CTE and found high variability in the neuroinflammatory pathology of brain injuries (35). No off-target binding of 3H-flortaucipir to MAO-B was observed under the present assay conditions, whereas off-target binding to MAO-A was identified by blocking with clorgyline (43.9% ± 4.6%; n = 3; Fig. 1B). Increases in MAO-A availability have been reported in CTE comorbidities (36,37) and could contribute to the off-target binding observed here. The present study quantified a Bmax (99.8 ± 53.8 nM; n = 4) and Kd (14.3 ± 6.6 nM; n = 4; mean ± SD) for stage IV CTE tau with 3H-flortaucipir for the first time, to our knowledge (Fig. 1C). The variability observed in Bmax between samples demonstrates how tau abundance within CTE stage subgroups varies, and larger sample sizes would be beneficial to further understand tau aggregation within CTE stages. Although off-target binding of 3H-flortaucipir to MAO-B may not confound accurate quantification of tau in human PET imaging studies with 18F-flortaucipir, MAO-A binding should be considered for in vivo imaging studies in patients who have sustained repetitive brain injuries or who have been identified as suspected-CTE cases.
Comparative Binding of 3H-Flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 in CTE Tissues
Radiotracer binding was compared among 3H-flortaucipir, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 and with AT8 immunostaining for tau aggregate distribution (Fig. 2). Displacing the MAO-A binding contribution of 3H-flortaucipir resulted in robust radiotracer binding in only the most severe CTE IV case, with minimal binding in 2 other CTE IV cases (Fig. 2), despite tau pathology in all CTE stages examined. In the most severe CTE IV case, 3H-flortaucipir signal blocked with clorgyline strongly aligned with AT8 immunostaining, 3H-MK-6240, and 3H-PI-2620 radiotracer binding. 3H-MK-6240 and 3H-PI-2620 were evaluated in all CTE stages, although radiotracer binding was again observed only in the most severe CTE IV case. 18F-MK-6240 was previously evaluated in a case study of a single retired Australian Rules football player in whom a CTE-like tau pattern was observed (18). To our knowledge, clinical PET research studies using 18F-PI-2620 in brain injury populations are yet to be reported; however, 18F-PI-2620 has been proposed for use in in vivo imaging studies of non-AD tauopathies (38,39). The present in vitro autoradiography studies show 3H-PI-2620 binding is similar to 3H-MK-6240. This work supports exploring the potential of 18F-MK-6240 and 18F-PI-2620 for PET imaging in patients with suspected mixed AD/CTE pathology or severe suspected CTE; further evaluation of these radiotracers in severe CTE tissues or high at-risk groups is required to determine the utility of this tracer for imaging CTE tau.
Effect of Ethanol Washes on Autoradiography Studies
Our concerns that ethanol washes are not physiologically relevant to evaluation of radiotracer binding in vitro, coupled with the risk of washing away nonspecific binding, led us to investigate the assays in the absence and presence of ethanol. Ethanol has been included in incubation and wash buffers in several in vitro characterization studies of 18F-flortaucipir, 18F-MK-6240, and 18F-PI-2620 (13,14,38). A comparison of autoradiography assay conditions with and without ethanol was performed in the current work (Supplemental Fig. 5). We showed that ethanol is not necessary to demonstrate specific radiotracer distribution and should be used with caution because ethanol washes were found to artificially increase the signal-to-noise ratio, reducing nonspecific binding while risking washing away of specific binding. In addition, ethanol washes cannot be conducted in vivo, therefore limiting the use of radiotracers that require this step to obtain a suitable specific binding window.
3H-APN-1607 Distribution in CTE and Off-Target Binding to Amyloid-β
18F-APN-1607 is an 18F-labeled derivative of 11C-PBB3 that has been translated for human PET imaging studies in AD patients and in the 4R-tau dominant tauopathy, progressive supranuclear palsy (40–42). APN-1607 has been shown to bind parallel to the area of Aβ filaments in tau protein aggregates (43,44). Off-target binding of 11C-PBB3 to Aβ has been previously described, but 18F-APN-1607 binding, if any, to Aβ has not yet been reported. Substantial binding of 3H-APN-1607 to Aβ was observed in CTE IV cases with a high amyloid plaque burden, as shown by displacement with the Aβ-targeting compound NAV-4694 (Fig. 3). CTE IV cases with a lower Aβ burden demonstrated lower total radiotracer binding and displacement by NAV-4694, showing 3H-APN-1607 off-target binding to Aβ under the present assay conditions.
Despite past reports in which APN-1607 demonstrated binding in 4R-tau dominant conditions (41), 3H-APN-1607 showed no binding in early-stage CTE cases, for which the dominant tau isoform found in neurons is 4R tau (45). These findings indicate limited utility of 3H-APN-1607 to image tau inclusions in early-stage CTE and further limitations of off-target binding in CTE cases with mixed pathology. 18F-APN-1607 is susceptible to photoisomerization, requiring all experimental procedures to be conducted in the absence of fluorescent light (46). These limitations will hinder the widespread use of 18F-APN-1607.
3H-CBD-2115 (47) showed elevated signal in CTE IV, compared with CTE I or II, and limitations of meningeal binding (Supplemental Fig. 6). RD3 immunostaining for 3R tau was also performed to show both 3R- and 4R-tau isoforms in CTE (Supplemental Fig. 7).
Heterogeneity of Tauopathies
Limitations of the present study include tissue availability; a larger sample size would allow further interpretation of tau PET radiotracer binding to tau pathology, as this work reveals variability in binding of several radiotracers between and within CTE stage subgroups. It would also be of value to include additional brain regions for analysis in future studies to explore tau PET tracer binding beyond the frontal cortex, for a greater representation of whole-brain imaging achieved with in vivo PET imaging studies. Recent computational studies have revealed different affinity binding sites for tau radiotracers in fibrils associated with different tauopathies (48). However, it was concluded that cryoelectron microscopy is not sufficient for the structure-based tracer discovery for certain targets, as they may have potential-but-hidden binding sites. In addition, variability in pathology is expected within CTE because many factors contribute to disease development and progression, including the type and frequency of brain injury, the anatomic region of impact, and concussive-versus-subconcussive impacts. Investigating these factors will provide opportunities into understanding how brain injuries contribute to CTE disease pathology and progression.
CONCLUSION
We have reported, for the first time to our knowledge, a Bmax and Kd for CTE tau with 3H-flortaucipir. Off-target binding of 3H-flortaucipir to MAO-A should be considered during in vivo PET imaging studies on patients who have sustained repetitive brain injuries or are suspected of having CTE. Although 3H-MK-6240 and 3H-PI-2620 do not bind optimally to tau aggregates in CTE, the respective 18F PET radiopharmaceuticals should be evaluated in clinical research studies of severe suspected CTE cases or in the presence of mixed AD/CTE pathology. 3H-APN-1607 showed limited utility to image tau inclusions in early-stage CTE and off-target binding to Aβ in CTE cases with mixed pathology. All radiotracers evaluated showed binding only in late-stage CTE cases. This study provides critical insights into CTE tau target density, off-target binding of tau PET tracers, and binding of tau PET tracers optimized for AD alongside tau immunostaining to inform in vivo PET imaging studies on suspected-CTE groups, contributing to the ultimate goal of imaging CTE in life.
DISCLOSURE
Cassis Varlow received a Canada Graduate Scholarship (doctoral) from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). Neil Vasdev received funding from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH; R01AG052414), Azrieli Foundation, Canada Foundation for Innovation, Ontario Research Fund, and Canada Research Chairs Program. Enigma Biomedical Group, Inc., and its affiliates (Cerveau Technologies and Meilleur Technologies) provided radiolabeled or unlabeled MK-6240, CBD-2115, and NAV-4694. Tissue was obtained from the Boston University Alzheimer’s Disease Research and CTE Center’s brain bank, also referred to as the Understanding Neurologic Injury and Traumatic Encephalopathy (UNITE) or Veterans Affairs–Boston University–Concussion Legacy Foundation (VA-BU-CLF) brain bank (funded by grants P30AG072978, U54NS115266, R01AG062348. and RF1AG057902). Neil Vasdev is a cofounder of MedChem Imaging, Inc. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Dr. Samuel Svensson from Oxiant Pharmaceuticals for support.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Can existing tau PET tracers, optimized for AD, be used to image CTE tau in vitro?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: This study showed that 3H-flortaucipir and 3H-APN-1607 display off-target binding to MAO-A and Aβ, respectively, in human CTE tissues. 3H-MK-6240 and 3H-PI-2620 bind CTE tau in severe- or mixed-pathology cases.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Off-target binding with 18F-flortaucipir and 18F-APN-1607 needs to be considered a confounding factor in PET imaging studies of patients with brain injuries. 18F-MK-6240 and 18F-PI-2620 are the most promising tau PET radiotracers for further evaluation in patients with severe suspected CTE.
REFERENCES
- 1. Banks SJ. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). In: Tousi B, Cummings J, eds. Neuro-Geriatrics: A Clinical Manual. Springer International Publishing; 2017:183–194. [Google Scholar]
- 2. McKee AC, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW, et al. The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2016;131:75–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bieniek KF, Cairns NJ, Crary JF, et al. The second NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2021;80:210–219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Montenigro PH, Baugh CM, Daneshvar DH, et al. Clinical subtypes of chronic traumatic encephalopathy: literature review and proposed research diagnostic criteria for traumatic encephalopathy syndrome. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2014;6:68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Omalu B, Hammers J. Letter: recommendation to create new neuropathologic guidelines for the post-mortem diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Neurosurgery. 2021;89:E97–E98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mez J, Alosco ML, Daneshvar DH, et al. Validity of the 2014 traumatic encephalopathy syndrome criteria for CTE pathology. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17:1709–1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Stein TD, Alvarez VE, McKee AC. Concussion in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2015;19:47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Okonkwo DO, Puffer RC, Minhas DS, et al. [18F]FDG, [11C]PiB, and [18F]AV-1451 PET imaging of neurodegeneration in two subjects with a history of repetitive trauma and cognitive decline. Front Neurol. 2019;10:831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Mantyh WG, Spina S, Lee A, et al. Tau positron emission tomographic findings in a former US football player with pathologically confirmed chronic traumatic encephalopathy. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77:517–521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Barrio JR, Small GW, Wong K-P, et al. In vivo characterization of chronic traumatic encephalopathy using [F-18]FDDNP PET brain imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:E2039–E2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mitsis EM, Riggio S, Kostakoglu L, et al. Tauopathy PET and amyloid PET in the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathies: studies of a retired NFL player and of a man with FTD and a severe head injury. Transl Psychiatry. 2014;4:e441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Dickstein DL, Pullman MY, Fernandez C, et al. Cerebral [18F]T807/AV1451 retention pattern in clinically probable CTE resembles pathognomonic distribution of CTE tauopathy. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:e900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Aguero C, Dhaynaut M, Normandin MD, et al. Autoradiography validation of novel tau PET tracer [F-18]-MK-6240 on human postmortem brain tissue. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Marquié M, Agüero C, Amaral AC, et al. [18F]-AV-1451 binding profile in chronic traumatic encephalopathy: a postmortem case series. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Omalu B, Small GW, Bailes J, et al. Postmortem autopsy-confirmation of antemortem [F-18]FDDNP-PET scans in a football player with chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Neurosurgery. 2018;82:237–246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Takahata K, Kimura Y, Sahara N, et al. PET-detectable tau pathology correlates with long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes in patients with traumatic brain injury. Brain. 2019;142:3265–3279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Small GW, Kepe V, Siddarth P, et al. PET scanning of brain tau in retired national football league players: preliminary findings. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21:138–144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Krishnadas N, Doré V, Lamb F, et al. Case report: 18F-MK6240 tau positron emission tomography pattern resembling chronic traumatic encephalopathy in a retired Australian Rules football player. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Stern RA, Adler CH, Chen K, et al. Tau positron-emission tomography in former National Football League players. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1716–1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Gorgoraptis N, Li LM, Whittington A, et al. In vivo detection of cerebral tau pathology in long-term survivors of traumatic brain injury. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:1–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Robinson ME, McKee AC, Salat DH, et al. Positron emission tomography of tau in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with blast neurotrauma. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21:101651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wooten DW, Ortiz-Terán L, Zubcevik N, et al. Multi-modal signatures of tau pathology, neuronal fiber integrity, and functional connectivity in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36:3233–3243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lesman-Segev OH, La Joie R, Stephens ML, et al. Tau PET and multimodal brain imaging in patients at risk for chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;24:102025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Marklund N, Vedung F, Lubberink M, et al. Tau aggregation and increased neuroinflammation in athletes after sports-related concussions and in traumatic brain injury patients: a PET/MR study. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;30:102665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Leuzy A, Chiotis K, Lemoine L, et al. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies: still a challenge. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1112–1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lin A, Charney M, Shenton ME, Koerte IK. Chapter 29: chronic traumatic encephalopathy—neuroimaging biomarkers. In: Hainline B, Stern RA, eds. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol 158. Elsevier; 2018:309–322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cselényi Z, Jönhagen ME, Forsberg A, et al. Clinical validation of 18F-AZD4694, an amyloid-β-specific PET radioligand. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:415–424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Baker SL, Harrison TM, Maass A, La Joie R, Jagust WJ. Effect of off-target binding on 18F-flortaucipir variability in healthy controls across the life span. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:1444–1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Hansen AK, Brooks DJ, Borghammer P. MAO-B inhibitors do not block in vivo flortaucipir ([18F]-AV-1451) binding. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018;20:356–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Murugan NA, Chiotis K, Rodriguez-Vieitez E, Lemoine L, Ågren H, Nordberg A. Cross-interaction of tau PET tracers with monoamine oxidase B: evidence from in silico modelling and in vivo imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1369–1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Vermeiren C, Motte P, Viot D, et al. The tau positron‐emission tomography tracer AV‐1451 binds with similar affinities to tau fibrils and monoamine oxidases. Mov Disord. 2018;33:273–281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Drake LR, Pham JM, Desmond TJ, et al. Identification of AV-1451 as a weak, nonselective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10:3839–3846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Ekblom J, Jossan SS, Oreland L, Walum E, Aquilonius SM. Reactive gliosis and monoamine oxidase B. In: Amine Oxidases: Function and Dysfunction. Springer; 1994:253–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Chancellor KB, Chancellor SE, Duke-Cohan JE, et al. Altered oligodendroglia and astroglia in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2021;142:295–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Varlow C, Knight AC, McQuade P, Vasdev N. Characterization of neuroinflammatory positron emission tomography biomarkers in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Commun. 2022;4:fcac019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Mahar I, Alosco ML, McKee AC. Psychiatric phenotypes in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;83:622–630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A, et al. Elevated monoamine oxidase A levels in the brain: an explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1209–1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Kroth H, Oden F, Molette J, et al. Discovery and preclinical characterization of [18F]PI-2620, a next-generation tau PET tracer for the assessment of tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2178–2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Brendel M, Barthel H, van Eimeren T, et al. Assessment of 18F-PI-2620 as a biomarker in progressive supranuclear palsy. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77:1408–1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Zhou XY, Lu JY, Liu FT, et al. In vivo 18F‐APN‐1607 tau positron emission tomography imaging in MAPT mutations: cross‐sectional and longitudinal findings. Mov Disord. 2022;37:525–534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Li L, Liu F-T, Li M, et al. Clinical utility of 18F-APN-1607 tau PET imaging in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord. 2021;36:2314–2323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Xu X, Ruan W, Liu F, et al. 18F-APN-1607 tau positron emission tomography imaging for evaluating disease progression in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;13:789054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Shi Y, Murzin AG, Falcon B, et al. Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease with PET ligand APN-1607. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2021;141:697–708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Zhou Y, Li J, Nordberg A, Ågren H. Dissecting the binding profile of PET tracers to corticobasal degeneration tau fibrils. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12:3487–3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Cherry JD, Kim SH, Stein TD, et al. Evolution of neuronal and glial tau isoforms in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol. 2020;30:913–925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kawamura K, Hashimoto H, Furutsuka K, et al. Radiosynthesis and quality control testing of the tau imaging positron emission tomography tracer [18F] PM‐PBB3 for clinical applications. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2021;64:109–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Lindberg A, Knight AC, Sohn D, et al. Radiosynthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of [18F]CBD-2115 as a first-in-class radiotracer for imaging 4R-tauopathies. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12:596–602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Murugan NA, Nordberg A, Ågren H. Cryptic sites in tau fibrils explain the preferential binding of the AV-1451 PET tracer toward Alzheimer’s tauopathy. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12:2437–2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]