Abstract
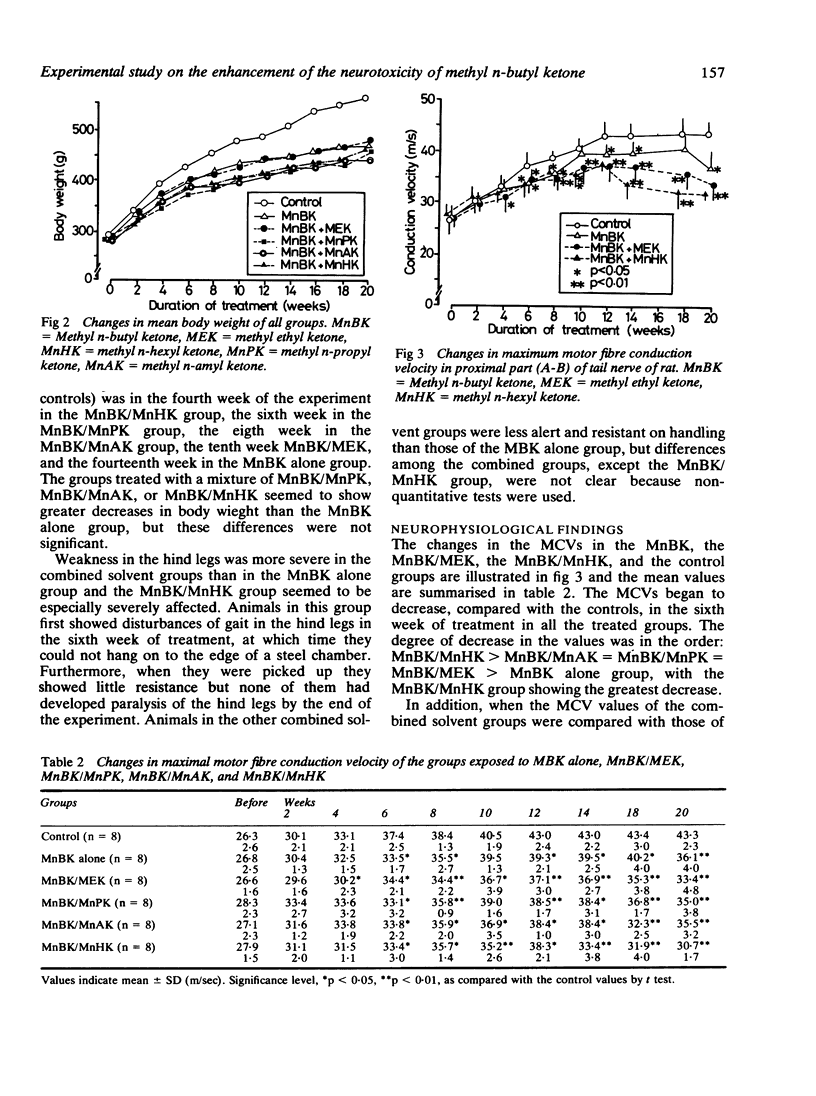
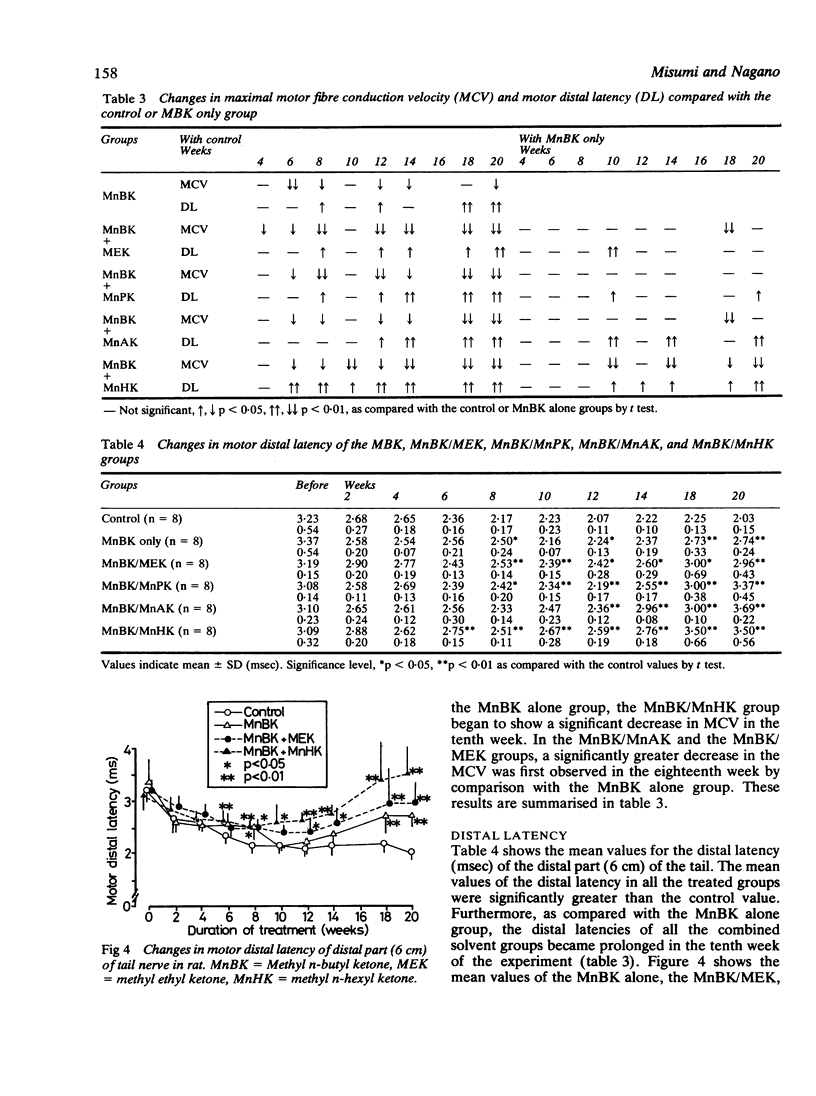
The neurotoxicity of methyl n-butyl ketone is known to be enhanced by combination with methyl ethyl ketone. This study was conducted to clarify the potentiating effect of aliphatic monoketones on the neurotoxicity of methyl n-butyl ketone. Rats were subcutaneously injected in the back with 4 mmol/kg/day of methyl ethyl ketone, methyl n-propyl ketone, methyl n-amyl ketone, or methyl n-hexyl ketone mixed with an equimolar dose of methyl n-butyl ketone five days a week for 20 weeks. The maximum motor fibre conduction velocity and the distal latency were measured every two weeks in the tail nerves of the treated animals and controls. All the monoketones tested enhanced the neurotoxicity of methyl n-butyl ketone. Of the compounds tested, methyl n-hexyl ketone, which had the longest carbon chain, enhanced the neurotoxicity of methyl n-butyl ketone most strongly. These results suggest that the length of the carbon chain of the aliphatic monoketones combined with methyl n-butyl ketone was related to the enhancement of the neurotoxicity of the neurotoxic compound.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Rahman M. S., Hetland L. B., Couri D. Toxicity and metabolism of methyl n-butyl ketone. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1976 Feb;37(2):95–102. doi: 10.1080/0002889768507418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenkirch H., Stoltenburg-Didinger G., Wagner H. M. Experimental data on the neurotoxicity of methyl-ethyl-ketone (MEK). Experientia. 1979 Apr 15;35(4):503–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01922732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenkirch H., Stoltenburg G., Wagner H. M. Experimental studies on hydrocarbon neuropathies induced by methyl-ethyl-ketone (MEK). J Neurol. 1978 Dec 7;219(3):159–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00314531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branchflower R. V., Pohl L. R. Investigation of the mechanism of the potentiation of chloroform-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity by methyl n-butyl ketone. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;61(3):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branchflower R. V., Schulick R. D., George J. W., Pohl L. R. Comparison of the effects of methyl-N-butyl ketone and phenobarbital on rat liver cytochromes P-450 and the metabolism of chloroform to phosgene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;71(3):414–421. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couri D., Abdel-Rahman M. S., Hetland L. B. Biotransformation of n-hexane and methyl n-butyl ketone in guinea pigs and mice. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1978 Apr;39(4):295–300. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couri D., Hetland L. B., Abdel-Rahman S., Weiss H. The influence of inhaled ketone solvent vapors on hepatic microsomal biotransformation activities. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;41(2):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couri D., Milks M. Toxicity and metabolism of the neurotoxic hexacarbons n-hexane, 2-hexanone, and 2,5-hexanedione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:145–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiVincenzo G. D., Hamilton M. L. Fate of n-butanol in rats after oral administration and its uptake by dogs after inhalation or skin application. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;48(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiVincenzo G. D., Hamilton M. L., Kaplan C. J., Dedinas J. Metabolic fate and disposition of 14C-labeled methyl n-butyl ketone in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;41(3):547–560. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(77)80009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiVincenzo G. D., Kaplan C. J., Dedinas J. Characterization of the metabolites of methyl n-butyl ketone, methyl iso-butyl ketone, and methyl ethyl ketone in guinea pig serum and their clearance. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;36(3):511–522. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen O., Alanen K. The competitive inhibition of p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid synthesis by aliphatic alcohols in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Oct;15(10):1465–1467. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Takeuchi Y., Hisanaga N., Ono Y. Changes of n-hexane metabolites in urine of rats exposed to various concentrations of n-hexane and to its mixture with toluene or MEK. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;53(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00406172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. L., Setzer J. V., Lewis T. R., Anger W. K. Effects of methyl n-butyl ketone behavior and the nervous system. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1977 Nov;38(11):567–579. doi: 10.1080/00028897708984401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi J., Nagano M. Neurophysiological studies on the relation between the structural properties and neurotoxicity of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds in rats. Br J Ind Med. 1984 Nov;41(4):526–532. doi: 10.1136/oem.41.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi J., Nagano M., Nomura S. [An experimental study on the neurotoxicity of 2-octanone and 2-hexanol, a metabolite of n-hexane]. Sangyo Igaku. 1982 Sep;24(5):475–484. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.24.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue J. L., Krasavage W. J., DiVincenzo G. D., Ziegler D. A. Commercial-grade methyl heptyl ketone (5-methyl-2-octanone) neurotoxicity: contribution of 5-nonanone. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;62(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(82)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Mendell J. R., Weiss H. S. Peripheral nerve changes induced by methyl n-butyl ketone and potentiation by methyl ethyl ketone. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1976 May;35(3):207–225. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197605000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T. Dose-dependent metabolic interaction between benzene and toluene in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;48(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Bischoff M. C., Schaumburg H. H. On the specific molecular configuration of neurotoxic aliphatic hexacarbon compounds causing central--peripheral distal axonopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;44(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Ono Y., Hisanaga N., Iwata M., Aoyama M., Kitoh J., Sugiura Y. An experimental study of the combined effects of n-hexane and methyl ethyl ketone. Br J Ind Med. 1983 May;40(2):199–203. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toftgård R., Nilsen O. G., Gustafsson J. A. Changes in rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and enzymatic activities after the inhalation of n-hexane, xylene, methyl ethyl ketone and methylchloroform for four weeks. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1981 Mar;7(1):31–37. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



