Abstract
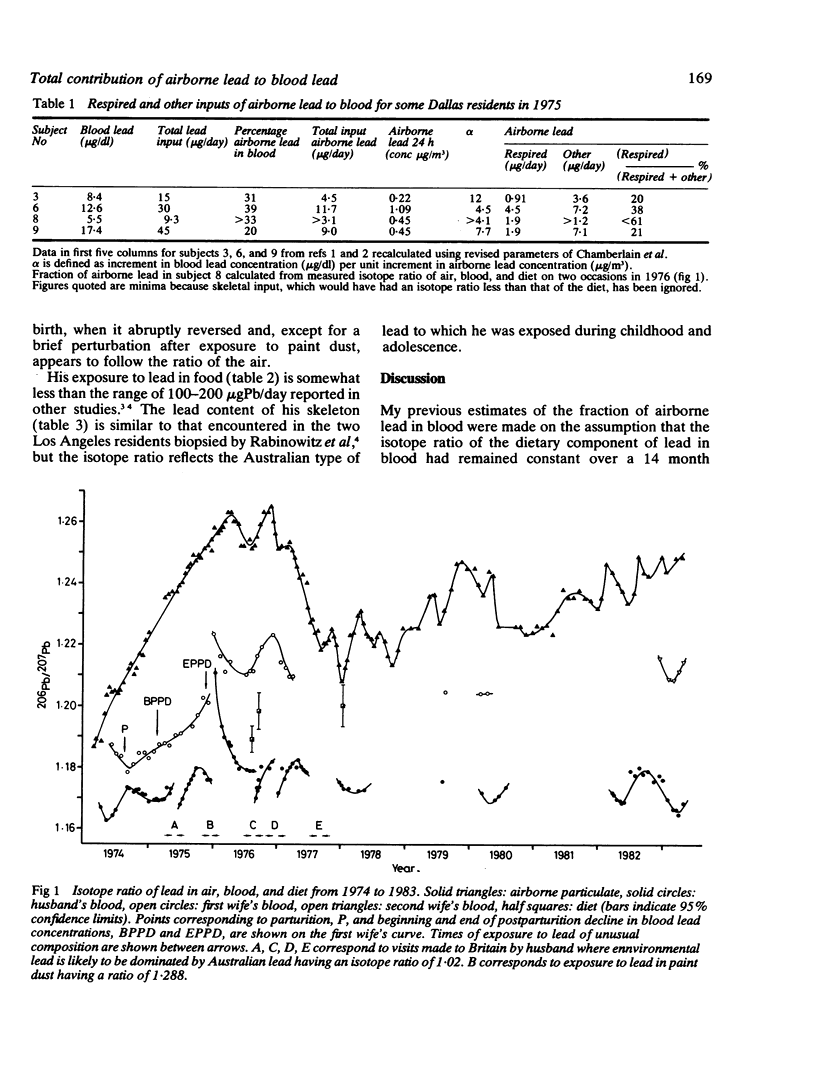
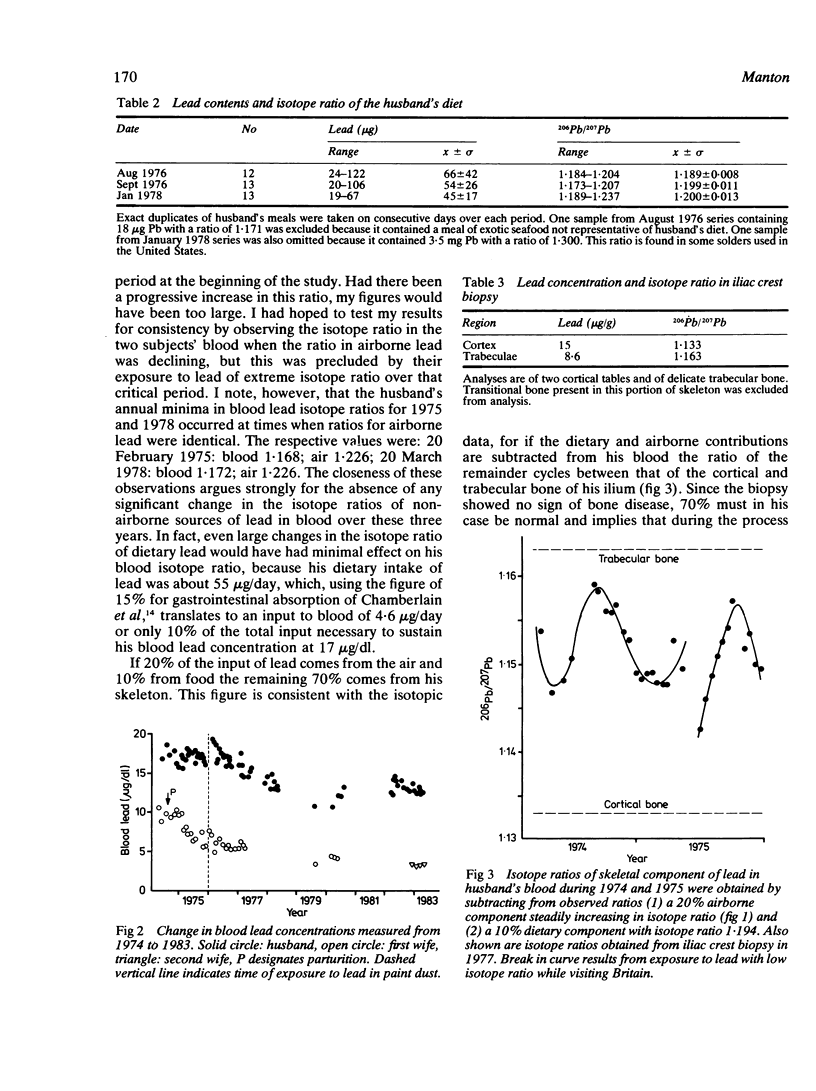
A nine year study of blood lead concentrations and isotope ratios carried out on a married couple shows that pulmonary deposition cannot account for all the airborne lead in blood; that lead from bone may comprise 70% of blood lead; and that during pregnancy blood lead may double due to mobilisation of lead from bone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annest J. L., Pirkle J. L., Makuc D., Neese J. W., Bayse D. D., Kovar M. G. Chronological trend in blood lead levels between 1976 and 1980. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 9;308(23):1373–1377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306093082301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain A. C., Clough W. S., Heard M. J., Newton D., Stott A. N., Wells A. C. Uptake of lead by inhalation of motor exhaust. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Dec 31;192(1106):77–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T. J., Earl J. L. Lead aerosols in the atmosphere: increasing concentrations. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. B., Coulston F., Wills H., Russell J. C. Clinical studies on men continuously exposed to airborne particulate lead. Environ Qual Saf Suppl. 1975;2:221–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaney R. P., Skillman T. G. Calcium metabolism in normal human pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):661–670. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek C. F. Levels of lead in the United States food supply. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1982 Jul;65(4):942–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbye A. C., Jr, Mahaffey K. R., Fiorino J. A., Corneliussen P. C., Jelinek C. F. Food exposures to lead. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:65–74. doi: 10.1289/ehp.74765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manton W. I. Sources of lead in blood. Identification by stable isotopes. Arch Environ Health. 1977 Jul-Aug;32(4):149–159. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1977.10667273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz M. B., Wetherill G. W., Kopple J. D. Kinetic analysis of lead metabolism in healthy humans. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):260–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI108467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepper L. B., Levin L. S. A survey of air and population lead levels in selected American communities. Environ Qual Saf Suppl. 1975;2:152–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



