Abstract
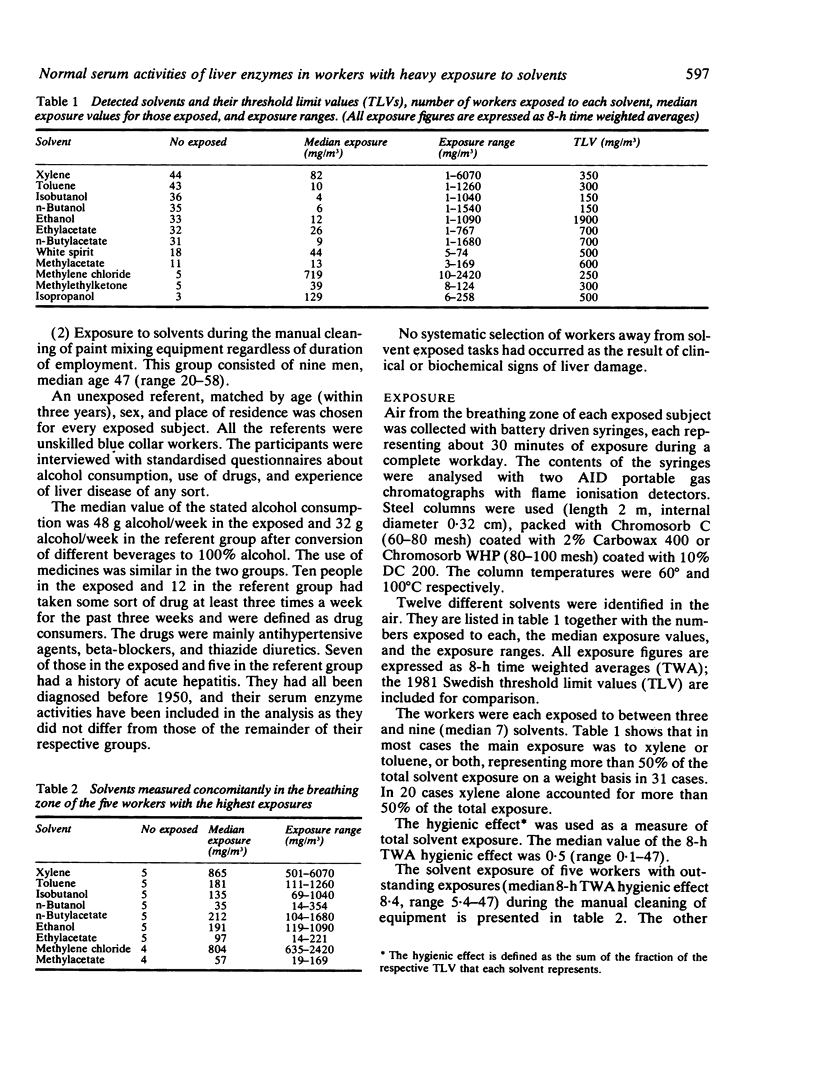
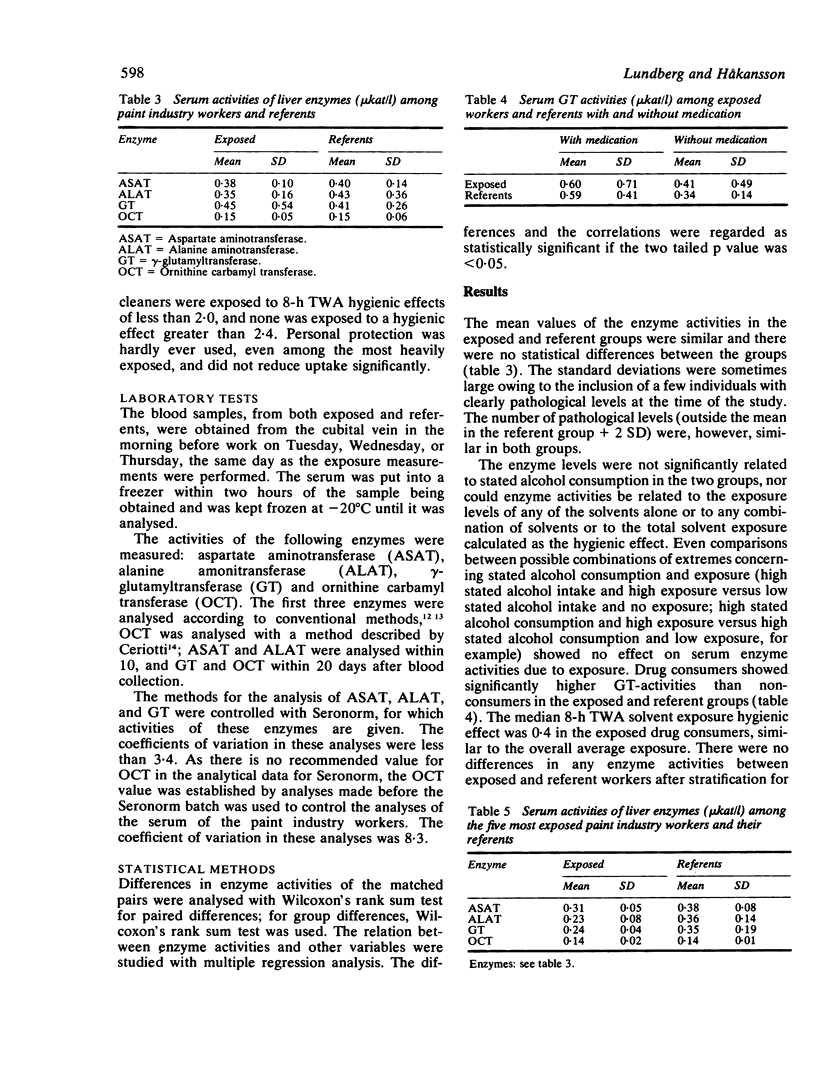
The serum activities of the liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, ornithine carbamyl transferase, and gamma-glutamyl transferase were examined in 47 paint industry workers and unexposed age matched referents. The workers were exposed to a mixture of industrial solvents, of which xylene was the main component in most cases. The median total exposure was about 50% of Swedish 1981 threshold limit values according to measurements of individual solvent exposure performed at the same time. No differences in enzyme activities were shown either when the whole exposed and referent groups were compared or when the five workers with outstanding solvent exposures of five times the TLV or more were compared with their referents. It is concluded that in most workers the liver seems to remain largely undamaged from inhalation exposure to a commonly used mixture of non-chlorinated solvents. In many workers this seems to hold true even for high exposures for limited periods.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ceriotti G. Optimal conditions for ornithine carbamyl transferase determination. A simple micromethod without deproteinization. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Aug 17;47(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish H. H., Adefuin J. Ethanol potentiation of halogenated aliphatic solvent toxicity. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1966 Jan-Feb;27(1):57–61. doi: 10.1080/00028896609342793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Døssing M., Arlien-Søborg P., Milling Petersen L., Ranek L. Liver damage associated with occupational exposure to organic solvents in house painters. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;13(2):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Døssing M. Changes in hepatic microsomal enzyme function in workers exposed to mixtures of chemicals. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Sep;32(3):340–346. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edling C. Interaction between drugs and solvents as a cause of fatty change in the liver? Br J Ind Med. 1982 May;39(2):198–199. doi: 10.1136/oem.39.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara E. Dose-related effects of m-xylene inhalation on the xenobiotic metabolism of the rat. Xenobiotica. 1982 Jun;12(6):345–352. doi: 10.3109/00498258209052474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. M. The expanding role of microsomal enzyme induction, and its implications for clinical chemistry. Clin Chem. 1980 May;26(6):691–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M., Axelson O., Blume J., Hogstedt C., Sundell L., Ydreborg B. Psychological function changes among house painters. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1977 Jun;3(2):91–99. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henningsen N. C., Ohlsson O., Mattiasson I., Trell E., Kristensson H., Hood B. Hypertension, levels of serum gamma glutamyl transpeptidase and degree of blood pressure control in middle-aged males. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(4):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb09716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Industrial solvents and the liver. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):129–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Industrial solvents and the liver. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):129–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurppa K., Husman K. Car painters' exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Serum activities of liver enzymes. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1982 Jun;8(2):137–140. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotaniemi E. A., Sutinen S., Sutinen S., Arranto A. J., Pelkonen R. O. Liver injury in subjects occupationally exposed to chemicals in low doses. Acta Med Scand. 1982;212(4):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1982.tb03202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traiger G. J., Plaa G. L. Chlorinated hydrocarbon toxicity. Potentiation by isopropyl alcohol and acetone. Arch Environ Health. 1974 May;28(5):276–278. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1974.10666486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tähti H., Kärkkäinen S., Pyykkö K., Rintala E., Kataja M., Vapaatalo H. Chronic occupational exposure to toluene. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1981;48(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00405932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A., Cherry N., Venables H. Solvent exposure and liver function. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1276–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


