Abstract
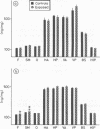
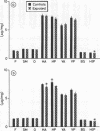
Two astroglial proteins S-100 and GFA, as well as DNA, were quantitatively determined in different regions of the gerbil brain after continuous long term exposure to moderate concentrations of dichloromethane. The intention of the experiment was to expose three groups of animals at three different solvent concentrations (210, 350, or 700 ppm) for three months. Because of the high mortality rate, however, the 700 ppm experiment was terminated after seven weeks. In the 350 ppm experiment half the exposed animals died and the exposure period was terminated after ten weeks. After the exposure period, the surviving gerbils in the 350 ppm exposure group and those from the 210 ppm group were allowed a postexposure solvent free period of four months. After exposure to 350 ppm, increased concentrations of the two astroglial proteins were found in the frontal and sensory motor cerebral cortex, compatible with astrogliosis in these regions. Exposure to 350 ppm and 210 ppm decreased the concentrations of DNA in the hippocampus. Moreover, after exposure at 350 ppm, DNA concentrations were also decreased in the cerebellar hemispheres. These results indicate a decreased cell density in these brain regions, probably due to cell loss. The neurotoxic effects were not found to correlate with the endogenous formation of carbon monoxide.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A. E., Anders M. W. Metabolism of dihalomethanes to formaldehyde and inorganic halide. I. In vitro studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Jul-Aug;4(4):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliff D. F., Knell A. J. Cerebral damage due to endogenous chronic carbon monoxide poisoning caused by exposure to methylene chloride. J Soc Occup Med. 1979 Jan;29(1):12–14. doi: 10.1093/occmed/29.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burek J. D., Nitschke K. D., Bell T. J., Wackerle D. L., Childs R. C., Beyer J. E., Dittenber D. A., Rampy L. W., McKenna M. J. Methylene chloride: a two-year inhalation toxicity and oncogenicity study in rats and hamsters. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1984 Feb;4(1):30–47. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(84)90217-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova-Schmitz M., Starr T. B., Heck H. D. Differentiation between metabolic incorporation and covalent binding in the labeling of macromolecules in the rat nasal mucosa and bone marrow by inhaled [14C]- and [3H]formaldehyde. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;76(1):26–44. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Cowan W. M., Moore B. W., Suntzeff V. The cellular localization of the two brain specific proteins, S-100 and 14-3-2. Brain Res. 1970 Feb 17;18(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Bignami A. Glial fibrillary acidic protein from normal and gliosed human brain. Demonstration of multiple related polypeptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;386(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Crosby C. J., Bignami A. Filament proteins in rat optic nerves undergoing Wallerian degeneration. Exp Neurol. 1981 Feb;71(2):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Fajardo M., Naughton S. A., Eng L. F. Degradation of glial fibrillary acidic protein by a calcium dependent proteinase: an electroblot study. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Bignami A., Gerstl B. An acidic protein isolated from fibrous astrocytes. Brain Res. 1971 May 7;28(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheuens J., Noppe M., Karcher D., Lowenthal A. Immunochemical determination and immunocytological localization of brain-specific protein alpha-albumin (GFA) in isolated astrocytes. Neurochem Res. 1980 Jul;5(7):757–768. doi: 10.1007/BF00964713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haan E. A., Boss B. D., Cowan W. M. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the "brain-specific" proteins 14-3-2 and S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7585–7589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Briving C., Hansson H. A., Rosengren L., Kjellstrand P., Stavron D., Swedin U., Wronski A. Trichloroethylene: long-lasting changes in the brain after rehabilitation. Neurotoxicology. 1981 Dec;2(4):659–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Kjellstrand P., Rosengren L., Wroński A., Briving C. Effects of trichloroethylene inhalation on proteins of the gerbil brain. Arch Toxicol. 1980 Jan;43(3):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00297584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke C., Ruppe K., Otto J. Untersuchungsergebnisse zur toxischen Wirkung von Dichlormethan bei Fussbodenlegern. Z Gesamte Hyg. 1974 Feb;20(2):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobi R., Studer M., Ruch F., Kuenzle C. C. The DNA content of cerebral cortex neurons. Determinations by cytophotometry and high performance liquid chromatography. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 9;305(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongen W. M., Lohman P. H., Kottenhagen M. J., Alink G. M., Berends F., Koeman J. H. Mutagenicity testing of dichloromethane in short-term mammalian tests systems. Mutat Res. 1981 Apr;81(2):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSANE J. M., ROBINS E. The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korr H. Proliferation of different cell types in the brain. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1980;61:1–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubic V. L., Anders M. W. Metabolism of dihalomethanes to carbon monoxide. II. In vitro studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Mar-Apr;3(2):104–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latov N., Nilaver G., Zimmerman E. A., Johnson W. G., Silverman A. J., Defendini R., Cote L. Fibrillary astrocytes proliferate in response to brain injury: a study combining immunoperoxidase technique for glial fibrillary acidic protein and radioautography of tritiated thymidine. Dev Biol. 1979 Oct;72(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh B., Johansson M. B., Mercke C., Cavallin-Stahl E. Enhancement of heme catabolism by caloric restriction in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Dec;30(4):421–427. doi: 10.3109/00365517209080280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O. A quantitative study of the glia of the Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum in mammals. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1979 Jan-Feb;5(1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1979.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mares V., Schultze B., Maurer W. Stability of DNA in Purkinje cell nuclei of the mouse. An autoradiographic study. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):665–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marietta M. P., Vesell E. S., Hartman R. D., Weisz J., Dvorchik B. H. Characterization of cytochrome P-450-dependent aminopyrine N-demethylase in rat brain: comparison with hepatic aminopyrine N-demethylation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Feb;208(2):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. J., Zempel J. A., Braun W. H. The pharmacokinetics of inhaled methylene chloride in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;65(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(82)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. J., Zempel J. A. The dose-dependent metabolism of [14C]methylene chloride following oral administration to rats. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1981 Feb;19(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(81)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin S. O., Nyström B., Haglid K., Hamberger A. Glial contribution to amino acid content and metabolism of the deafferented dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res. 1984;11(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W. A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):739–744. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez V. J., Olney J. W., Cicero T. J., Moore B. W., Bahn B. A. Wallerian degeneration in rabbit optic nerve: cellular localization in the central nervous system of the S-100 and 14-3-2 proteins. J Neurochem. 1970 Apr;17(4):511–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putz V. R., Johnson B. L., Setzer J. V. A comparative study of the effects of carbon monoxide and methylene chloride on human performance. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 May-Jun;2(5):97–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren L. E., Aurell A., Kjellstrand P., Haglid K. G. Astrogliosis in the cerebral cortex of gerbils after long-term exposure to 1,1,1-trichloroethane. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Dec;11(6):447–455. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren L. E., Wronski A., Briving C., Haglid K. G. Long lasting changes in gerbil brain after chronic ethanol exposure: a quantitative study of the glial cell marker S-100 and DNA. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1985 Mar-Apr;9(2):109–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1985.tb05528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueger D. C., Huston J. S., Dahl D., Bignami A. Formation of 100 A filaments from purified glial fibrillary acidic protein in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T. A structure-activity relationship of some chlorinated hydrocarbons. Arch Environ Health. 1979 Mar-Apr;34(2):69–75. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1979.10667371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrou D., Lübbe I., Haglid K. G. Immunelektrophoretische Quantifizierung des hirnspezifischen S-100 Proteins. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;29(3):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00685263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. D., Fisher T. N., Hosko M. J., Peterson J. E., Baretta E. D., Dodd H. C. Experimental human exposure to methylene chloride. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Nov;25(5):342–348. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. D., Hake C. L. Paint-remover hazard. JAMA. 1976 Jan 26;235(4):398–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winek C. L., Collom W. D., Esposito F. Accidental methylene chloride fatality. Forensic Sci Int. 1981 Sep-Oct;18(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0379-0738(81)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winneke G., Fodor G. G. Dichloromethane produces narcotic effect. Occup Health Saf. 1976 Mar-Apr;45(2):34-5, 49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]