Abstract
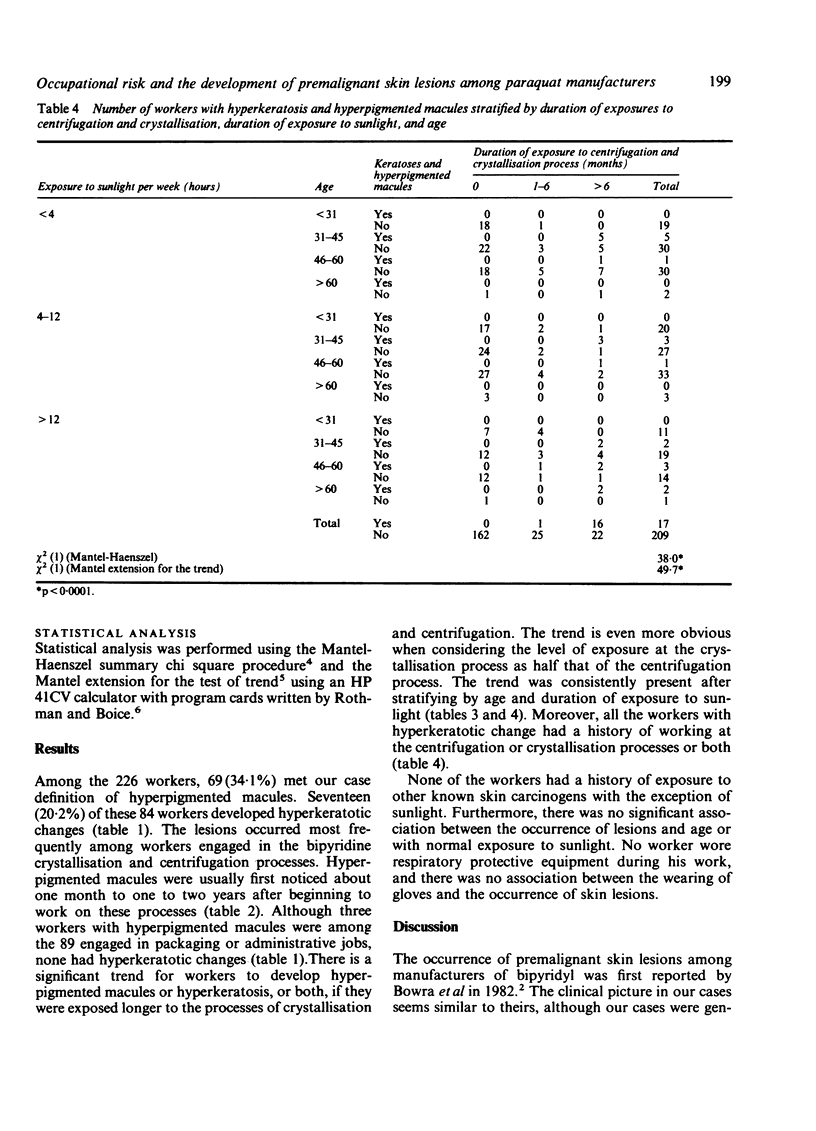
The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence rate and possible aetiological factors of premalignant skin lesions observed among paraquat manufacturers. A total of 228 workers in 28 factories were interviewed and independently examined by a dermatologist during site inspection in 1985. Information concerning past working experience, current toxic exposures, other risk factors of hyperpigmented macules and keratosis, and the past and present manufacturing processes of each factory was collected. Sixty nine cases of hyperpigmented macules and 17 of hyperkeratosis were found. Typical macules were irregular in shape, pin head size, hyperpigmented, with or without hyperkeratosis, and usually distributed symmetrically over the forearms, hands, neck, and upper chest, where exposure to sunlight was maximal. Six patients with hyperkeratotic lesions subsequently had biopsies performed and two showed Bowenoid changes. Eighty per cent (28 cases) and 67% (38 cases) of workers developed hyperpigmented macules if they had ever been engaged in bipyridine centrifugation and crystallisation, respectively; there were three workers 3% with such lesions among those who performed packaging or administrative jobs, or both. There was a significant trend (p less than 0.0001) for workers to develop hyperpigmented macules and hyperkeratosis the longer they had been exposed to centrifugation or crystallisation, or both, independent of age and the duration of exposure to sunlight. Evidence is presented to suggest that sunlight is a necessary cofactor and that the aetiological agent was produced during high temperature sodium process of bipyridine synthesis, and possibly bipyridine isomer(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowra G. T., Duffield D. P., Osborn A. J., Purchase I. F. Premalignant and neoplastic skin lesions associated with occupational exposure to "tarry" byproducts during manufacture of 4,4'-bipyridyl. Br J Ind Med. 1982 Feb;39(1):76–81. doi: 10.1136/oem.39.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn C. E., Keir W. Nail damage in spray operators exposed to paraquat. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Oct;28(4):399–403. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. K. A clinical survey of paraquat formulation workers. Br J Ind Med. 1979 Aug;36(3):220–223. doi: 10.1136/oem.36.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



