Abstract
Introduction
This study examines health‐care costs attributed to dementia diseases in the 10 years prior to, during, and 6 years after diagnosis.
Methods
Using administrative register data for people diagnosed with dementia (2010–2016) in southern Sweden (n = 21,184), and a comparison group without dementia, health‐care costs over 17 years were examined using longitudinal regression analysis.
Results
Average annual health‐care costs per person were consistently higher before diagnosis in the dementia group (10 years before: Swedish krona (SEK) 2063, P < .005 and 1 year before: SEK8166, P < .005). At diagnosis, health‐care costs were more than twice as high (SEK44,410, P < .005). Four to 6 years after diagnosis, there was no significant different in costs compared to comparators.
Discussion
Excess health‐care cost arise as early as 10 years before a formal diagnosis of dementia, and while there is a spike in cost after diagnosis, health‐care costs are no different 4 years after. These findings question currently accepted assumptions on costs of dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer´s disease, dementia, diagnosis, health‐care costs, Sweden
1. BACKGROUND
Dementia currently ranks as one of the leading causes of death and disability, 1 generating a great burden to the people living with dementia diseases (hereafter referred to as “dementia”), their family, and society. As the risk of developing dementia doubles every 5 years after age 65, and as many countries are experiencing population growth among the most elderly, 2 the prevalence and associated health‐care costs may also be accelerating. In 2018, >50 million people worldwide were estimated to live with dementia and this number is expected to rise to >152 million by the year 2050. 3
As rates of dementia rise, policy is increasingly motivated to consider economists’ perspectives and to more precisely consider what is driving costs. Decision makers require reliable, and up‐to‐date, information of the consequences of dementia to plan services and set policy appropriately. Furthermore, understanding of the underlying factors that explain these consequences of dementia also help to identify and evaluate specific intervention options.
The global cost of dementia is estimated to be US$1 trillion per year. 3 Analysis of health‐care cost can provide useful information of the origins and extent of the care burden related to particular diseases. There are several studies estimating the cost of dementia in different country settings. For instance, a recent systematic review of 26 studies estimated that the annual cost per person with dementia in Europe and the United States was €32,507 and €43,899, respectively (2015 price year). 4 However, many of the studies were lacking a comparison group—that is, a cognitively healthy population 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 —making it very hard to measure the excess health‐care cost of dementia. In addition, most studies in the review were based on cross‐sectional data, 4 which provide no information about the development of cost of dementia over time.
Furthermore, previous studies provide inconsistent findings on the question of whether incipient dementia leads to an increase in health‐care use. For example, an American study showed that there were no differences in medical care use between people with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and matched controls 1 year before or 4 years after the diagnosis. 13 A German study revealed that use of ambulatory medical care services is about 50% higher among people with dementia compared to controls during the year before diagnosis and remain on a relatively high level during the year after. 14 Based on data from the Medicare system in the United States, Albert et al. showed that participants having incipient AD had high primary care expenditures already 1 to 2 years before the diagnosis compared to people without the disease. 15
In Sweden, several studies have estimated different cost aspects of dementia. 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 In a comprehensive analysis from a societal perspective, Wimo et al. 16 used a combination of bottom‐up and top‐down methods to estimate a total cost of 398,000 Swedish Krona (SEK) (€45,000) per person with dementia in 2012.
The aim of this study was to explore health‐care costs attributed to dementia over a period of 17 years, and provide insights into costs one decade before diagnosis, estimate how much costs increase at diagnosis, and examine the trend in the development of costs 6 years after diagnosis. As previous studies have shown that the cognitive impairment of dementia may develop up to 18 years prior to diagnosis, 21 , 22 our hypothesis was that increased health‐care use can be observed several years before dementia has been formally diagnosed.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Data
Sweden has a long history of national registers that are available for research purposes. The unique Personal Identification Number enables the linkage of data from different registers to a specific individual. 23 The dementia population in this study was defined based on the International Classification of Diseases (ICD)‐10 of F00.0–F00.2, F00.9, G30.0, G30.1, G30.8, and G30.9 for AD diagnoses as well as F01.1‐F01.3, F01.8‐F02.0, F02.2‐F02.4, F02.8, F03.9, F03‐P, F10.6‐7A, G32.0, and G31.8 for other types of dementia. 24 A comparison group was constructed by linking (1:1)* individuals from the Swedish general population without dementia diagnosis based on the factors sex, age, and municipality of residence. The comparators were linked at the time of diagnosis of each person in the dementia population (the index date).
RESEARCH IN CONTEXT
Systematic Review: While several studies have addressed health‐care costs related to dementia diseases, many have not included a comparison group, making it difficult to establish to what extent dementia per se is linked to increased costs. Most previous studies are also cross‐sectional, and thus little is known about the development of costs before and after diagnosis.
Interpretation: This analysis finds significant differences in health‐care costs in the 10 years prior to diagnosis, and challenges assumptions of the estimated cost post‐diagnosis by showing that costs of dementia are not significantly different 4 years after diagnosis.
Future Directions: Further research is needed to explore what is driving the excess health‐care costs before diagnosis and why the excess cost decreases in the years after. Future research should also explore the impact of dementia on other costs within the societal perspective, for example, cost related to social care and informal care before and after diagnosis.
The main data source for the study was the Region Skåne's Healthcare Utilisation Database, which includes all people living with dementia in Region Skåne (southern Sweden), identified as having a first dementia diagnosis during the years 2010 through 2016. To all individuals in the dataset, yearly information was linked from a number of national registers, such as the health registers at the National Board of Health and Welfare (NBHW) 25 and the socioeconomic databases at Statistics Sweden, including the Longitudinal Integrated Database for Health Insurance and Labour Market Studies (LISA). 26 National data from the NBHW was used to ensure that the comparison group had not received dementia diagnoses in other regions of Sweden before moving to southern Sweden. The data enabled us to examine individuals over a 17‐year period, including the year of diagnosis, 10 years before, and 6 years after diagnosis.
The study was approved by the Regional Research Ethics Board at Lund University (dnr 2017/554).
2.2. Main variables used in the analysis
The main outcome variable in the analysis was the direct health‐care cost per person per year adjusted to the price level of 2016 based on the Swedish consumer price index. 27 This included inpatient, outpatient, and primary care (both in the public and private health‐care sector) provided by the regional health‐care sector in southern Sweden, Region Skåne. Municipal health‐care costs, such as costs of home care and nursing homes, and pharmaceuticals costs were not included. The cost of each health‐care episode was based on the Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) codes where diagnoses that are similar in terms of medical and resource use are grouped. The yearly total cost for a health‐care unit was divided by the total amount of DRG points produced, which was then used to calculate a cost per DRG code. This is done routinely by Region Skåne, the public health‐care provider in southern Sweden. Missing cost information in the health‐care use database was imputed on a yearly basis in several steps, separately for inpatient care and outpatient care. See Data S1 in supporting information for further details.
The presence of dementia was defined as a binary variable (1 = dementia group and 0 = comparison group). A set of potentially confounding factors, possibly impacting both dementia and health‐care costs, were also identified and included sex, highest attained educational level, being foreign (born outside Sweden or both parents born outside Sweden), number of children, marital status (married or cohabitant) and the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) including data from up to 5 years before diagnosis. Thus, dementia was not included in the estimated index. The CCI is a method for categorizing comorbidities of patients based on the ICD codes. Based on the risk of mortality, each comorbidity category is given an associated weight (between 0 and 6), and the sum of all weights results in a single comorbidity score for a patient. 28 An alternative comorbidity index was also explored, the Elixhauser Comorbidity Index (ECI), which is an extension of the CCI including a larger set of comorbidities. 29
2.3. Statistical analysis
The effect of dementia on health‐care costs was analyzed using ordinary least squares regression with individual‐level clustered standard errors to correct for the panel structure of the data, controlling for sex, year of birth, educational level, foreign background, number of children, marital status, and the CCI, in the 17‐year longitudinal panel. By interacting dummy variables for each year from diagnosis with the dementia variable, the average annual health‐care cost of people with dementia and the comparison group were predicted at each year before and after diagnosis. A large sample size allows use of simple methods when the underlying distribution of the dependent variable is non‐normal as the analysis depends on means and variances of the sample. 30
The analyses include only years in which the individuals are alive during the full year and costs that occurred during the year of death were not included. All the analyses were performed using Stata version 16. 31
2.4. Sensitivity analyses
The robustness of the results was tested in three separate sensitivity analyses.
2.4.1. Analysis limited to people alive during the full study period
The first analysis included only individuals that were alive until the year of diagnosis (or the corresponding year for the comparison group). After that year, people may die and those in worse health with a higher need of more health‐care resources, are at higher risk of dying.
2.4.2. Analysis limited to people with 16 years of follow‐up
The second analysis included only individuals that can be followed for 16 years (the maximum time possible to follow for each individual to using data from 2001–2016 and a population diagnosed between 2010 and 2016). This includes those diagnosed in 2010, followed 9 years before and 6 years after, and those diagnosed in 2011, followed 10 years before and 5 years after. Individuals diagnosed in later years, 2012 to 2016, had a shorter follow‐up and were excluded in this sensitivity analysis.
2.4.3. Analysis based on an alternative “broader” classification of the dementia population
The final sensitivity analysis was based on a broader classification of dementia included additional diagnoses related to cognitive failure (ICD‐10: F049, F050, F059, F067, F78, F099, F09‐P, R410‐R413, R418, R418A, R418P, R418W, and Z032) that were reported for people 70 years or older. This analysis was performed because it has been shown that the prevalence of undetected dementia is very high, not only in Sweden 32 but also globally, 33 and the diagnoses above have previously been shown to be linked to underreported dementia in Region Skåne. 24
3. RESULTS
3.1. Study population
The study population included 21,184 individuals with dementia and one comparator each. The average age at diagnosis/index was 81.9 years and 40.7% were men (Table 1). People in the dementia group were slightly less educated and more likely to have a foreign background. Fewer were married or cohabitant and it was somewhat more common not to have children in the dementia group. Additionally, the difference in CCI score (1.55 vs. 1.38, P < .0001) indicated that the dementia group was in worse health during the 5 years before diagnosis (see Table S1 in supporting information for information about the distributions of each individual comorbidity in the score). During the 6 years of follow‐up, a greater proportion of the dementia group had died compared to the comparison group (50.1% vs. 29.4%, P < .0001).
TABLE 1.
Population characteristics at diagnosis
| Dementia | Comparison | P a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of individuals | 21,184 | 21,184 | |
| Male sex, n (%) | 8611 (40.7) | 8611 (40.7) | 1.000 |
| Year of birth, mean (SD) | 1931 (9.5) | 1931 (9.5) | 1.000 |
| Year of diagnosis/index, mean (SD) | 2013 (1.92) | 2013 (1.92) | 1.000 |
| Age at diagnosis/index, mean (SD) | 81.9 (9.3) | 81.9 (9.3) | 1.000 |
| Highest educational degree, n (%) | |||
| Compulsory | 10,683 (50.4) | 10,352 (48.9) | 0.001 |
| Upper secondary | 6828 (32.2) | 6990 (33.0) | 0.093 |
| Higher education | 3049 (14.4) | 3314 (15.6) | <0.001 |
| Missing | 624 (3.0) | 528 (2.5) | 0.004 |
| Foreign background, n (%) | 2748 (13.0) | 2381 (11.2) | <0.001 |
| Married or cohabitant, n (%) | 6258 (29.5) | 7267 (34.3) | <0.001 |
| Number of children, n (%) | |||
| None | 3367 (15.9) | 3131 (14.8) | 0.002 |
| 1–2 | 11,711 (55.3) | 11,998 (56.6) | 0.005 |
| 3–4 | 5288 (25.0) | 5287 (25.0) | 0.991 |
| ≥5 | 818 (3.9) | 768 (3.6) | 0.201 |
| Charlson index, mean (SD) | 1.55 (1.91) | 1.38 (1.87) | <0.001 |
| Deceased during the 6 years after diagnoses/index | 10,608 (50.1) | 6222 (29.4) | <0.001 |
Abbreviation: SD, standard deviation.
t‐test and test of proportions.
3.2. The excess cost to health care from dementia
During the 10 years before diagnosis, the predicted average annual health‐care costs per person in the dementia group were without exception higher compared to the health‐care costs in the comparison group, which is presented in Table 2 and illustrated in Figure 1. There was an excess cost per person in the dementia group ranging from SEK 2063 (13% higher, P < .005) to SEK 8166 (24% higher, P < .005) 10 years and 1 year before diagnosis, respectively. During the year of diagnosis, the health‐care cost increased substantially for the people with dementia, to SEK 82,056 (95% confidence interval [CI] 80,056–83,758) which is a 118% higher cost compared to the comparison group (SEK 37,647, 95% CI 36,590–38,703). In the years after diagnosis, the health‐care costs in the dementia group decreased compared to the year of diagnosis and 4 years after, the average health‐care cost was similar to the costs of the comparison group. See Table S2 in supporting information for full results from the underlying regression. Controlling for the alternative comorbidity index (ECI) had little impact on the overall results; however, a slight decrease in the excess cost of dementia prior to diagnosis was seen.
TABLE 2.
Predicted health‐care costs of people with dementia and controls 10 years before and 6 years after diagnosis (expressed in Swedish krona, SEK, of 2016 prices)
| n (Dementia and comparison) | Dementia | Comparison | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Difference | ||||
| Years before | ||||||||
| 10 | 34,674 | 18,007 | 17,251 | 18,764 | 15,944 | 15,340 | 16,549 | 2,063 a |
| 9 | 42,368 | 19,430 | 18,731 | 20,129 | 17,295 | 16,696 | 17,893 | 2,135 a |
| 8 | 42,368 | 21,110 | 20,395 | 21,825 | 18,779 | 18,161 | 19,396 | 2,332 a |
| 7 | 42,368 | 23,096 | 22,318 | 23,873 | 19,577 | 18,926 | 20,228 | 3,519 a |
| 6 | 42,368 | 24,731 | 23,935 | 25,528 | 21,765 | 21,106 | 22,425 | 2,966 a |
| 5 | 42,368 | 27,348 | 26,494 | 28,202 | 22,953 | 22,276 | 23,629 | 4,395 a |
| 4 | 42,368 | 29,526 | 28,665 | 30,388 | 25,233 | 24,524 | 25,942 | 4,293 a |
| 3 | 42,368 | 31,800 | 30,889 | 32,710 | 27,788 | 26,947 | 28,630 | 4,011 a |
| 2 | 42,368 | 35,621 | 34,608 | 36,633 | 30,673 | 29,844 | 31,502 | 4,947 a |
| 1 | 42,368 | 41,541 | 40,461 | 42,621 | 33,375 | 32,482 | 34,268 | 8,166 a |
| Diagnosis | 38,867 | 82,056 | 80,354 | 83,758 | 37,647 | 36,590 | 38,703 | 44,410 a |
| Years after | ||||||||
| 1 | 31,235 | 56,789 | 55,292 | 58,287 | 37,925 | 36,760 | 39,091 | 18,864 a |
| 2 | 23,669 | 49,029 | 47,495 | 50,563 | 38,035 | 36,663 | 39,407 | 10,994 a |
| 3 | 16,595 | 45,034 | 43,286 | 46,782 | 40,101 | 38,528 | 41,674 | 4,933 a |
| 4 | 11,201 | 42,816 | 40,639 | 44,993 | 39,751 | 37,953 | 41,549 | 3,065 |
| 5 | 6,593 | 41,089 | 38,380 | 43,797 | 41,296 | 38,885 | 43,707 | –207 |
| 6 | 3,007 | 42,653 | 38,788 | 46,517 | 43,338 | 39,558 | 47,118 | –685 |
Notes: Adjusting for sex, year of birth, educational level, foreign background, number of children, marital status and Charlson Comorbidity Index based on 5 years before diagnosis.
Statistically significant at a 5% level of significance. For full regression results see Table S2.
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval.
FIGURE 1.
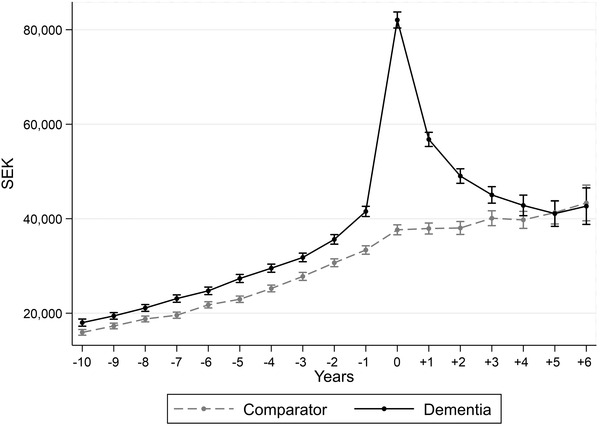
Predicted average health‐care cost per patient at diagnosis as well as 10 years before and 6 years after. 95% confidence intervals indicated by the whiskers. Expressed in Swedish krona, SEK, of 2016 prices
Overall, the development of costs over time were similar also when considering men and women separately (Figure 2). However, 4 years after diagnosis the excess health‐care cost of men with dementia reverted to a similar level as before diagnosis, with about 10% higher costs, while the costs for women with dementia were similar or slightly lower compared to the comparison group.
FIGURE 2.
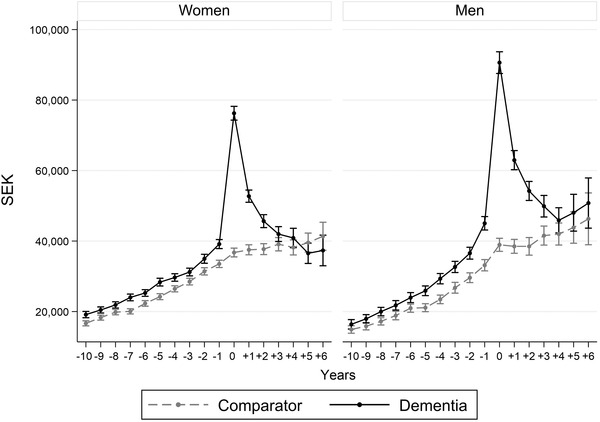
Predicted average health‐care cost per patient at diagnosis as well as 10 years before and 6 years after by sex. 95% confidence intervals indicated by the whiskers. Expressed in Swedish krona, SEK, of 2016 prices
Figure 3 shows the average health‐care cost per person (a), as well as the proportion of the population with any health‐care cost each year (b), separately for each type of health care. Inpatient care was the costliest type of care throughout the study period, followed by outpatient care. Higher costs for people with dementia could be seen in all three types of care before diagnosis, particularly for inpatient care, while 4 years after diagnosis, the costs of the dementia group were not statistically significantly higher in any of the care types.
FIGURE 3.
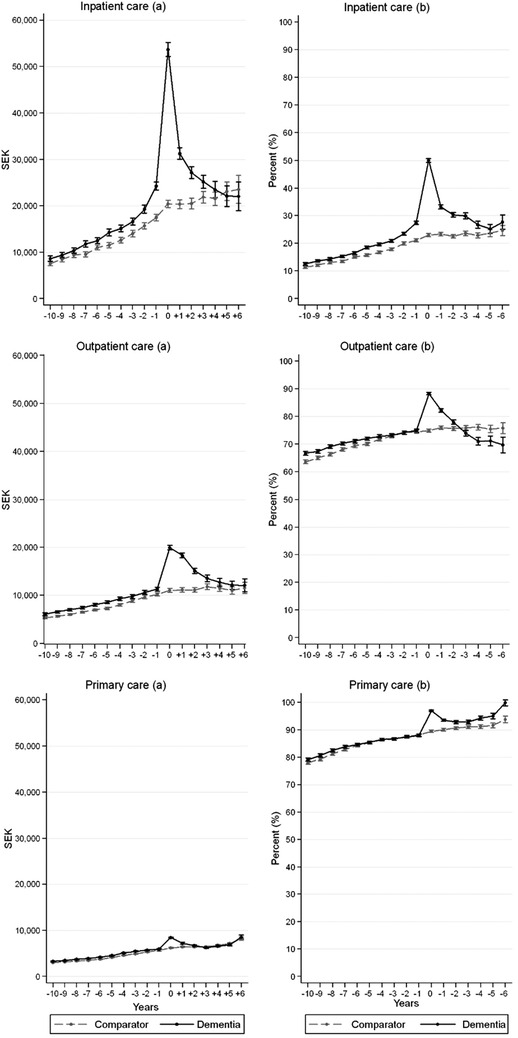
Predicted average health‐care cost per patient (A) and proportion of patients accessing any health care (B) at diagnosis as well as 10 years before and 6 years after by type of health care. 95% confidence intervals indicated by the whiskers. Expressed in Swedish krona, SEK, of 2016 prices
While inpatient care generated the most annual costs, it was the least common type of care (15% to 28% of people with dementia before diagnosis). Outpatient care was consumed by 66% to 74% of people with dementia and primary care by 79% to 89% of people with dementia. Overall, a larger proportion of people with dementia consumed inpatient care. However, 4 years after diagnosis no difference could be observed. The proportion of people with dementia consuming outpatient care decreased after diagnosis, both compared to the comparison group but also compared to the period before diagnosis. The proportion consuming primary care was similar before diagnosis, while increasing in the dementia group after diagnosis compared to the comparison group.
3.3. Sensitivity analyses
3.3.1. Analysis limited to people alive during the full study period
As can be noted in Figure 1, a break in the general upward trend of the health‐care costs over time can be seen also for the comparators at the index year (the year of diagnosis for the dementia group). Figure S1 in supporting information shows that when including only individuals alive during the full study period (total n = 25,538; of which dementia: n = 10,576 [41%] and comparator: n = 14,962 [59%]), the trend for people with dementia was similar to the main analysis although the total costs were lower due to the selection of an overall healthier population. However, for the comparators the upward trend in health‐care costs over time remains stable, suggesting that the break seen for the comparators in the main analysis is caused by the study design.
3.3.2. Analysis limited to people with 16 years of follow‐up
In Figure S2 in supporting information, a trend similar to the baseline estimates is noted when basing the analysis on the subset of people who could be followed for the full 16 years (total n = 6201; of which dementia: n = 2217 [36%] and comparator: n = 3984 [64%]). However, the health‐care costs were somewhat lower compared to the main analysis reflecting that this selection of individuals were both younger and healthier.
3.3.3. Analysis based on the “broader” classification of the dementia population
The broader classification of dementia resulted in a larger study sample (31,261 people with dementia with one comparator each; see Table S3 in supporting information). The results based on this broader classification were similar to the results based on the narrower standard classification of the dementia population (see Table S4 and Table S5 in supporting information). Figure S3 in supporting information shows annual health‐care costs for both the broader and the narrower dementia population and the comparators. The health‐care costs were very similar throughout the study period, although slightly higher during the year before and during diagnosis for the broader population. The analysis based on the broad population also showed a slightly larger difference in costs between the dementia group and the comparison group in the years after diagnosis; however, after 5 years the differences were not statistically significant.
4. DISCUSSION
The rationale for this study was to estimate the excess health‐care cost of dementia to shed light on the dementia disease burden, which is interesting in its own right but also because the excess health‐care cost represents an important piece of information in economic evaluations. The rapidly growing use of economic evaluations in health‐related decisions in Sweden, and other countries, enhances the need for accurate cost estimates. Our results show that people that will develop dementia have elevated health‐care costs as early as 10 years prior to diagnosis (ranging from 13% to 25% higher costs 10 to 1 year prior, respectively). This finding indicates higher health‐care needs long before being formally diagnosed with dementia by the health‐care system. During the year of diagnosis, people with dementia have more than twice the cost (SEK 44,410 [US$ 5187†]; 34 118% higher). In the subsequent years after diagnosis, the excess health‐care costs of dementia decline and after 4 years, the costs are comparable to the comparators. Similar patterns could also be seen when the cost of out‐ and inpatient, and primary care were analyzed separately. Inpatient care was the main cost driver and accounted for the main part of the excess cost.
The higher cost of the dementia population at the prediagnosis period is in line with other studies 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 and is also supported by studies showing that the cognitive impairment of AD dementia may occur up to 18 years before diagnosis. 21 , 22 The peak in the cost at the year of diagnosis may be explanied by the distress people with dementia and their famillies often express before diagnosis, which might lead to a greater contact with the health‐care system and the testing and/or costly diagnostic procedures that eventually confirm a dementia diagnosis. 36 , 39
Our finding of reduced health‐care cost after the year of diagnosis is in line with studies based on Medicare expenditures of people with dementia in the United States, which indicate that some inpatient and post‐acute care services used after the diagnosis of dementia are preventable. 36 , 39 , 40 Although the elderly care system in Sweden is different than in the United States, a similar explanation could be feasible also in a Swedish health‐care setting. Moreover, in Sweden, receiving a formal dementia diagnosis often provides access to other types of care, such as nursing home care and home care. 41 This might help persons with dementia to avoid situations that could otherwise result in a health‐care need. The costs related to these services are covered by municipalities and are considered social care costs, not belonging to the health‐care sector. Another explanation might be that the disease itself contributes to difficulties in expressing needs and preferences, thereby reducing the contact with the health‐care sector. Finally, the decreased excess health‐care costs after diagnosis could be a result of people with diagnosed dementia being less prioritized in the health‐care system.
Our results show that the estimated average health‐care costs of a person with dementia range from SEK 56,789 (US$ 6633) 1 year after diagnosis to SEK 42,653 (US$ 4982) 6 years after. This includes all types of health care that this relatively old patient group consumes, also related to other disease. The estimate is higher compared to the previously estimated health‐care cost of SEK 18,382 (US$ 2713‡) per person with dementia in Sweden in 2012. 16 The higher costs estimated in our study for 2016 could in part be related to overall increased cost in the health‐care sector since 2012 but is more likely to be driven by substantial differences in study design, data collection, and methods. The previous study did also present an estimate of costs related to dementia solely (“net costs”). However, this estimate was not presented separately for health‐care–related costs and therefore is not directly comparable to the results from our study.
A strength of this study is the use of individual‐level data from various registers covering southern Sweden. This rich dataset allowed us to account for several potential confounding demographic and socioeconomic factors and thereby account for the fact that the onset of dementia is not random but could be associated with lifestyle factors. The focus on one region in Sweden, as opposed to all of Sweden, allowed us to identify cases based on diagnosis also from primary care data, which is not available on a national level in Sweden. This was essential to capture the total dementia population and it also enabled us to study the full impact of dementia on total health‐care costs. We are aware of regional differences across Sweden but the advantages of focusing on Region Skåne (a more comprehensive identification of the population and coverage of health‐care costs) was considered to highly outweigh the advantages of using national level data (better generalizability). Our data also allowed sensitivity analyses to explore the concern of underdiagnosis using an alternative broader definition of dementia and the results showed that our findings are robust also taking this concern into account.
A general weakness of our study is that, while we control for many key observable factors in our regression estimations, we can never rule out that there may also be other hard‐to‐measure unobserved factors that may explain the differences in health‐care cost between the dementia group and the comparison group. However, this problem is always present in studies based on non‐experimental data, and we expect that the controlling factors, such as age, education, and comorbidity, included in our models, will at least reduce most of the potential bias from these unobserved factors. Controlling for an alternative comorbidity index (the ECI) with a larger set of comorbidities compared to the CCI resulted in similar results; however, in the years prior to diagnosis the excess cost of dementia was slightly reduced. While this could indicate that the ECI is able to capture more potential confounding, it could also indicate that it removes part of the effect of pre‐diagnoses dementia if the extended set of comorbidities capture health‐care consumption related to the cognitive decline often seen several years before the formal diagnosis of dementia has been made.
As the aim of this study was to explore the excess health‐care cost related to dementia, before and after diagnosis, further research is needed to explore the impact of dementia on other costs within a societal perspective. Most previous studies have shown that costs outside the health‐care system, such as costs related to informal care, are higher compared to the direct health‐care–related costs in the case of dementia. 4 , 16 , 42 Pharmaceutical costs related to dementia is also an area which could be further explored. Additionally, future research should explore what is driving the increased health‐care use before diagnosis. Our results suggest that increased use of inpatient care plays an important part; however, what specific health issues are causing this need can be further examined.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Håkan Toresson is an owner of Cell Invent AB as well as a board member in Cell Invent AB and Vivobakt AB. Johan Jarl have received consulting fees from Ramboll. Dominic Trépel has received funding from the Global Brain Health Institute. Sofie Persson, Sanjib Saha, and Ulf–G. Gerdtham have nothing to disclose.
FUNDING SOURCES
The study was performed based on funding from the Government Grant for Clinical Researc (“ALF”) Region Skåne and from seven municipalities in Skåne, Sweden (Burlöv, Båstad, Lomma, Simrishamn, Vellinge, Eslöv, and Örkelljunga). The Health Economics Program at Lund University receives core funding from Government Grant for Clinical Research. The Clinical Memory Research Unit at Lund University has received funding from Region Skåne and Stohne foundation. The funding sources played no part in the study design, analysis and interpretation of the data, or in the writing of the manuscript and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank Prof. Elisabet Londos at the Clinical Memory Research Unit at Lund University and the Memory Clinic at Skåne University Hospital and staff at the seven municipalities in Skåne, Sweden (Burlöv, Båstad, Lomma, Simrishamn, Vellinge, Eslöv, and Örkelljunga) for helpful comments and suggestions on the study.
Persson S, Saha S, Gerdtham U‐G, Toresson H, Trépel D, Jarl J. Healthcare costs of dementia diseases before, during and after diagnosis: Longitudinal analysis of 17 years of Swedish register data. Alzheimer's Dement. 2022;18:2560–2569. 10.1002/alz.12619
Footnotes
The full database on which this study is based included up to five comparators for each person with dementia. However, the high age of people living with dementia made it difficult to find five comparators for each person matched on sex, age, and municipality of residence, which resulted in an unbalanced comparison group. Therefore, only one comparator (the first eligible draw in the matching prosses) for each person with dementia was included in this study.
Average exchange rate 2016: US$1 = SEK8.5613.
Average exchange rate 2012: US$1 = SEK6.7754.
REFERENCES
- 1. The World Health Organization . The top 10 causes of death . 2020. 2020‐10‐21]; Available from: https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/the‐top‐10‐causes‐of‐death
- 2. United Nations World Population Ageing. 2017, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division.
- 3. Patterson C. World Alzheimer report 2018: The State Of The Art Of Dementia Research: New Frontiers. Alzheimer's Disease International (ADI). 2018:32‐36. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Cantarero‐Prieto D, Leon PL, Blazquez‐Fernandez C, Juan PS, Cobo CS. The economic cost of dementia: a systematic review. Dementia. 2019;18(8):2637‐2657. p. 1471301219837776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Connolly S, Gillespie P, O'shea E, Cahill S, Pierce M. Estimating the economic and social costs of dementia in Ireland. Dementia. 2014;13(1):5‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hojman DA, Duarte F, Ruiz‐Tagle J, Budnich M, Delgado C, Slachevsky A. The cost of dementia in an unequal country: the case of Chile. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Holmerová I, Hort J, Rusina R, Wimo A, Šteffl M. Costs of dementia in the Czech Republic. Eur J Health Econ. 2017;18(8):979‐986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kelley AS, Mcgarry K, Gorges R, Skinner JS. The burden of health care costs for patients with dementia in the last 5 years of life. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163(10):729‐736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Leicht H, König H‐H, Stuhldreher N, et al. Predictors of costs in dementia in a longitudinal perspective. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e70018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Michalowsky B, Flessa S, Eichler T, et al. Healthcare utilization and costs in primary care patients with dementia: baseline results of the DelpHi‐trial. Eur J Health Econ. 2018;19(1):87‐102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Yang Z, Zhang K, Lin P‐J, Clevenger C, Atherly A. A longitudinal analysis of the lifetime cost of dementia. Health Serv Res. 2012;47(4):1660‐1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Zhu CW, Scarmeas N, Torgan R, et al. Longitudinal study of effects of patient characteristics on direct costs in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2006;67(6):998‐1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Leibson C, Owens T, O'brien P, et al. Use of physician and acute care services by persons with and without Alzheimer's disease: a population‐based comparison. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999;47(7):864‐869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Eisele M, Van Den Bussche H, Koller D. Utilization patterns of ambulatory medical care before and after the diagnosis of dementia in Germany – results of a case‐control study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010;29(6):475‐483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Albert SM, Glied S, Andrews H, Stern Y, Mayeux R. Primary care expenditures before the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2002;59(4):573‐578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wimo A, Jönsson L, Fratiglioni L, et al. The societal costs of dementia in Sweden 2012 ‐ relevance and methodological challenges in valuing informal care. Alzheimer's Re Ther. 2016;8(1):59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wimo A, Karlsson G, Sandman PO, Corder L, Winblad B. Cost of illness due to dementia in Sweden. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;12(8):857‐861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Jönsson L, Jönhagen ME, Kilander L, et al. Determinants of costs of care for patients with Alzheimer's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006;21(5):449‐459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Wimo A, Winblad B. Societal burden and economics of vascular dementia: preliminary results from a Swedish‐population‐based study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2003;15(Suppl 1):251‐256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Wimo A, Religa D, Spångberg K, Edlund A‐K, Winblad B, Eriksdotter M. Costs of diagnosing dementia: results from SveDem, the Swedish Dementia Registry. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;28(10):1039‐1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Beason‐Held LL, Goh JO, An Y, et al. Changes in brain function occur years before the onset of cognitive impairment. J Neurosci. 2013;33(46):18008‐18014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Rajan KB, Wilson RS, Weuve J, Barnes LL, Evans DA. Cognitive impairment 18 years before clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia. Neurology. 2015;85(10):898‐904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ludvigsson JF, Otterblad‐Olausson P, Pettersson BU, Ekbom A. The Swedish personal identity number: possibilities and pitfalls in healthcare and medical research. Eur J Epidemiol. 2009;24(11):659‐667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Region Skåne, Region Skåne's strategic development plan for equal dementia care (Region Skånes strategiska utvecklingsplan för jämlik demensvård). 2017.
- 25. The National Board of Health and Welfare (Socialstyrelsen). Registers . 2020. 2020‐11‐20]; Available from: https://www.socialstyrelsen.se/en/statistics‐and‐data/registers/
- 26. Statistics Sweden . Longitudinal integrated database for health insurance and labour market studies (LISA). 2020 2020‐11‐20]; Available from: https://www.scb.se/en/services/guidance‐for‐researchers‐and‐universities/vilka‐mikrodata‐finns/longitudinella‐register/longitudinal‐integrated‐database‐for‐health‐insurance‐and‐labour‐market‐studies‐lisa/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27. Statistics Sweden . Consumer Price Index (CPI) . 2021; Available from: https://www.scb.se/en/finding‐statistics/statistics‐by‐subject‐area/prices‐and‐consumption/consumer‐price‐index/consumer‐price‐index‐cpi/
- 28. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, Mackenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373‐383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36(1):8‐27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Mihaylova B, Briggs A, O'hagan A, Thompson SG. Review of statistical methods for analysing healthcare resources and costs. Health Econ. 2011;20(8):897‐916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. StataCorp , STATA 16 . 2019: College Station, TX, USA: [Google Scholar]
- 32. Rizzuto D, Feldman AL, Karlsson IK, Dahl Aslan AK, Gatz M, Pedersen NL. Detection of dementia cases in two swedish health registers: a validation study. J Alzheimer's Dis 2018;61(4):1301‐1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Lang L, Clifford A, Wei Li, et al. Prevalence and determinants of undetected dementia in the community: a systematic literature review and a meta‐analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(2):e011146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. OECD . Exchange rates. Available from: https://data.oecd.org/conversion/exchange‐rates.htm#indicator‐chart
- 35. Zhu CW, Cosentino S, Ornstein K, et al. Medicare utilization and expenditures around incident dementia in a multiethnic cohort. J Gerontol: Series A. 2015;70(11):1448‐1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. White L, Fishman P, Basu A, Crane PK, Larson EB, Coe NB. Medicare expenditures attributable to dementia. Health Serv Res. 2019;54(4):773‐781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Lin P‐J, Zhong Y, Fillit HM, Chen E, Neumann PJ. Medicare expenditures of individuals with Alzheimer's disease and related dementias or mild cognitive impairment before and after diagnosis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64(8):1549‐1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Geldmacher DS, Kirson NY, Birnbaum HG, et al. Pre‐diagnosis excess acute care costs in Alzheimer's patients among a US Medicaid population. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2013;11(4):407‐413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Mccormick WC, Kukull WA, Van G, et al. Symptom patterns and comorbidity in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42(5):517‐521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Bynum JPW, Rabins PV, Weller W, Niefeld M, Anderson GF, Wu AW. The relationship between a dementia diagnosis, chronic illness, medicare expenditures, and hospital use. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(2):187‐194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wimo A, Elmståhl S, Fratiglioni L, et al. Formal and informal care of community‐living older people: a population‐based study from the Swedish National study on aging and care. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(1):17‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Wimo A, Jönsson L, Bond J, Prince M, Winblad B. The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010. Alzheimer's Dement. 2013;9(1):1‐11.e3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information
Supporting information


