Abstract
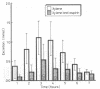
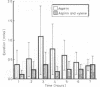
In a series of experiments to investigate interactions between industrial solvents and common medications the interaction between m-xylene and aspirin was studied. As both these substances are metabolised and excreted as glycine conjugates there would possibly be competition for this conjugation pathway. Five male volunteers were exposed on separate occasions to m-xylene by inhalation (100 ppm), aspirin (1500 mg) by mouth, and m-xylene and aspirin together under controlled conditions in an exposure chamber. Urine and blood samples were collected and analysed for m-xylene, aspirin, and their metabolites. The amounts of the major glycine conjugates produced from m-xylene (m-methylhippuric acid) and aspirin (salicyluric acid) were significantly reduced by about 50% when m-xylene and aspirin were coadministered. There appears to be a mutual inhibition on the formation of the respective glycine conjugates. It is suggested that the inhibition is due to competition for either the enzymes, acyl-CoA synthetase, or glycine N-acylase. These findings have implications in the biological monitoring of workers exposed to m-xylene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsel L. P., Levy G. Drug biotransformation interactions in man. II. A pharmacokinetic study of the simultaneous conjugation of benzoic and salicylic acids with glycine. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Mar;58(3):321–326. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600580307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Døssing M., Baelum J., Hansen S. H., Lundqvist G. R. Effect of ethanol, cimetidine and propranolol on toluene metabolism in man. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1984;54(4):309–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00378584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt A. J., Caldwell J., Smith R. L. The metabolism of aspirin in man: a population study. Xenobiotica. 1986 Mar;16(3):239–249. doi: 10.3109/00498258609043527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A., Woollard R. C. STRIPE: an interactive computer program for the analysis of drug pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 May;9(3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Amsel L. P. Kinetics of competitive inhibition of salicylic acid conjugation with glycine in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Aug;15(8):1033–1038. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Spassowski M., Henschler D. Metabolism of trichloroethylene in man. III. Interaction of trichloroethylene and ethanol. Arch Toxicol. 1975;33(3):173–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00311271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riihimäki V., Savolainen K., Pfäffli P., Pekari K., Sippel H. W., Laine A. Metabolic interaction between m-xylene and ethanol. Arch Toxicol. 1982 Mar;49(3-4):253–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00347873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwandi I. S., Bevan J. A. Antagonism of lobeline by ganglion-blocking agents at afferent nerve endings. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jul;153(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. K., Ottley T. W. The use of a transportable mass spectrometer for the direct measurement of industrial solvents in breath. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1981 Dec;8(12):606–610. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200081209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. K., Robertson S. M., Waldron H. A., Gompertz D. Effect of alcohol on the kinetics of mandelic acid excretion in volunteers exposed to styrene vapour. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Feb;40(1):75–80. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]