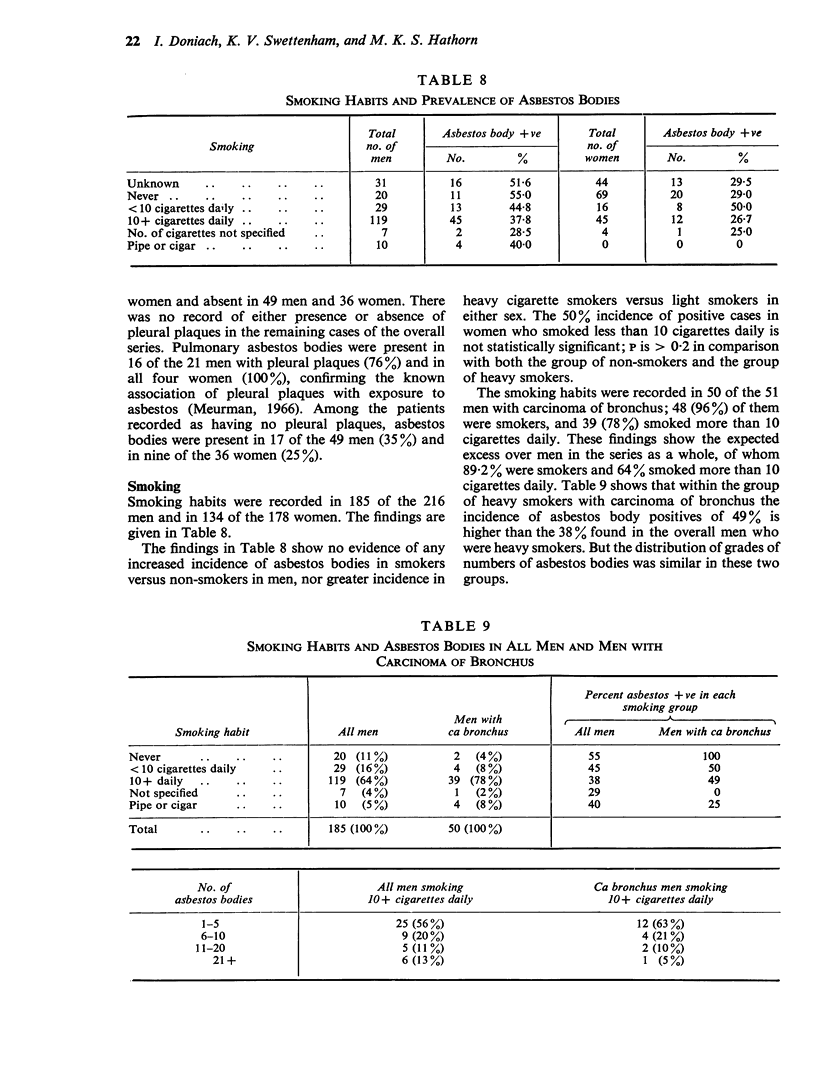
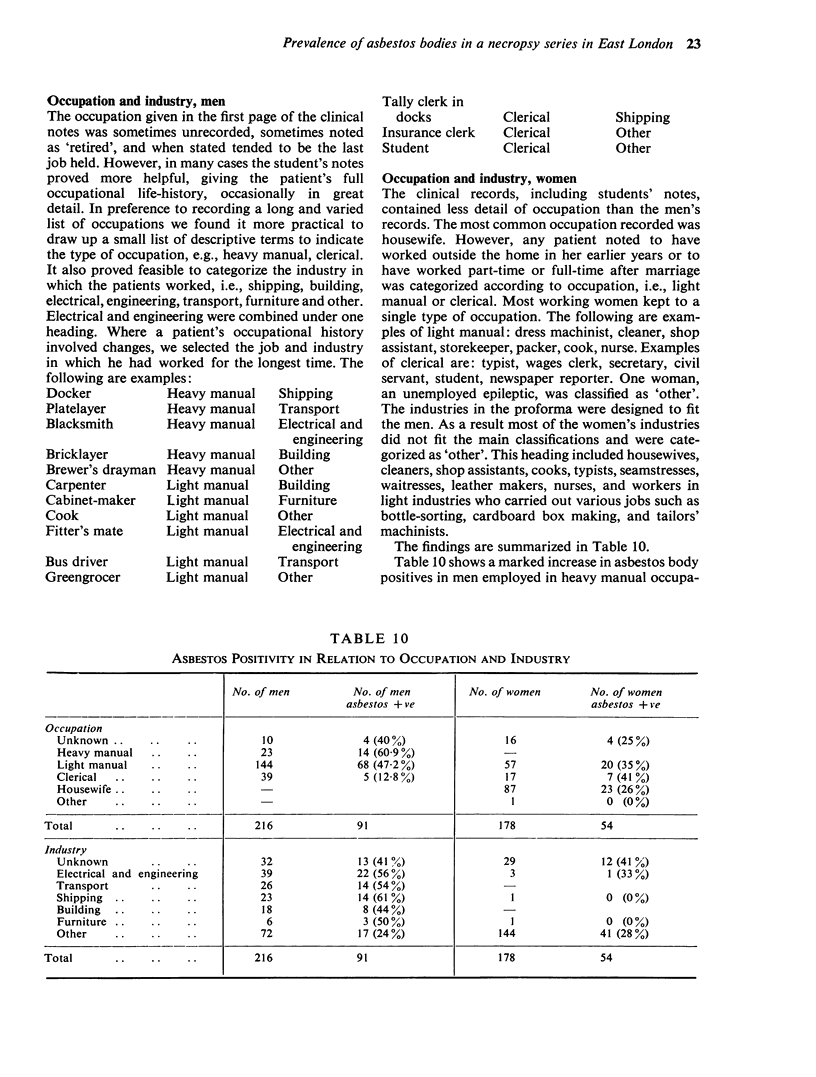
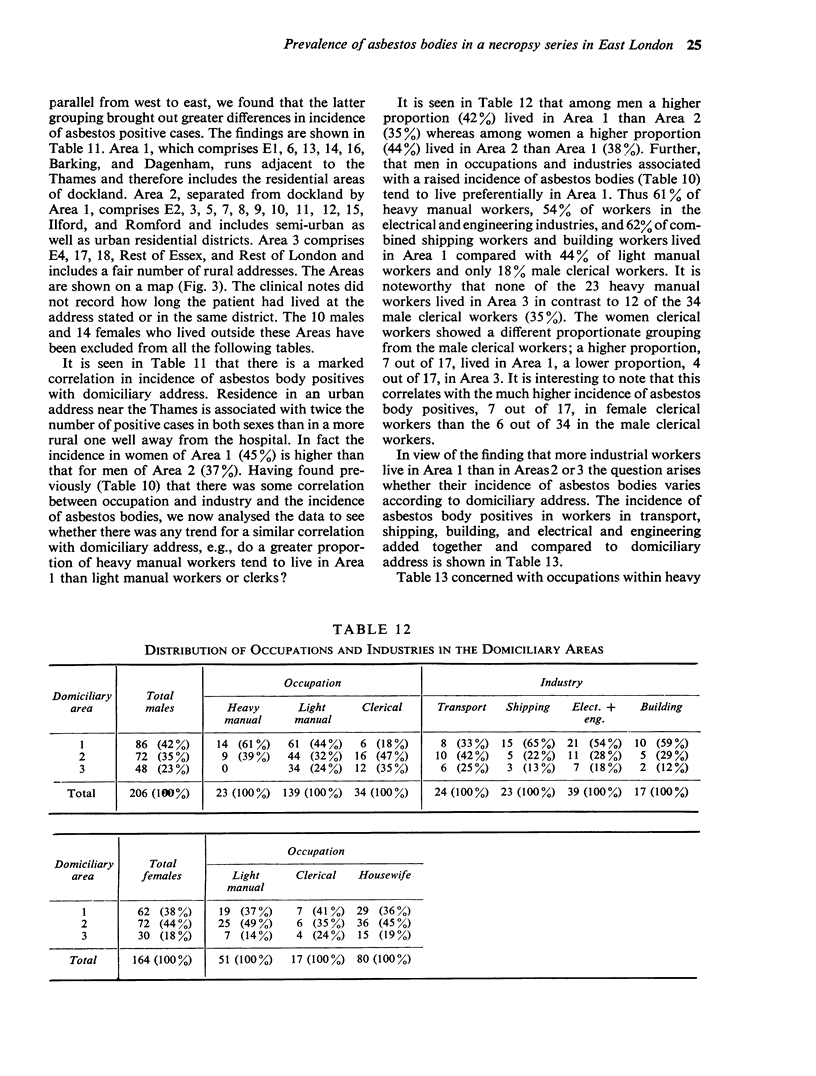
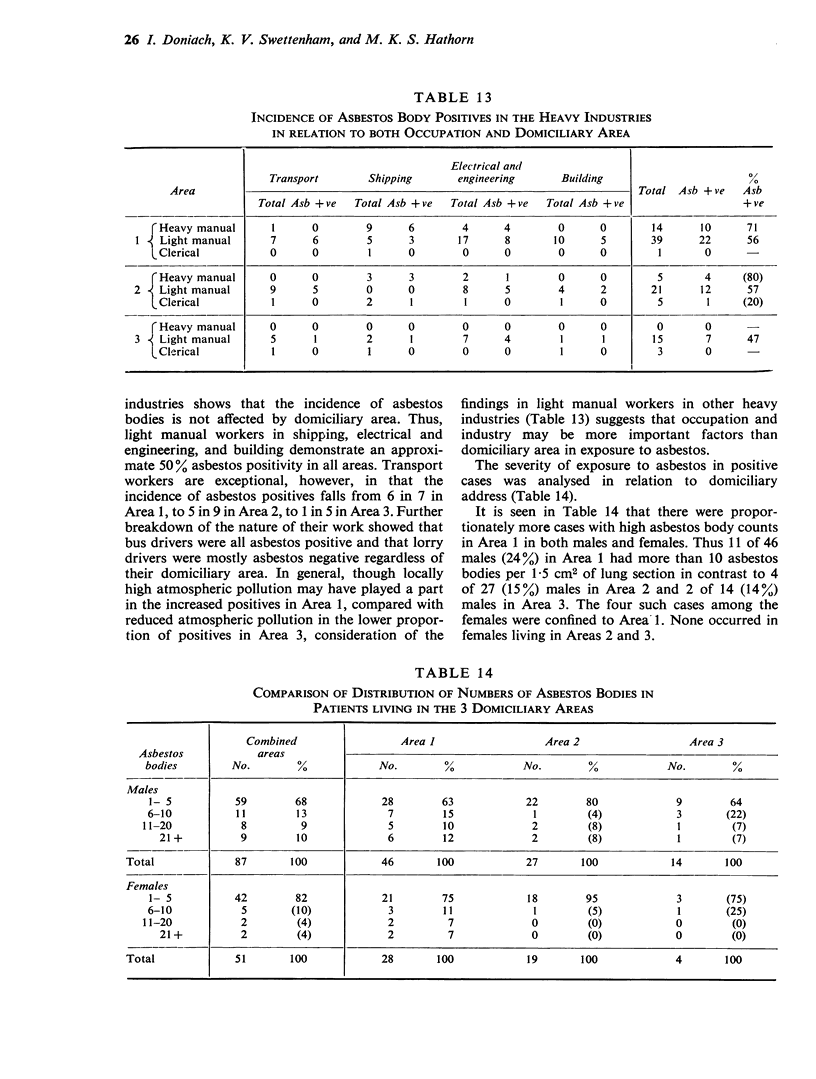
Abstract
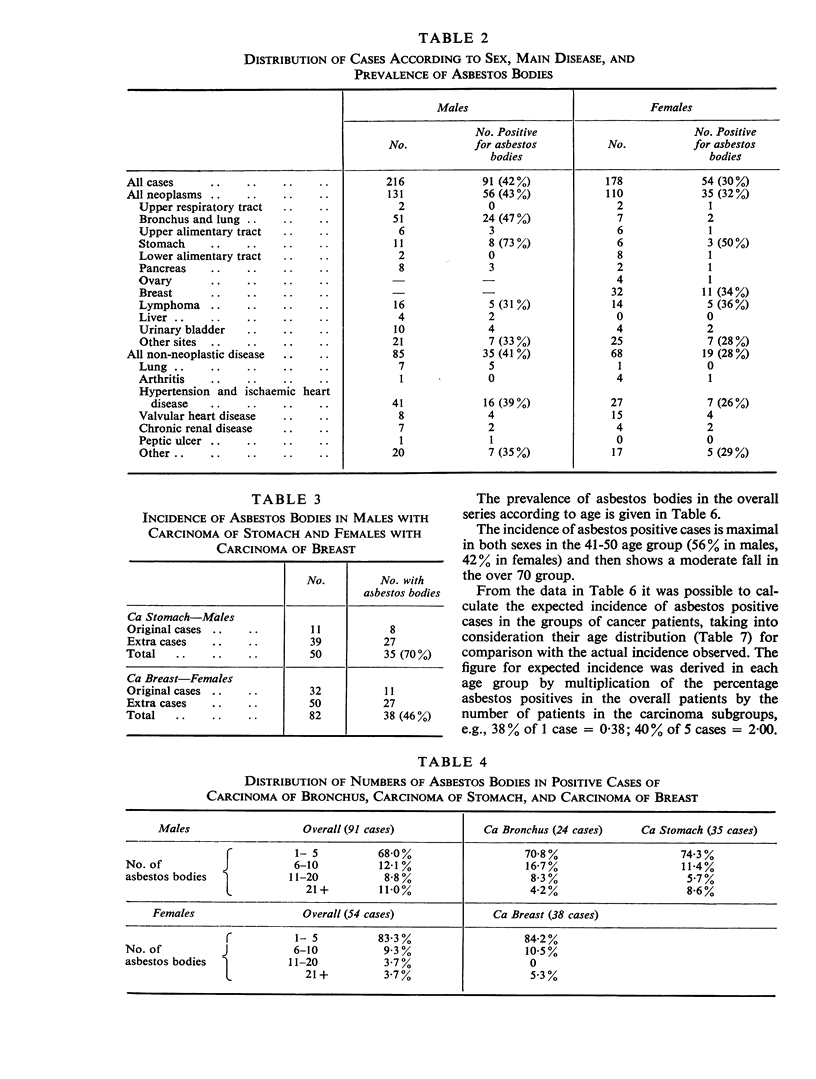
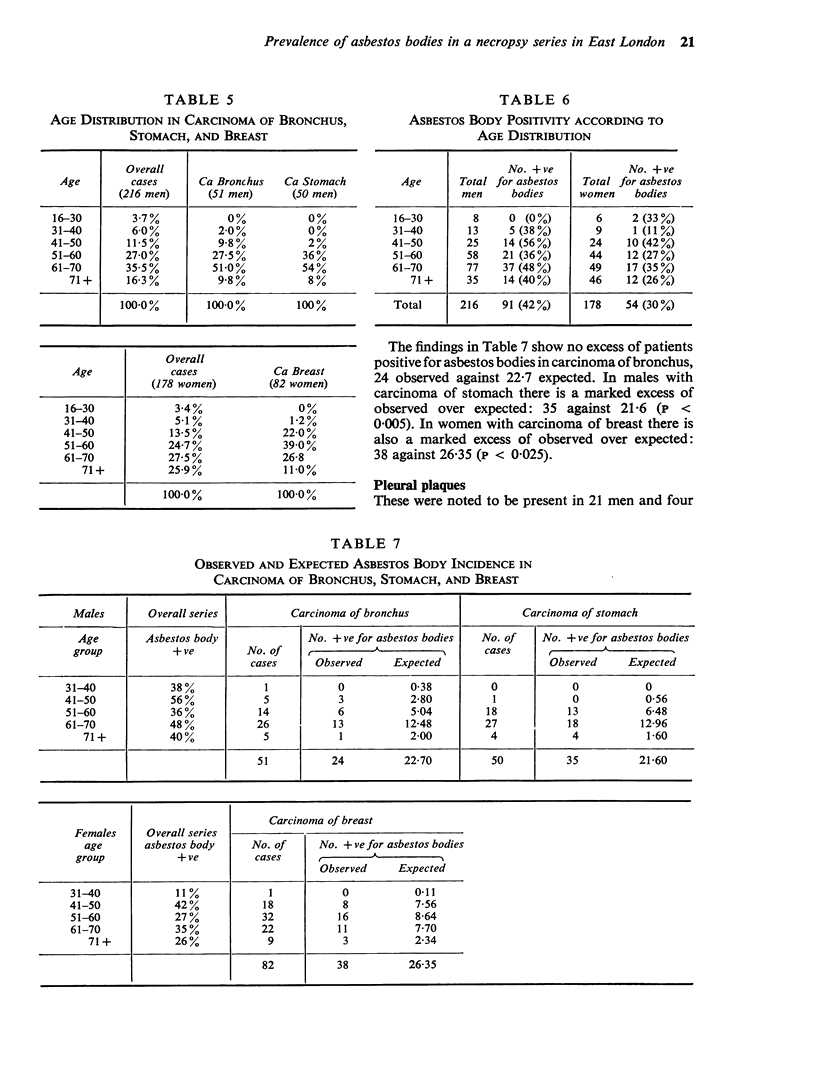
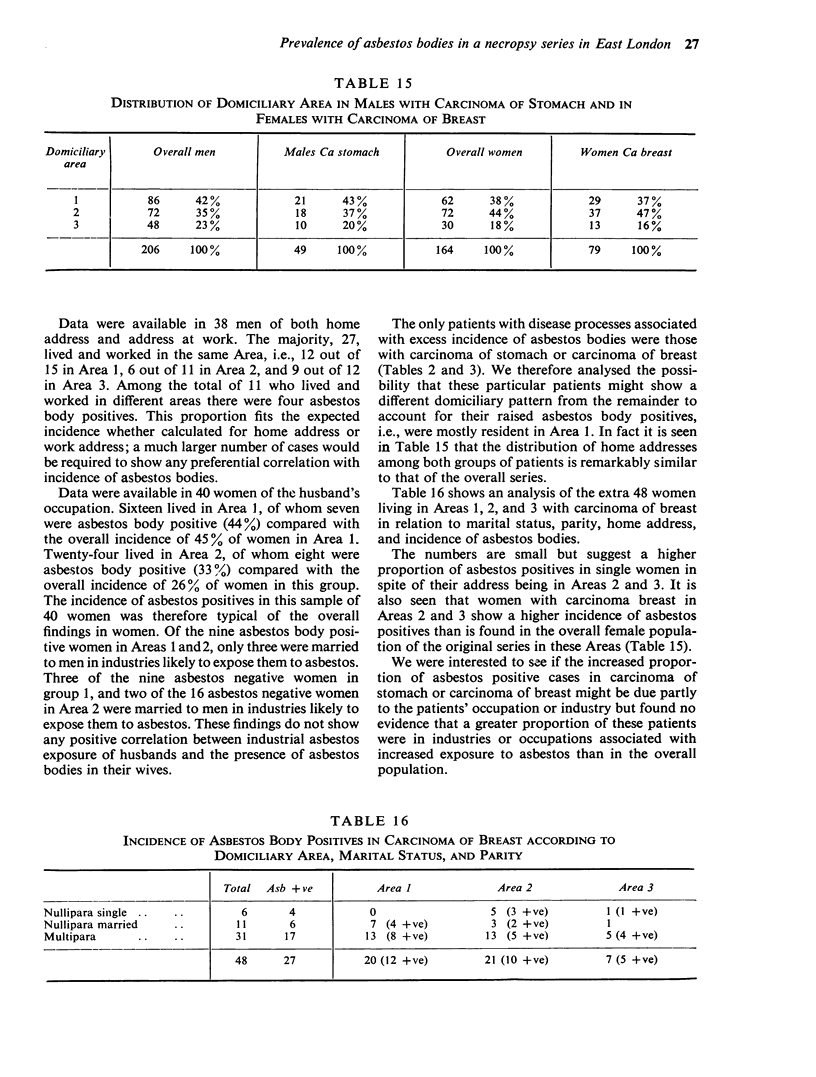
The prevalence of asbestos bodies was measured in lung sections in a necropsy series carried out at the London Hospital (1965-66) after exclusion of all known asbestos factory workers and cases of asbestosis and of mesothelioma. Associations were sought between the presence and number of asbestos bodies with the patients' sex, domiciliary address, occupation, industry, and diseases recorded at necropsy. Asbestos bodies were present in 42% of the 216 men in the series and in 30% of the 178 women. The number of bodies in the positive cases was small in comparison with the numbers seen typically in asbestosis; thus there were less than 6 asbestos bodies per 6-75 mm-3 lung tissue in 107 of the total 145 positive cases in contrast to 1 000 or more in asbestosis. In comparison with the overall series, an increased number of asbestos body positives was present in males with carcinoma of stomach and females with carcinoma of breast. In view of this finding lung sections were counted in further post-mortem examples of these carcinomas making a total of 50 males with carcinoma stomach and 82 females with carcinoma breast. Thirty-five positive cases were found in the carcinoma stomach group as against 22-7 expected and 38 in the carcinoma breast group against 26-35 expected. There was no excess of observed over expected asbestos body positives in 51 males with carcinoma of bronchus. There was an excess of asbestos body positives (60-9%) in heavy manual workers and in both heavy and light manual male workers in the shipping (61%), electrical and engineering (56%), and transport (54%) industries. The incidence in male clerical workers was 12-8%. The incidence of asbestos body positives according to home address was highest (53% in males, 45% in females) in patients living in the industrial and cockland area due east of the hospital. The incidence fell in the less industrial areas north-east of the hospital. Consideration of possible environmental sources of the inhaled asbestos suggests that in this survey occupation, industry, and comiciliary area all play a part. The comparatively minor intensity of asbestos pollution in our positive cases showed a positive association with carcinoma of stomach and breast, possibly playing a direct pathogenic role in carcinoma of stomach. No positive association was identified with any other neoplastic disease including carcinoma of bronchus.
Full text
PDF

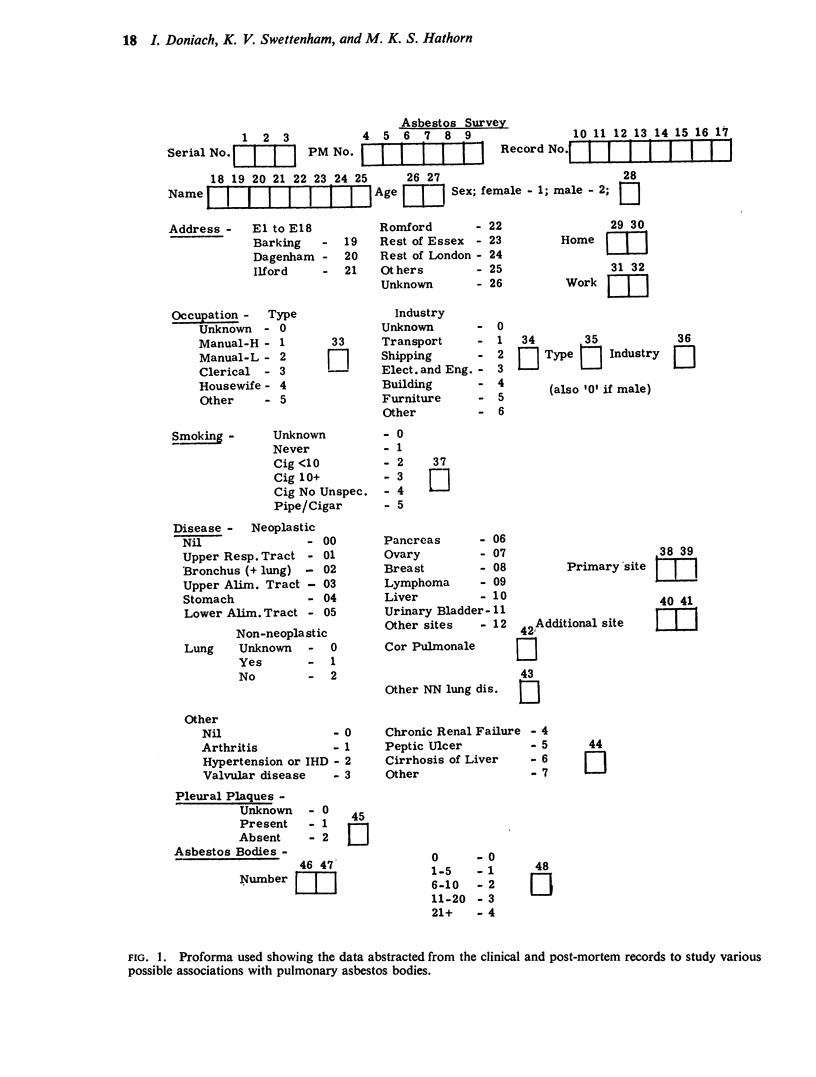





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft T. Asbestos bodies in routine necropsies on Tyneside: a pathological and social study. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 9;1(5592):614–618. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5592.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMES P. C., MCCAUGHEY W. T., WADE O. L. DIFFUSE MESOTHELIOMA OF THE PLEURA AND ASBESTOS. Br Med J. 1965 Feb 6;1(5431):350–353. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5431.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmes P. C., Simpson M. J. Insulation workers in Belfast. 3. Mortality 1940-66. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jul;28(3):226–236. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.3.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enterline P., de Coufle P., Henderson V. Respiratory cancer in relation to occupational exposures among retired asbestos workers. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Apr;30(2):162–166. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. F., Holmes S., Doll R., Hill I. D. Mortality from lung cancer and other causes among workers in an asbestos textile factory. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Oct;25(4):293–303. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merliss R. R. Talc-treated rice and Japanese stomach cancer. Science. 1971 Sep 17;173(4002):1141–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4002.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse M. L. A study of the mortality of workers in an asbestos factory. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Oct;26(4):294–301. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse M. L., Thompson H. Mesothelioma of pleura and peritoneum following exposure to asbestos in the London area. Br J Ind Med. 1965 Oct;22(4):261–269. doi: 10.1136/oem.22.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. H. Asbestos bodies in lungs at necropsy. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jul;20(4):570–573. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIKOFF I. J., CHURG J., HAMMOND E. C. ASBESTOS EXPOSURE AND NEOPLASIA. JAMA. 1964 Apr 6;188:22–26. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060270028006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. G., KASCHULA R. O., MACDONALD R. R. Asbestos as a modern urban hazard. S Afr Med J. 1963 Jan 19;37:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson J. G., Graves W. M., Jr Asbestos as an urban air contaminant. Arch Pathol. 1966 May;81(5):458–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]