Abstract
Poly(2-vinylpyridine 1-oxide) inhibits the cytotoxic effects of quartz in cell cultures but the syndiotactic polymer behaves differently from the isotactic and atactic polymers. In each case approximately 1-0 mg/m2 of the polymer represents the adsorption maximum. No difference has been found between the adsorption isotherms of the stereoisomeric polymers or the stability of the adsorbed layers. The layers are not removed by repeated washing. The observations do not support the theory that the poly(2-vinylpyridine 1-oxide) is active because it coats the quartz surface.
Full text
PDF
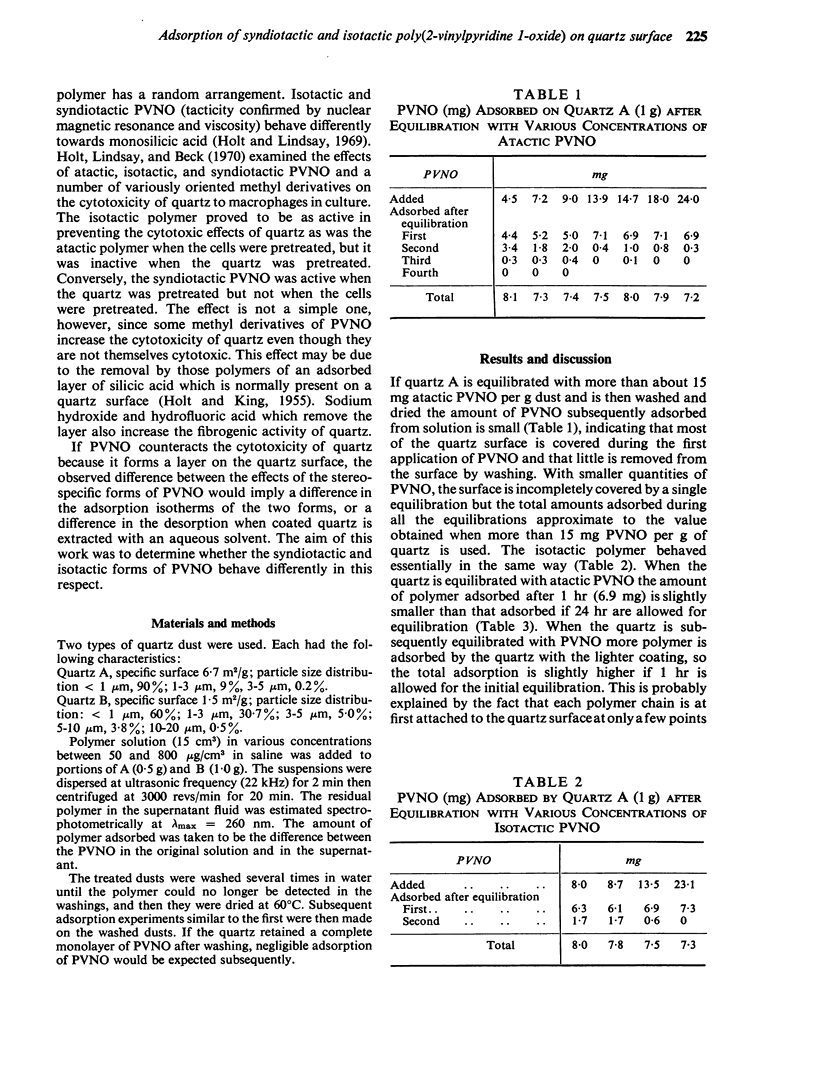
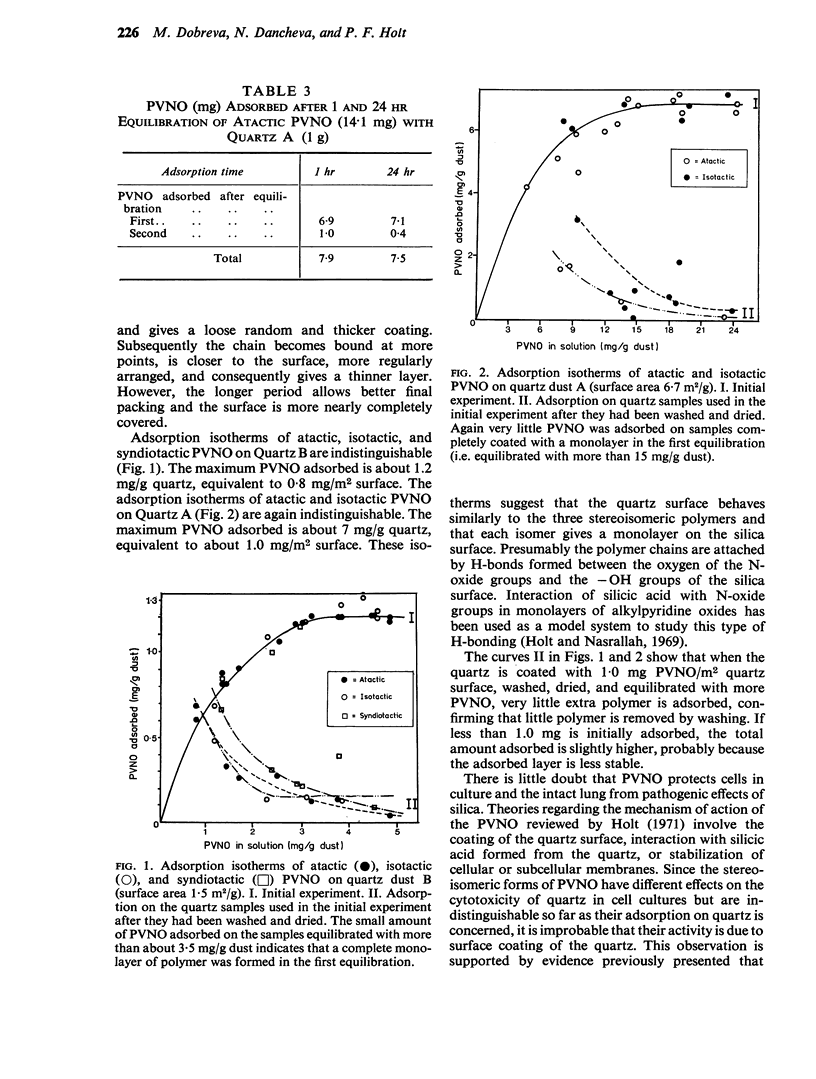

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK E. G., BRUCH J., BROCKHAUS A. [Alteration of the cytotoxic effect of quartz on mouse fibroblasts (strain L) by polyvinylpyridine-N-oxide]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;59:568–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. F., Lindsay H., Beck E. G. Some derivatives of polyvinylpyridine 1-oxides and their effect on the cytotoxicity of quartz in macrophage cultures. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;38(1):192–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. F. Poly(vinylpyridine oxides) in pneumoconiosis research. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jan;28(1):72–77. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLIPKOETER H. W., BROCKHAUS A. [Inhibition of experimental silicosis by subcutaneous administration of polyvinylpyridine-N-oxide]. Klin Wochenschr. 1961 Nov 15;39:1182–1189. doi: 10.1007/BF01532453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


