Abstract
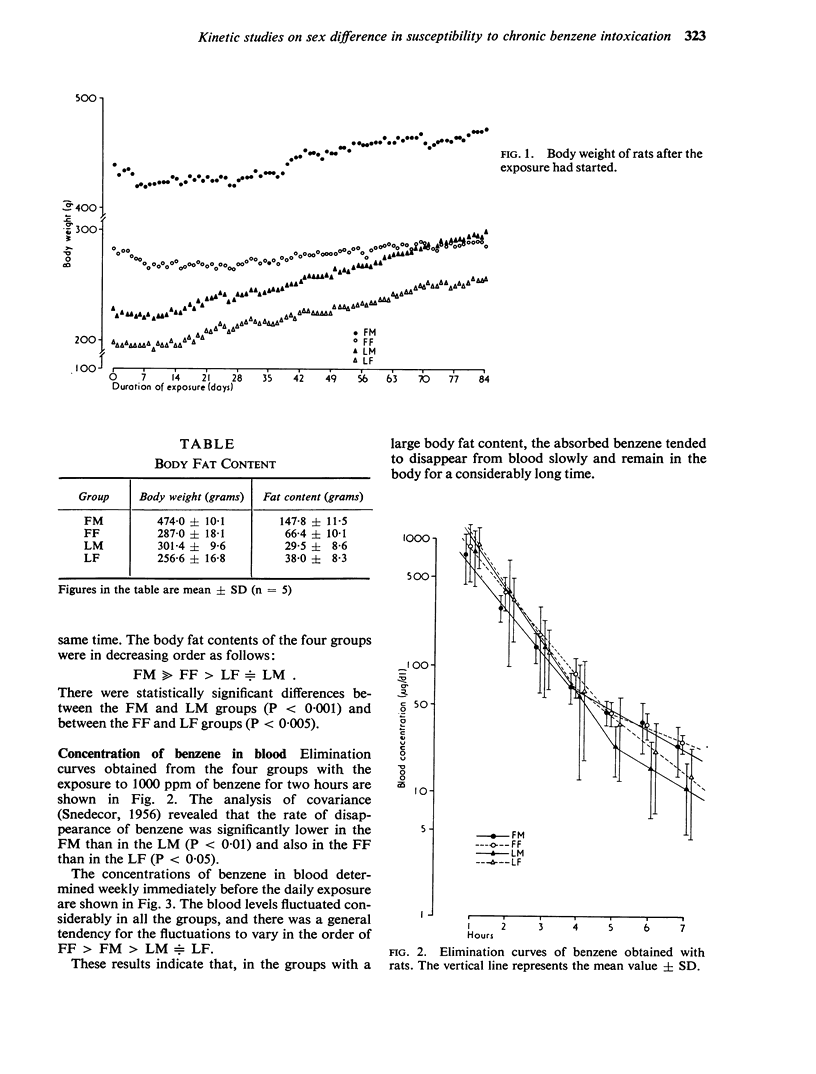
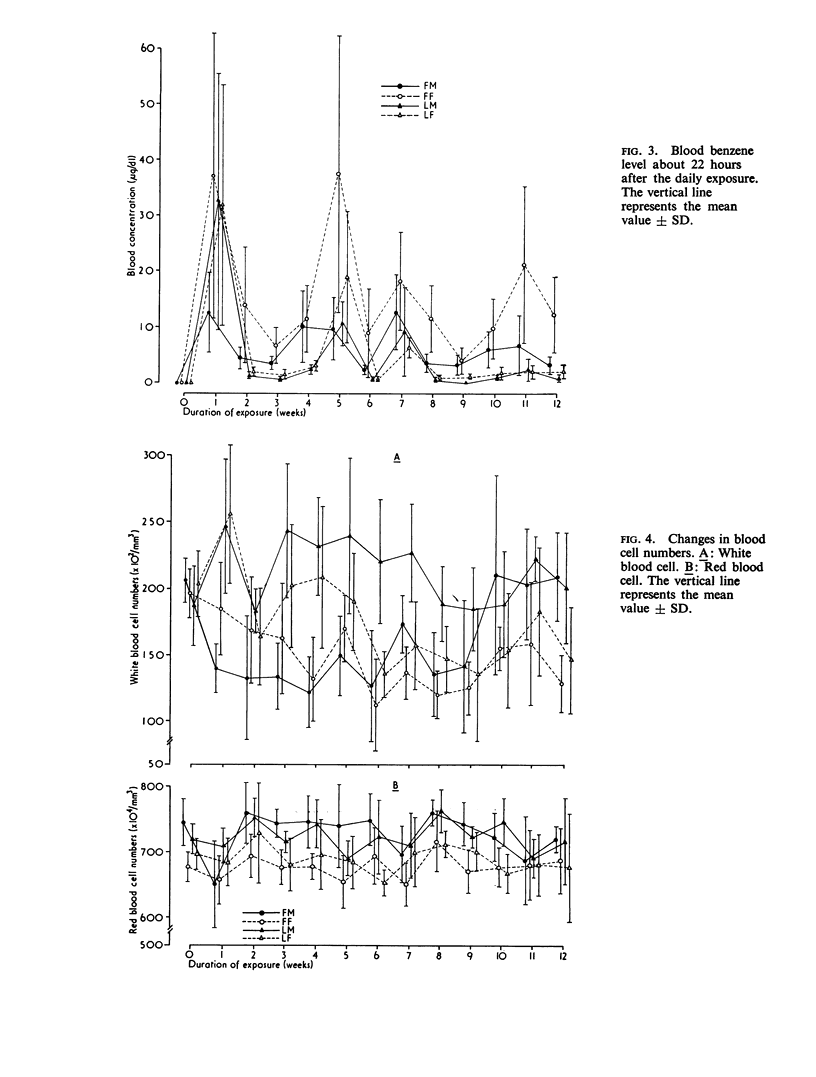
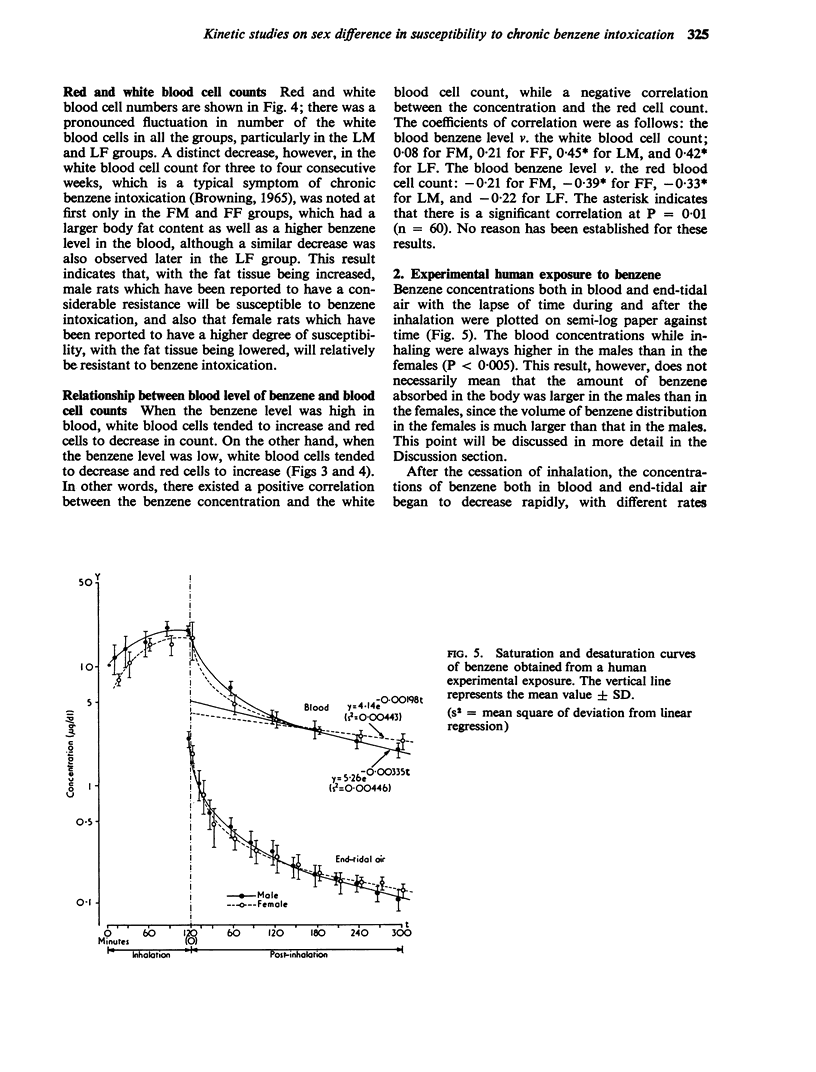
The sex difference in the susceptibility to haematopoietic disorders induced by benzene was studied kinetically with a special reference to its relation with the body fat content. In rats of both sexes with a large body fat content, benzene was eliminated more slowly and remained in the body for a longer time than in rats with a small body fat content. In accord with this finding, the decrease in white blood cell numbers during a chronic benzene exposure was observed only in the groups of rats which had a large volume of fat tissue. In an experimental human exposure, the elimination of benzene was slower in the females than in the males. The kinetic study revealed that the slower elimination in the females is due primarily to the bulky distribution of body fat tissue in that sex. From these results obtained from the experimental exposure of men and rats to benzene, it was concluded that the human female, with her massive body fat tissue, shows an inherent disposition to be susceptible to a chemical such as benzene which has a high affinity with fat tissue.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOTH J., GILLETTE J. R. The effect of anabolic steroids on drug metabolism by microsomal enzymes in rat liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Sep;137:374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON R. L., SHULTICE R. W., FOUTS J. R. Factors affecting drug metabolism by liver microsomes. IV. Starvation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Feb;103:333–335. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIROKAWA T. Studies on the poisoning by benzol and its homologues. IV. Experimental studies on the sexual differences of blood picture. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1955 Jun;8(3):275–281. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.8.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKEDA M. ENZYMATIC STUDIES ON BENZENE INTOXICATION. J Biochem. 1964 Mar;55:231–243. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYS A., BROZEK J. Body fat in adult man. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):245–325. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R. Sex-related differences in drug metabolism. Drug Metab Rev. 1974;3(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/03602537408993737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Takanaka A., Takayanagi M. Studies on the mechanism of sex difference in drug-oxidizing activity of liver microsomes. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1968 Dec;18(4):482–489. doi: 10.1254/jjp.18.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Gibaldi M. Pharmacokinetics of drug action. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:85–98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. E., McLean E. K. The effect of diet and 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(p-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) on microsomal hydroxylating enzymes and on sensitivity of rats to carbon tetrachloride poisoning. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):564–571. doi: 10.1042/bj1000564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J. S., BUKOVSKY J. Studies on an N-demethylating system in rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Mar;131:275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T., Fujiwara Y. Determination of benzene and toluene in blood by means of a syringe-equilibration method using a small amount of blood. Br J Ind Med. 1975 Aug;32(3):210–214. doi: 10.1136/oem.32.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T., Fujiwara Y., Hirosawa K. Pharmacokinetics of benzene and toluene. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1974;33(3):169–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00538916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seawright A. A., McLean A. E. The effect of diet on carbon tetrachloride metabolism. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1055–1060. doi: 10.1042/bj1051055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


