Abstract
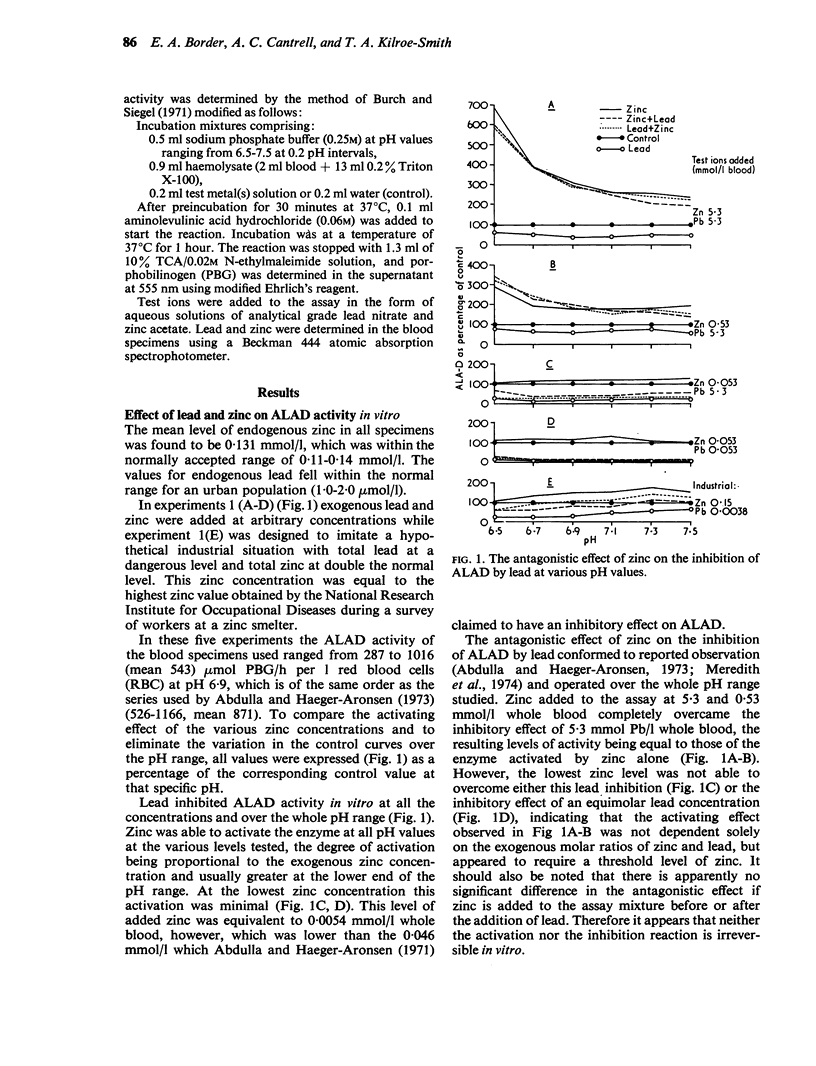
The antagonistic effect of zinc on inhibibition of human aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) by lead was examined in vitro. The phenomenon was studied at pH 6.5-7.5 . Zinc and lead were added at concentrations ranging from physiological levels to levels far in excess of those expected in heavy industrial exposure. ALAD activity of normal blood assayed in the presence of zinc was unaffected by exogenous lead if the added zinc concentration was above 0.53 mmol/l blood, or double the normal endogenous level, and was of the order found in heavy industrial exposure to zinc. In this case, ALAD assay values were appreciably raised and might have fallen into the normal range in spite of a dangerous total blood lead of over 0.0048 mmol/l. When zinc was added in vitro to blood from a worker with a blood lead level of 0.0043 mmol/l the ALAD values obtained were also raised and did not reflect the dangerous level of lead in the patient.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdulla M., Haeger-Aronsen B. ALA-dehydratase activation by zinc. Enzyme. 1971;12(6):708–710. doi: 10.1159/000459608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Siegel A. L. Improved method for measurement of delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity of human erythrocytes. Clin Chem. 1971 Oct;17(10):1038–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


