Abstract
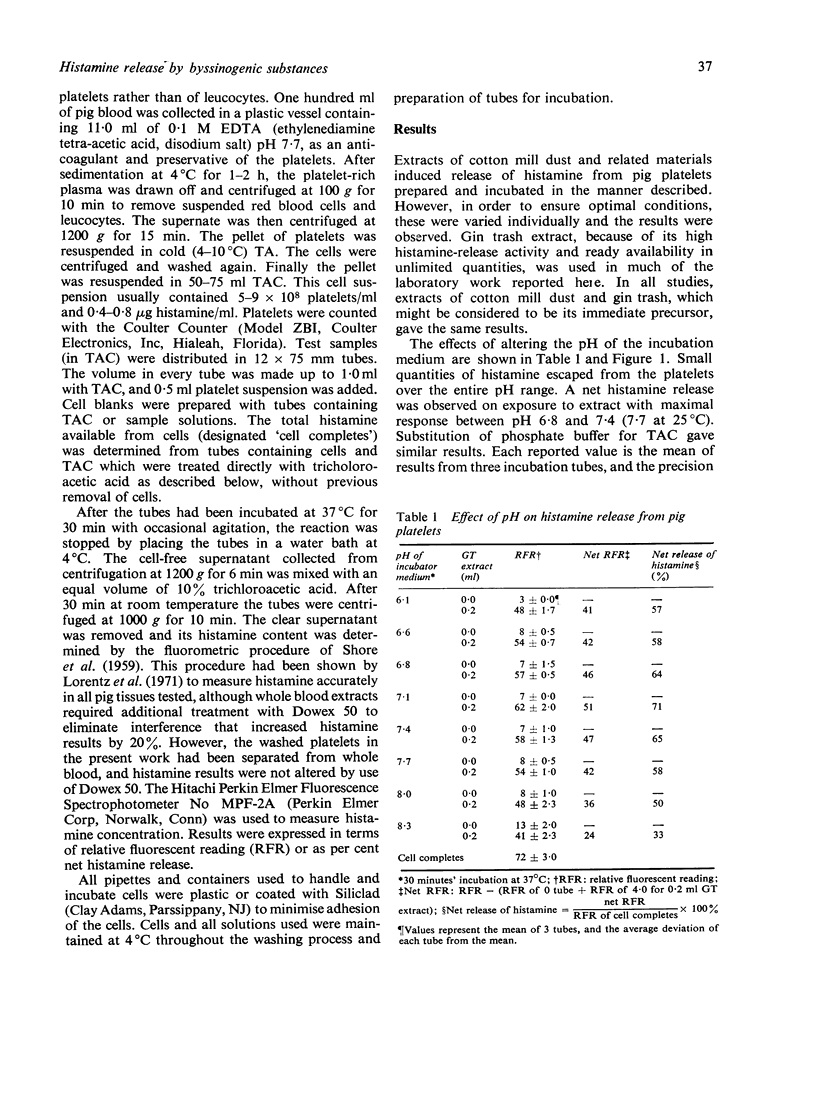
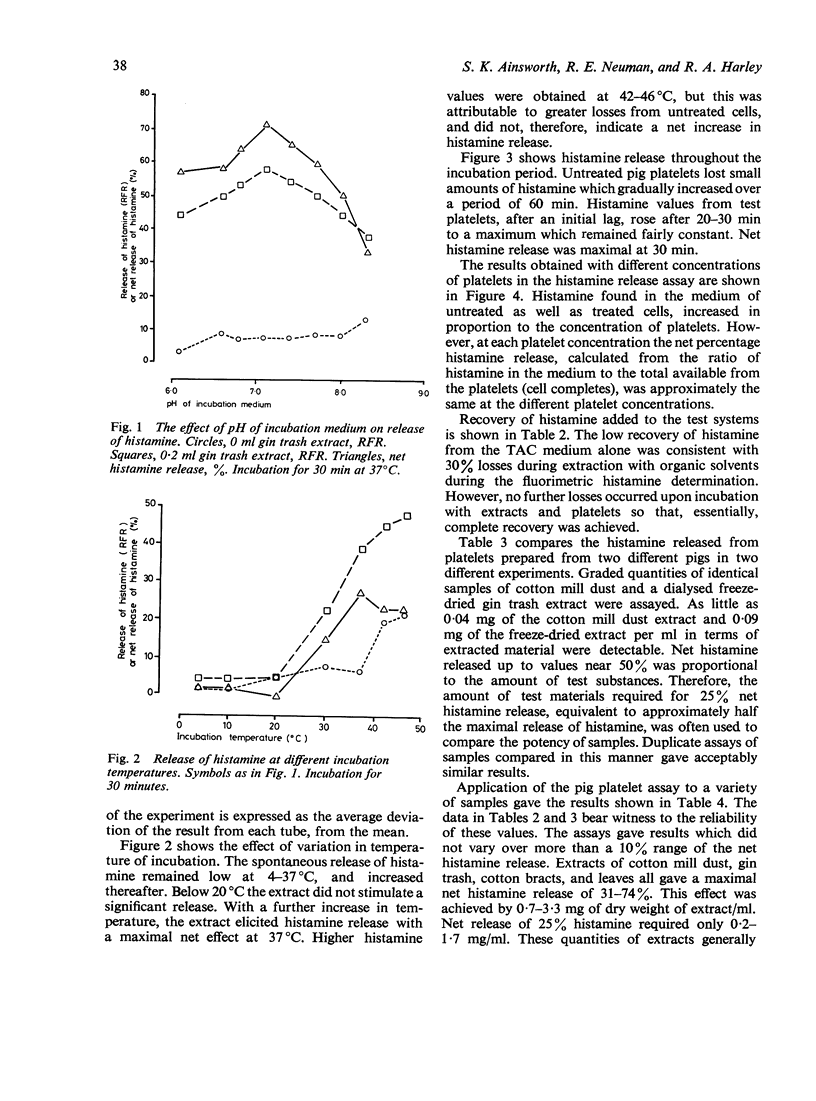
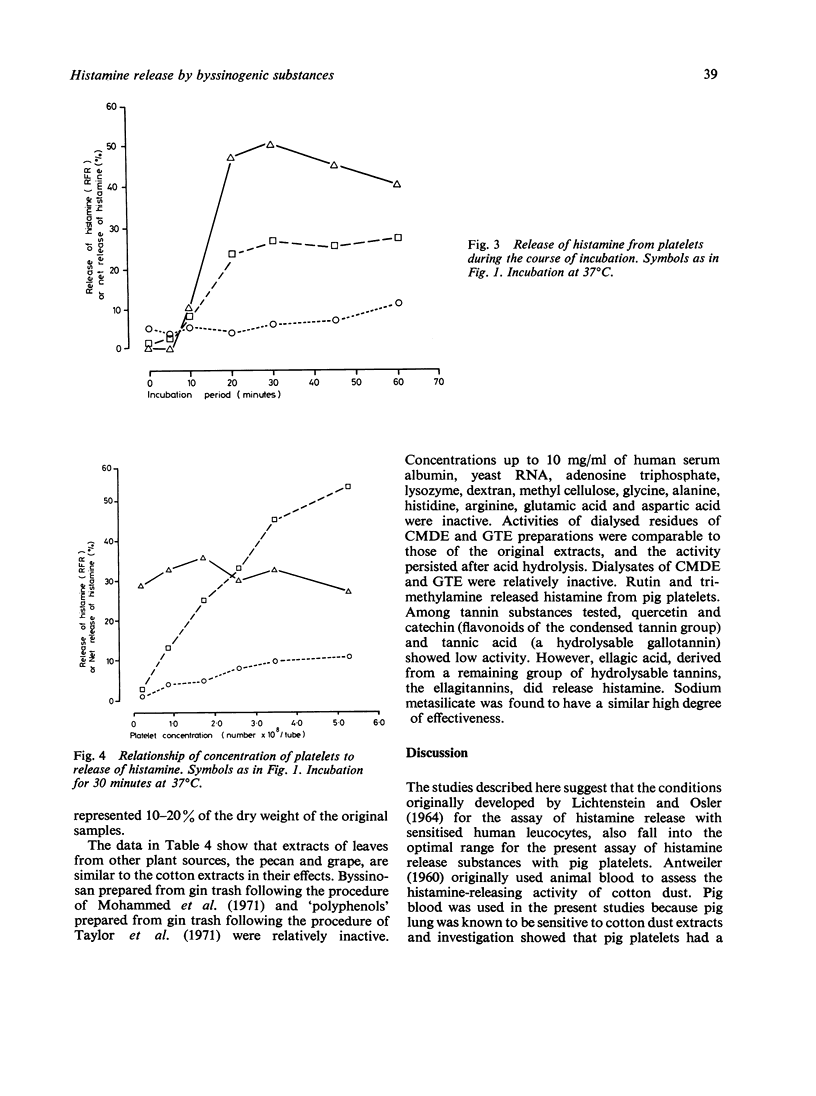
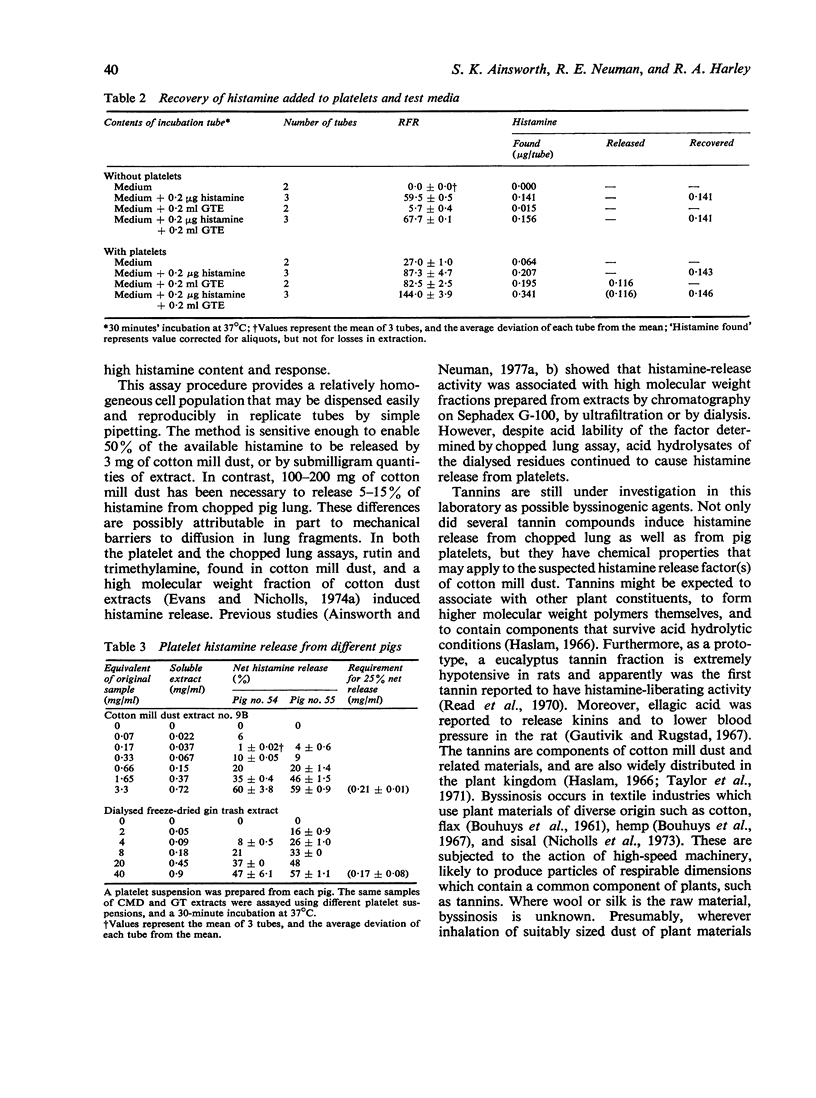
Previous reports suggest that byssinosis, an asthma-like condition among textile workers, may be mediated in part by histamine liberated following inhalation of dust. A simple, sensitive, and reliable procedure using pig platelets which contain the unusually high concentration of 0.8-1.6 microgram histamine/10(9) cells has been devised for the assay of histamine-releasing factors in cotton mill dust and related materials, and has yielded results generally in accordance with earlier assays using chopped lung tissue. As little as 50--100 microgram of total extractable substances from cotton mill dust can be measured. The activity of the extract is associated with the non-dialysable high molecular weight portion. However, conditions of acid hydrolysis do not destroy the activity. Extracts of leaves from different varieties of plant are highly potent, which suggests that the factors responsible for byssinosis are widely distributed plant components, present in textile fibre plants and converted to a respirable form by handling processes. Ellagic acid and sodium metasilicate release histamine from pig platelets, and represent new classes of compounds with possible roles in the aetiology of byssinosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTWEILER H. Observations about a histamine liberating substance in cotton dust. Ann Occup Hyg. 1960 Jul;2:152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOUHUYS A. Prevention of Monday dyspnea in byssinosis: a controlled trial with an antihistamine drug. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1963 May-Jun;4:311–314. doi: 10.1002/cpt196343311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOUHUYS A., van DUYN, van LENNEP H. Byssinosis in flax workers. Arch Environ Health. 1961 Nov;3:499–509. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1961.10663061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergentz S. E., Ljungqvist U., Lewis D. H. The distribution of platelets, fibrin, and erythrocytes in various organs following thrombin infusion: an experimental study in dogs with and without antifibrinolytic therapy. Surgery. 1972 Feb;71(2):190–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomski H., Otawski J., Bomska H. Hämatologische und serologische Untersuchungen bei Byssinose-gefährdeten Arbeitern. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1971;27(4):309–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhuys A., Barbero A., Lindell S. E., Roach S. A., Schilling R. S. Byssinosis in hemp workers. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Apr;14(4):533–544. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen J., Srivastava K. C. The synthesis of prostaglandins in human platelets. Lipids. 1972 Apr;7(4):246–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02533221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Nicholls P. J. Studies of the mechanism of histamine release from lung tissue in vitro by cotton dust extracts. Agents Actions. 1974 Dec;4(5):304–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01964931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautvik K. M., Rugstad H. E. Kinin formation and kininogen depletion in rats after intravenous injection of ellagic acid. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Nov;31(3):390–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb00406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. D., Halprin C. M., Kilburn K. H., Merchant J. A., Ujda J. R. Differential aerosol challenge studies in byssinosis. Arch Environ Health. 1973 Mar;26(3):120–124. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1973.10666238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. R., Merchant J. A., Kilburn K. H., Hamilton J. D. Byssinosis and respiratory diseases of cotton mill workers. J Occup Med. 1972 Mar;14(3):199–206. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197203000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungqvist U., Bergentz S. E., Lewis D. H. The distribution of platelets, fibrin and erythrocytes in various organs following experimental trauma. Eur Surg Res. 1971;3(5):293–300. doi: 10.1159/000127568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCULLAGH EP Trends in medicine ancient and modern. GP. 1959 Nov;30:145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. Mast cells and anaphylaxis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 26;103:264–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed Y. S., el-Gazzar R. M., Adamyova K. Byssinosan, an aminopolysaccharide isolated from cotton dust. Carbohydr Res. 1971 Dec;20(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls P. J., Evans E., Valić F., Zuskin E. Histamine-releasing activity and bronchoconstricting effects of sisal. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Apr;30(2):142–145. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. W., Naguwa G. S., Wigington J. J., Lenney J. F. A histamine liberator in the tannin fraction of the Eucalypts. Lloydia. 1970 Dec;33(4):461–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Religa Z., Maśliński C. Histamine metabolism in experimental silicosis. I. Experiments on the isolated rat lung and on guinea pig lung homogenates and sections. Life Sci II. 1970 Jun 22;9(12):689–700. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Nordstrand A. Pulmonary cell reactions after exposure to cotton dust extract. Br J Ind Med. 1974 Jul;31(3):220–223. doi: 10.1136/oem.31.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel G., Engels H. W., Meyer-Burgdorff C. Serotonin and histamine in platelets in the course of operation with extracorporeal circulation. Agents Actions. 1973 Oct;3(3):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01965727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Massoud A. A., Lucas F. Studies on the aetiology of byssinosis. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Apr;28(2):143–151. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. F., Eidson G., Hatcher J. D. Influence of cotton dust inhalation on free lung cells in rats and guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


