Abstract
Metabolic studies were performed on men exposed to nitrobenzene vapour under experimental conditions. Absorption was estimated by the analysis of urine for p-nitrophenol. About half as much vapour was absorbed through the skin as through the lungs.
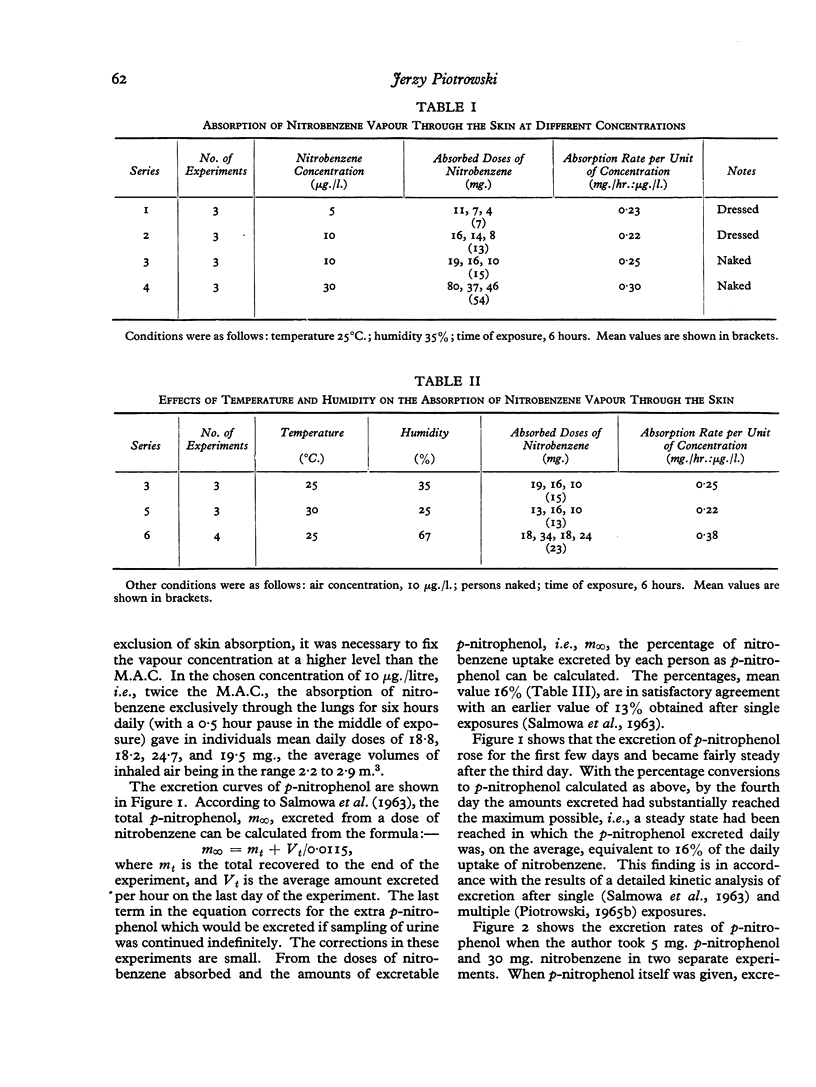
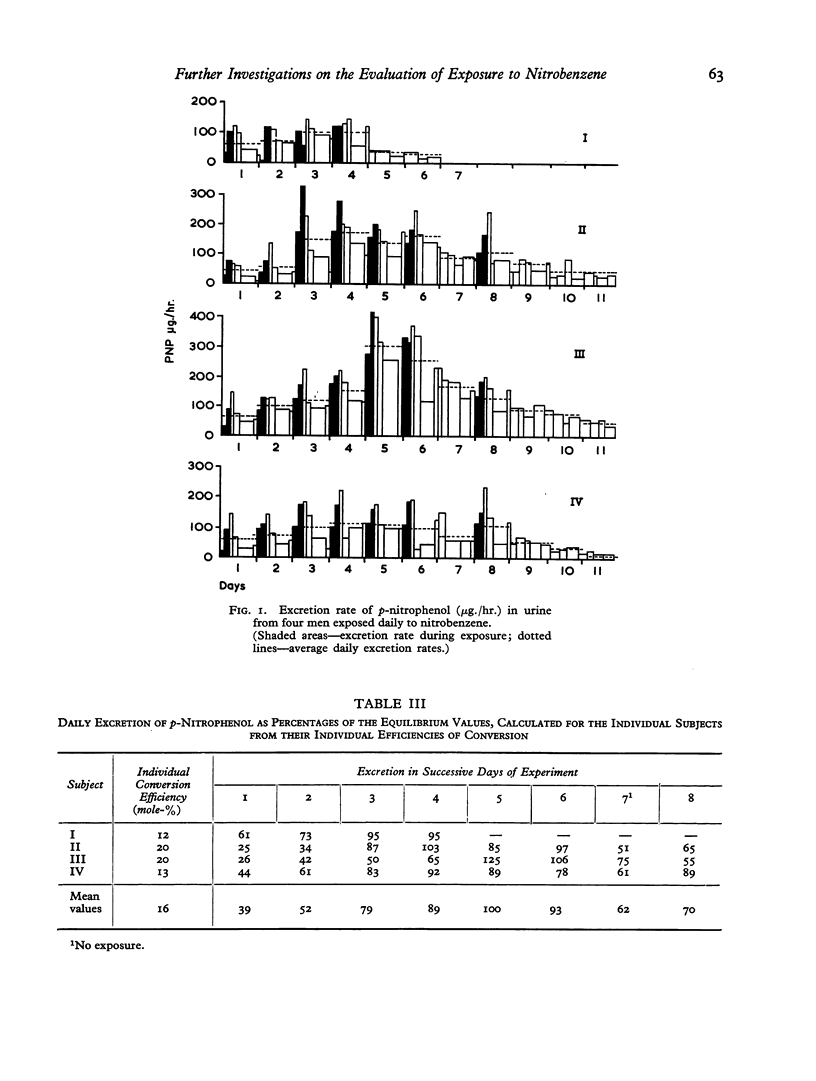
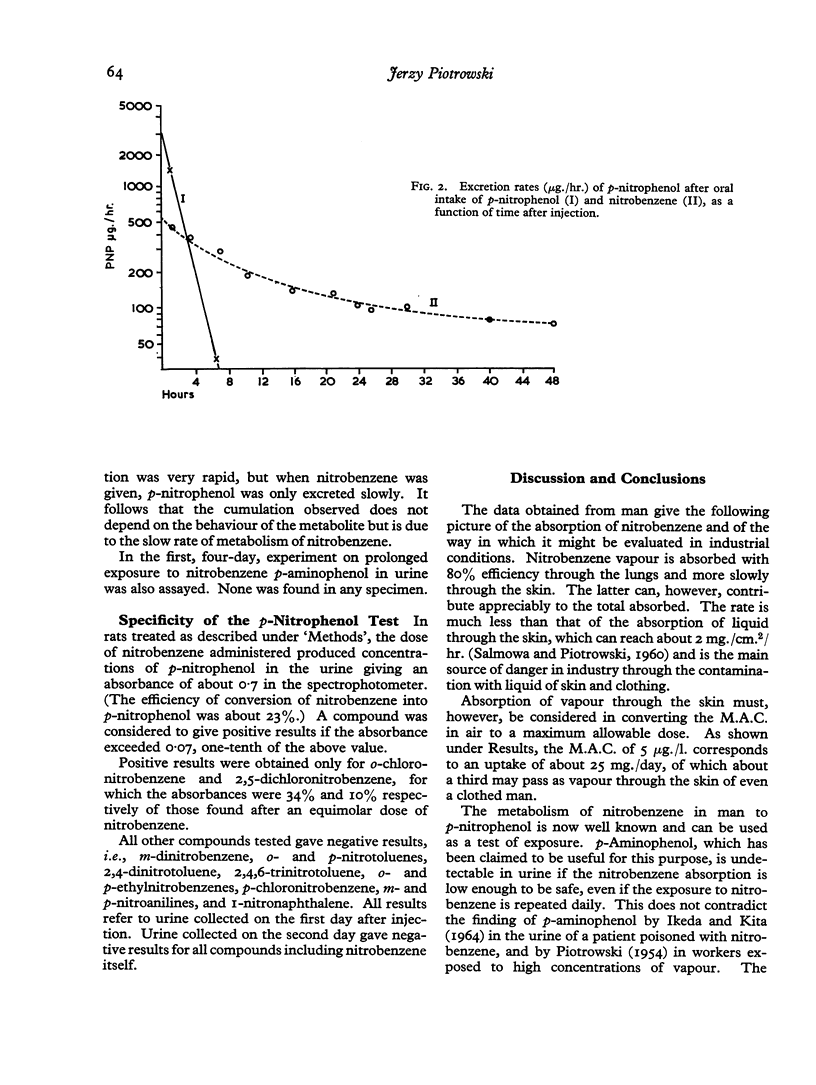
In inhalation studies the accumulation of nitrobenzene in the course of repeated exposures was investigated. It was found that p-nitrophenol was excreted in the urine in increasing amounts on successive days of exposure, reaching, by the end of a week, levels approximately two and a half times as high as on the first day.
The specificity of the p-nitrophenol test on urine was studied using rats. Of all nitro-compounds investigated only chloronitrobenzenes, especially the ortho-isomer, gave interfering compounds in the urine. o-Chloronitrobenzene gave lower results than nitrobenzene by a factor of 3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- VLACHOVA D. Mikrostanovení parathionu v ovzdusí a v roztocích. Prac Lek. 1956 Aug;8(4):289–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


