Abstract
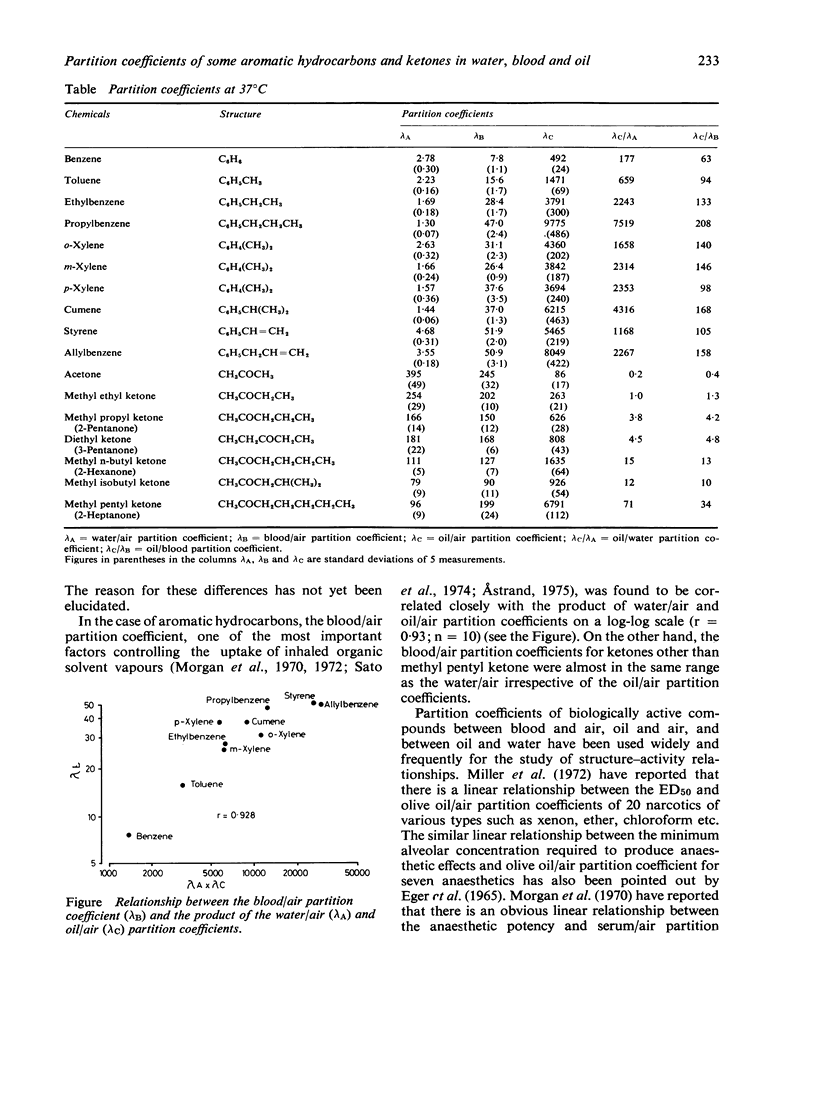
Water/air, blood/air, oil/air, oil/water, and oil/blood partition (or solubility) coefficients of 17 aromatic hydrocarbons and ketones were measured by a newly developed vial-equilibration method, which needs no direct measurements of the concentration either in the liquid or in the air phase, but only the gas chromatographic peak heights of the air in the sample (in which a test material is contained) and reference vessels (containing no test material). It was found that the blood/air partition coefficients for aromatic hydrocarbons are correlated closely with the product of water/air and oil/air partitiion coefficients, whereas those for ketones are almost in the same range as the water/air, irrespective of the oil/air partition coefficients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrand I. Uptake of solvents in the blood and tissues of man. A review. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1975 Dec;1(4):199–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eger E. I., 2nd, Brandstater B., Saidman L. J., Regan M. J., Severinghaus J. W., Munson E. S. Equipotent alveolar concentrations of methoxyflurane, halothane, diethyl ether, fluroxene, cyclopropane, xenon and nitrous oxide in the dog. Anesthesiology. 1965 Nov-Dec;26(6):771–777. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196511000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W., Paton W. D., Smith E. B., Smith R. A. Physicochemical approaches to the mode of action of general anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1972 Apr;36(4):339–351. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197204000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Black A., Belcher D. R. Studies on the absorption of halogenated hydrocarbons and their excretion in breath using 38 Cl tracer techniques. Ann Occup Hyg. 1972 Nov;15(2):273–283. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/15.2-4.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Black A., Belcher D. R. The excretion in breath of some aliphatic halogenated hydrocarbons following administration by inhalation. Ann Occup Hyg. 1970 Dec;13(4):219–233. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/13.4.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T., Fujiwara Y. Determination of benzene and toluene in blood by means of a syringe-equilibration method using a small amount of blood. Br J Ind Med. 1975 Aug;32(3):210–214. doi: 10.1136/oem.32.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T., Fujiwara Y., Hirosawa K. Pharmacokinetics of benzene and toluene. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1974;33(3):169–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00538916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood R. J. Ostwald solubility coefficients of some industrially important substances. Br J Ind Med. 1976 May;33(2):106–107. doi: 10.1136/oem.33.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rees H. The partition coefficients of styrene between blood and air and between oil and blood. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1974 Mar 12;33(1):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00538978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



