Abstract
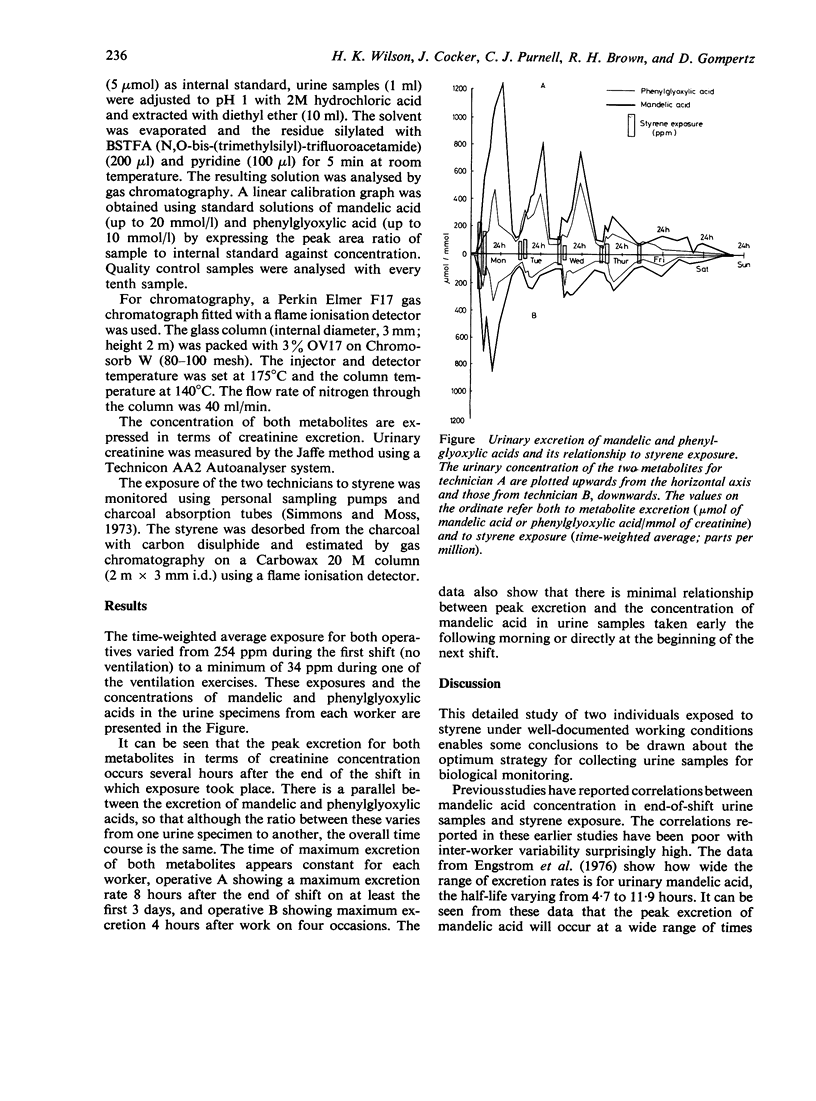
Urinary excretion of mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids by two technicians building glass-reinforced plastic boats has been measured over a 7-day period. Peak excretion of both metabolites occurred several hours after the end of exposure. There was little relationship between urinary mandelic acid concentrations measured at the end of shift and the maximum excretion observed in samples collected after this time. It is suggested that sampling strategies devised to monitor workers exposed to styrene should reflect maximum excretion rates of urinary mandelic acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A rapid colorimetric method for the determination of phenylglyoxylic and mandelic acids. Its application to the urinalysis of workers exposed to styrene vapour. Br J Ind Med. 1970 Apr;27(2):150–154. doi: 10.1136/oem.27.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardodej Z., Bardodejova E. Biotransformation of ethyl benzene, styrene, and alpha-methylstyrene in man. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1970 Mar-Apr;31(2):206–209. doi: 10.1080/0002889708506230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström K., Härkönen H., Kalliokoski P., Rantanen J. Urinary mandelic acid concentration after occupational exposure to styrene and its use as a biological exposure test. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1976 Mar;2(1):21–26. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M., Molyneux M., Sharp T., Bailey A., Hollingdale-Smith P. The practical application of the Portion Diffusion Sampler for the measurement of time weighted average exposure to volatile organic substances in air. Ann Occup Hyg. 1977 Dec;20(4):357–363. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/20.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin M., Bauer D. Human exposure to styrene. II. Quantitative and specific gaschromatographic analysis of urinary mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids as an index of styrene exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1976 Apr 28;37(1):57–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00409364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Imamura T., Hayaskh M., Tabuchi T., Hara I. Evaluation of hippuric, phenylglyoxylic and mandelic acids in urine as indices of styrene exposure. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1974;32(1):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00539099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibman K. C. Metabolism and toxicity of styrene. Environ Health Perspect. 1975 Jun;11:115–119. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7511115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibman K. C., Ortiz E. Epoxide intermediates in microsomal oxidation of olefins to glycols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jun;173(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan A. J., Bend J. R. The metabolism of styrene oxide in the isolated perfused rat liver. Identification and quantitation of major metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos. 1977 Jul-Aug;5(4):363–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. H., Moss I. M. Measurement of personal exposure to 1,1,1-trichloroethane and trichloroethylene using an inexpensive sampling device and battery-operated pump. Ann Occup Hyg. 1973 Apr;16(1):47–49. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/16.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slob A. A new method for determination of mandelic acid excretion at low level styrene exposure. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Oct;30(4):390–393. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.4.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roosmalen P. B., Drummond I. Simultaneous determination by gas chromatography of the major metabolites in urine of toluene, xylenes and styrene. Br J Ind Med. 1978 Feb;35(1):56–60. doi: 10.1136/oem.35.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


