Abstract
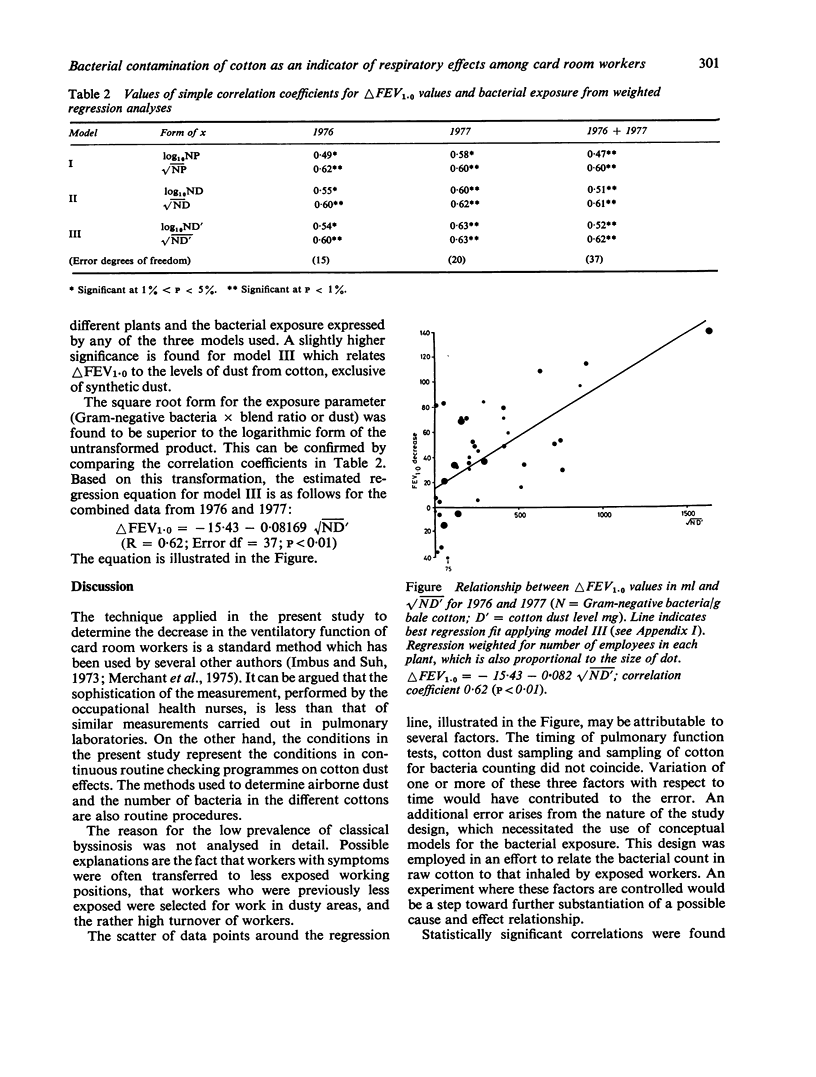
The influence of the bacterial contamination of cotton dust on the development of pulmonary symptoms has been investigated. The pulmonary function of card room workers in 23 US cotton mills was tested before and after the Monday working shift. A significant relation was found between the delta FEV1.0 decrement and the vertical elutriator dust level in the different mills. An improved correlation was obtained when the number of Gram-negative bacteria cultured from the bale cotton used in the different mills was employed in the exposure description. The results support earlier epidemiological and experimental studies, which demonstrate the importance of the Gram-negative bacteria in the development of pulmonary symptoms among workers in cotton mills.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavagna G., Foà V., Vigliani E. C. Effects in man and rabbits of inhalation of cotton dust or extracts and purified endotoxins. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Oct;26(4):314–321. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinkotai F. F., Lockwood M. G., Rylander R. Airborne micro-organisms and prevalence of byssinotic symptoms in cotton mills. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1977 Oct;38(10):554–559. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbus H. R., Suh M. W. Byssinosis: a study of 10,133 textile workers. Arch Environ Health. 1973 Apr;26(4):183–191. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1973.10666253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant J. A., Halprin G. M., Hudson A. R., Kilburn K. H., McKenzie W. N., Hurst D. J., Bermazohn P. Responses to cotton dust. Arch Environ Health. 1975 May;30(5):222–229. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERNIS B., VIGLIANI E. C., CAVAGNA C., FINULLI M. The role of bacterial endotoxins in occupational diseases caused by inhaling vegetable dusts. Br J Ind Med. 1961 Apr;18:120–129. doi: 10.1136/oem.18.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Nordstrand A. Pulmonary cell reactions after exposure to cotton dust extract. Br J Ind Med. 1974 Jul;31(3):220–223. doi: 10.1136/oem.31.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Nordstrand A., Snella M. C. Bacterial contamination of organic dusts: effects on pulmonary cell reactions. Arch Environ Health. 1975 Mar;30(3):137–140. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiter R., Neal P. A., Caminita B. H. Etiology of Acute Illness Among Workers Using Low-grade Stained Cotton. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1942 Dec;32(12):1345–1359. doi: 10.2105/ajph.32.12.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. F., Eidson G., Hatcher J. D. Influence of cotton dust inhalation on free lung cells in rats and guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


