Abstract
Objective
The risk of recurrence after atrial fibrillation (AF) catheter ablation (AFCA) is higher in women than in men. However, it is unknown whether a sex difference exists in antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) responsiveness among patients with recurrence.
Methods
Among 2999 consecutive patients (26.5% women, 58.3±10.9 years old, 68.1% paroxysmal AF) who underwent de novo AFCA, we compared and evaluated the sex differences in rhythm outcome in 1094 patients with recurrence and in 788 patients who subsequently underwent rhythm control with AAD.
Results
During a follow-up of 48.2±34.9 months, 1094 patients (36.5%) had AF recurrence after AFCA, and 508 of 788 patients (64.5%) had AF recurrence under AAD. Although the rhythm outcome of a de novo AFCA was worse (log-rank p=0.041, HR 1.28, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.59), p=0.031) in women, AAD response after postprocedural recurrences was better in women than in men (log-rank p=0.003, HR 0.75, 95% CI 0.59 to 0.95, p=0.022), especially in women older than 60 years old (log-rank p=0.003). In 249 patients who underwent repeat procedure after AAD use, the pulmonary vein (PV) reconnection rate (62.7% vs 76.8%, p=0.048) was lower in women than in men but not the existence of extra-PV trigger (37.8% vs 25.4%, p=0.169).
Conclusions
Although women showed worse rhythm outcomes than men after AFCA, the post-AFCA AAD response was better in elderly women than in men.
Trial registration number
Keywords: atrial fibrillation, catheter ablation
Introduction
Sex differences are emerging as an important issue in various cardiovascular diseases. The prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF) has reached 1.6% in the South Korean population and is continuously increasing.1 The incidence of AF is notably higher in men, but the proportion of women with AF increases with age.2 Women with AF have more severe symptoms, a lower quality of life and a higher risk of stroke and mortality than men.3 Nevertheless, a lower proportion of women receive AF catheter ablation (AFCA) compared with men.4 AFCA not only improves AF-related symptoms, it also has positive clinical effects on reducing heart failure mortality, hospitalisations and the incidence of cerebral infarctions, in addition to improving cognitive function in patients with AF.5–7 However, AF is a progressive disease and recurs continuously during the long-term follow-up after AFCA.8 Repeat ablation has been found to significantly improve the rhythm outcome for recurrent AF after AFCA.9 Nevertheless, only select patients undergo repeat ablation procedures because of economic burden or personal preference after a post-AFCA recurrence. As the Korean medical insurance does not cover all repeat AFCAs, antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) are often used as an alternative method when the burden of recurrent AF is not high or the associated symptoms are not significant. In recurrent AF after AFCA, a better AAD response is expected due to the significantly reduced AF burden and atrial critical mass achieved by the pulmonary vein (PV) isolation (PVI) during de novo AFCA.10 Although rhythm outcomes of both de novo and repeat AFCAs are worse in women than in men,11 the sex differences in the efficacy and safety of AAD, to our knowledge, have not yet been studied in patients with AF recurrence after AFCA. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the existence of a sex difference in AAD responsiveness among patients with recurrent AF after AFCA.
Methods
Study population
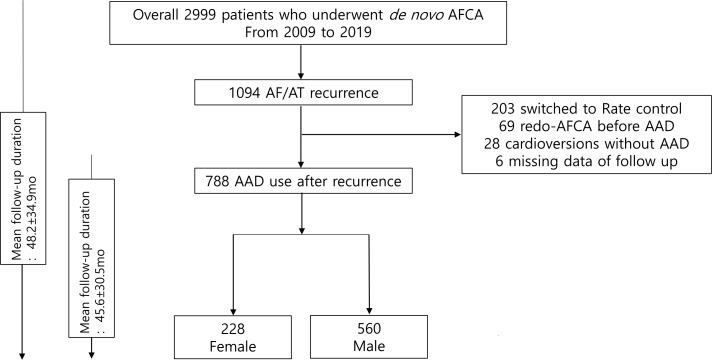
Patients or the public were not involved in the design, conduct, reporting or dissemination plans of our research. We included 2999 patients, who underwent a de novo AFCA between 2009 and 2019, in the Yonsei AF ablation cohort. Of these, 1094 patients experienced clinical recurrences of AF after AFCA (figure 1). A total of 788 patients used AADs after the clinical recurrence. Patients who did not visit the outpatient clinic after clinical recurrence were excluded. We maintained rate control in patients with sinus node dysfunction, no significant symptoms or those who refused rhythm control. AF recurrence was defined as any episode of AF or atrial tachycardia lasting over 30 s.
Figure 1.
Study design. AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AF, atrial fibrillation; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; AT, atrial tachycardia.
Electrophysiological mapping and catheter ablation
We performed electroanatomical mapping using a three-dimensional (3D) electroanatomical mapping system (NavX; Abbott Inc, Minnetonka, Minnesota, USA, or CARTO; Biosense Webster Inc, Diamond Bar, California, USA) merged with 3D spiral CT. To conduct circumferential PVI, we used an open-irrigated tip catheter (Celsius, Johnson & Johnson; Navistar ThermoCool, Biosense Webster; ThermoCool SF, Biosense Webster; ThermoCool SmartTouch, Biosense Webster; Coolflex, St. Jude Medical; FlexAbility, St. Jude Medical; and TactiCath, St. Jude Medical). After circumferential PVI, we confirmed electrical PVI and bidirectional block. Additional linear ablation, such as posteroinferior line, roof line, anterior line, left lateral isthmus line, right atrial ablation and/or complex fractionated electrograms, was performed at the operator’s discretion. After completion of the circumferential PVI or extra-PV ablation, isoproterenol infusion (5–10 µg/min) was administered to map the extra-PV triggers. If mappable AF triggers or frequent premature atrial complex (PAC) were present, we carefully mapped and ablated the non-PV triggers.
Postablation management and follow-up
The patients visited the outpatient clinic at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months and every 6 months thereafter or whenever symptoms occurred after the AFCA. According to the guidelines,12 a rhythm follow-up was performed using ECGs and 24 hours Holter monitoring at 3, 6 and 12 months, every 6 months for 2 years, and then annually after the AFCA.12 We identified the symptoms of the PAC and AF episodes and the percentage of PACs during Holter recordings. Moreover, we recommended ECG whenever patients had palpitation. We diagnosed clinical recurrence when an AF recurrence lasting over 30 s occurred following a 3-month blanking period.
Management of AF recurrence
We prescribed AADs for rhythm control first for patients with AF recurrence, and then electrical cardioversion was performed unless sinus rhythm was restored. After the sinus rhythm was restored, patients using AADs underwent ECG recordings during every visit with regular 24 hours Holter monitoring in the outpatient clinic. The definition of AF recurrence after AAD use and that of AF recurrence after AFCA were the same. Repeat ablation was recommended if an atrial arrhythmia persisted during the AAD treatment or recurred after sinus rhythm conversion with AADs. Following repeat ablation, the management and follow-up schedule were the same as those after the de novo procedure.
Statistical analysis
To compare the baseline variables, we used the Student’s t-test for the continuous variables. The results of the analysis of variance are expressed as the mean±SD. Categorical variables were analysed using the Pearson’s χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test, with variables reported as numbers (percentage). We performed Cox regression analysis to identify the factors related to AF recurrence after de novo AFCA and AAD use. We evaluated the assumption of proportional hazard by using testing of Schoenfeld residuals. The risk of AF recurrence after de novo AFCA and AAD use was analysed using the Kaplan-Meier method. We used the median value to set the cut-off value for age. To adjust the selection bias between men and women, we conducted propensity score (PS) matching analyses. For de novo AFCA patients, we performed PS matching with a calliper 0.25 and without replacement in 1:1 ratio based on age, AF type, body surface area (BSA), left atrium (LA) diameter, left ventricular ejection fraction, the ratio of the early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to the early mitral annular velocity (E/Em) and heart failure. For the patients with AAD use, we used PS matching with a calliper 0.2 and without replacement in 1:1 ratio based on age, AF type, BSA, LA diameter, left ventricular ejection fraction, E/Em, heart failure and empirical extra-PV ablation. Then, we compared the responses to de novo AFCA and AAD use between men and women, respectively. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (V.25; IBM Corp) for Windows and R (V.3.1.0; The R Foundation, www.R-project.org), with statistical significance set at a p<0.05.
Results
Sex differences in the included population
Among the 2999 patients who underwent a de novo AFCA, 794 were women and 2205 were men (table 1). The women were older (p<0.001), had a lower BSA (p<0.001), lower proportions of a persistent type (p=0.002) and vascular disease (p=0.003), higher proportions of heart failure (p<0.001), smaller LA dimension (p<0.001), higher E/Em (p<0.001) and more frequent extra-PV triggers (p<0.001) compared with the men. Locations of extra-PV triggers are described in online supplemental table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients with a de novo ablation
| Overall (n=2999) |
Female (n=794) |
Male (n=2205) |
P value | |
| Age, years | 58.3±10.9 | 61.1±10.7 | 57.2±10.8 | <0.001 |
| Persistent AF (%) | 956 (31.9) | 218 (27.5) | 738 (33.5) | 0.002 |
| BSA | 1.8±0.2 | 1.6±0.1 | 1.9±0.2 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| Heart failure | 352 (11.7) | 122 (15.4) | 230 (10.4) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1381 (46.0) | 378 (47.6) | 1003 (45.5) | 0.324 |
| Diabetes | 453 (15.1) | 109 (13.7) | 344 (15.6) | 0.228 |
| Stroke or TIA | 337 (11.2) | 104 (13.1) | 233 (10.6) | 0.061 |
| Vascular disease | 316 (10.5) | 61 (7.7) | 255 (11.6) | 0.003 |
| CHA2DS2VASc score | 1.7±1.5 | 2.6±1.5 | 1.4±1.4 | <0.001 |
| Non-gender CHA2DS2VA score |
1.4±1.4 | 1.6±1.5 | 1.4±1.4 | <0.001 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| LA dimension, mm | 41.4±6.2 | 40.6±6.3 | 41.6±6.2 | <0.001 |
| LV ejection fraction, % | 63.1±8.4 | 64.8±8.0 | 62.5±8.4 | <0.001 |
| E/Em | 10.2±4.4 | 12.2±5.4 | 9.5±3.8 | <0.001 |
| LAA flow velocity, cm/s (n=1421) | 48.2±22.1 | 45.0±22.0 | 49.5±22.1 | 0.001 |
| LA voltage (n=2119) | 1.3±0.7 | 1.1±0.6 | 1.4±1.4 | <0.001 |
| Procedure time, min | 171.5±55.9 | 170.5±52.8 | 171.8±56.9 | 0.553 |
| Ablation time, s | 4429.5±1702.9 | 4235.4±1594.9 | 4499.4±1735.2 | <0.001 |
| Ablation lesions (%) | ||||
| CPVI | 2999 (100) | 794 (100) | 2205 (100) | |
| CTI | 2651 (88.5) | 704 (88.9) | 1947 (88.4) | 0.771 |
| Empirical extra-PV LA ablation* | 932 (31.1) | 230 (29.0) | 702 (31.8) | 0.146 |
| Posterior box | 873 (29.1) | 217 (27.3) | 656 (29.8) | 0.214 |
| Anterior line | 633 (21.1) | 157 (19.8) | 476 (21.6) | 0.310 |
| Mitral isthmus line | 141 (4.7) | 38 (4.8) | 103 (4.7) | 0.982 |
| CFAE ablation | 140 (4.7) | 23 (2.9) | 117 (5.3) | 0.008 |
| Extra-PV trigger (n=1864) | 217 (11.6) | 86 (16.3) | 131 (9.8) | <0.001 |
Variables are presented as the mean±SD or count (percentage).
*Additional ablation lesions other than the pulmonary veins in the LA.
AF, atrial fibrillation; BSA, body surface area; CFAE, complex fractionated atrial electrograms; CPVI, circumferential pulmonary vein isolation; CTI, carvotricuspid isthmus; E/Em, the ratio of the early diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E) to the early mitral annular velocity (Em); LA, left atrium; LAA, left atrium appendage; LV, left ventricle; PV, pulmonary vein; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
heartjnl-2021-320601supp001.pdf (385.9KB, pdf)
After the de novo AFCA, 1094 patients (36.5%) had recurrent AF. Online supplemental table 2 summarises the rhythm outcomes of de novo AFCA. AADs were maintained in 28.5% of patients at discharge and 38.2% of patients after 3 months of AFCA. Among 788 patients who received AADs after post-AFCA recurrence, the baseline characteristics of women compared with men were consistent with those at the time of the de novo AFCA (table 2). The time to recurrence after the de novo procedure was longer (p=0.007), the procedure time was shorter (p=0.014) and the proportion of empirical extra-PV LA ablation was lower (p<0.001) in women than in men (table 2). However, the incidence of extra-PV trigger during de novo AFCA did not differ between the sexes in this patient group (p=0.217).
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of patients with AAD use after AF recurrence
| AAD user after recurrence (n=788) |
Female (n=228) |
Male (n=560) |
P value | |
| Age, years | 59.1±10.5 | 61.2±10.5 | 58.3±10.3 | <0.001 |
| Persistent AF (%) | 317 (40.2) | 68 (29.8) | 249 (44.5) | <0.001 |
| BSA | 1.8±0.2 | 1.7±0.1 | 1.9±0.2 | <0.001 |
| Total follow-up, mo | 45.6±30.5 | 42.6±27.2 | 46.8±31.7 | 0.063 |
| Time (recurrence ~de novo AFCA), mo | 21.9±22.3 | 25.3±22.4 | 20.5±22.1 | 0.007 |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| Heart failure | 94 (11.9) | 39 (17.1) | 55 (9.8) | 0.006 |
| Hypertension | 387 (49.1) | 120 (52.6) | 267 (47.7) | 0.237 |
| Diabetes | 134 (17.0) | 35 (15.4) | 99 (17.7) | 0.494 |
| Stroke or TIA | 101 (12.8) | 32 (14.0) | 69 (12.3) | 0.593 |
| Vascular disease | 99 (12.6) | 24 (10.5) | 75 (13.4) | 0.326 |
| Non-gender CHA2DS2VASc score |
1.5±1.4 | 1.7±1.5 | 1.5±1.4 | 0.029 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| LA dimension, mm | 42.5±6.3 | 40.9±6.0 | 43.2±6.3 | <0.001 |
| LV ejection fraction, % | 62.6±8.3 | 63.7±8.1 | 62.2±8.3 | 0.015 |
| E/Em | 10.4±4.3 | 12.2±5.2 | 9.7±3.6 | <0.001 |
| Procedure time, min | 186.4±59.3 | 178.8±51.9 | 189.5±61.8 | 0.014 |
| Ablation time, s | 4925.8±1806.0 | 4580.1±1561.8 | 5065.7±1879.2 | <0.001 |
| Ablation lesions (%) | ||||
| CPVI | 788 (100.0) | 228 (100.0) | 560 (100.0) | |
| CTI | 716 (91.1) | 204 (89.9) | 512 (91.6) | 0.528 |
| Empirical extra-PV LA ablation* | 329 (41.8) | 71 (31.1) | 258 (46.1) | <0.001 |
| Extra-PV trigger | 72 (14.9) | 29 (18.0) | 43 (13.3) | 0.217 |
| AAD use after recurrence (%) | 0.944 | |||
| Class IC | 294 (37.3) | 86 (37.7) | 208 (37.1) | |
| Class III | 494 (62.7) | 142 (62.3) | 352 (62.9) | |
| Amiodarone | 269 (34.1) | 63 (27.6) | 206 (36.8) | 0.018 |
Variables are presented as the mean±SD or count (percentage).
*Additional ablation lesions other than the pulmonary veins in the LA.
AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AF, atrial fibrillation; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; BSA, body surface area; CPVI, circumferential pulmonary vein isolation; CTI, carvotricuspid isthmus; E/Em, the ratio of the early diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E) to the early mitral annular velocity (Em); LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; PV, pulmonary vein; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Sex difference in rhythm outcome after AFCA and AADs
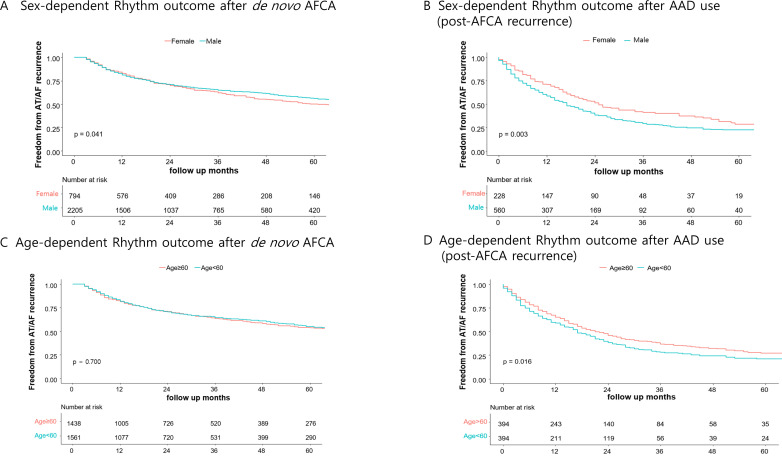
The rhythm outcome of the overall de novo ablation population was poorer in women than in men during the follow-up of 48.2±34.9 months (log-rank p=0.041, figure 2A; off-AAD log-rank p=0.004; online supplemental figure 1A), but AAD response after recurrence was significantly better in women than in men (follow-up 45.6±30.5 months, log-rank p=0.003, figure 2B). In Cox regression analyses for AF recurrence after AFCA, female sex (HR 1.28, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.59, p=0.031), LA dimension (HR 1.23, 95% CI 1.11 to 1.36, p<0.001), extra-PV triggers (HR 1.75, 95% CI 1.39 to 2.20, p<0.001) and persistent AF (HR 1.40, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.71, p=0.001) were independently associated with AF recurrence after AFCA (table 3). In Cox regression analyses for AF recurrence after AAD among the patients with post-AFCA recurrence, being female (HR 0.75, 95% CI 0.59 to 0.96, p=0.022) and age (HR 0.83, 95% CI 0.76 to 0.92, p<0.001) had a protective effect (table 4). Therefore, female sex was a risk factor for post-AFCA recurrence but a protective factor for AF recurrence under AADs.
Figure 2.
Risk of AF recurrence according to the sex after the de novo AFCA (A) and AAD use in patients with AF recurrence after AFCA (B) and according to the age after de novo AFCA (C) and AAD use in patients with AF recurrence after AFCA (D). AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AF, atrial fibrillation; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; AT, atrial tachycardia.
Table 3.
Cox regression analysis of AF recurrence after de novo AFCA
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
| HR (95% CI) |
P value | HR (95% CI) |
P value | |
| Age* | 1.03 (0.97 to 1.09) | 0.389 | 1.03 (0.94 to 1.14) | 0.506 |
| Female | 1.14 (1.00 to 1.30) | 0.043 | 1.28 (1.02 to 1.59) | 0.031 |
| Persistent AF | 1.66 (1.47 to 1.87) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.15 to 1.71) | 0.001 |
| BSA* | 0.98 (0.92 to 1.05) | 0.587 | 0.94 (0.83 to 1.07) | 0.339 |
| LA dimension, mm* | 1.28 (1.21 to 1.36) | <0.001 | 1.23 (1.11 to 1.36) | <0.001 |
| LV ejection fraction, %* | 0.94 (0.89 to 0.99) | 0.028 | ||
| E/Em* | 1.05 (0.99 to 1.12) | 0.079 | 0.92 (0.83 to 1.01) | 0.084 |
| Heart failure | 1.30 (1.09 to 1.55) | 0.004 | 1.00 (0.77 to 1.31) | 0.991 |
| Hypertension | 1.06 (0.94 to 1.20) | 0.311 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.08 (0.92 to 1.27) | 0.353 | ||
| Stroke or TIA | 1.14 (0.95 to 1.36) | 0.159 | ||
| Vascular disease | 1.05 (0.88 to 1.26) | 0.609 | 1.08 (0.85 to 1.37) | 0.540 |
| Ablation time* | 1.11 (1.05 to 1.18) | 0.001 | 1.09 (0.96 to 1.22) | 0.181 |
| Empirical extra-PV LA ablation† | 1.39 (1.23 to 1.57) | <0.001 | 1.12 (0.91 to 1.37) | 0.302 |
| Extra-PV triggers (n=1864) | 1.78 (1.44 to 2.21) | <0.001 | 1.75 (1.39 to 2.20) | <0.001 |
*Numerical data were divided by SD.
†Additional ablation lesions other than the pulmonary veins in the LA.
AF, atrial fibrillation; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; BSA, body surface area; E/Em, the ratio of the early diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E) to the early mitral annular velocity (Em); LA, left atrial; LV, left ventricular; PV, pulmonary vein; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Table 4.
Cox regression analysis of AF recurrence after AAD use
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
| HR (95% CI) |
P value | HR (95% CI) |
P value | |
| Age* | 0.89 (0.82 to 0.97) | 0.005 | 0.83 (0.76 to 0.92) | <0.001 |
| Female | 0.74 (0.61 to 0.91) | 0.003 | 0.75 (0.59 to 0.96) | 0.022 |
| Persistent AF | 1.24 (1.04 to 1.47) | 0.018 | 1.10 (0.87 to 1.38) | 0.430 |
| BSA* | 1.09 (1.00 to 1.19) | 0.047 | 0.96 (0.86 to 1.08) | 0.477 |
| LA dimension, mm* | 1.07 (0.98 to 1.16) | 0.131 | 1.00 (0.90 to 1.11) | 0.958 |
| LV ejection fraction, %†* | 0.89 (0.82 to 0.96) | 0.004 | ||
| E/Em* | 1.02 (0.93 to 1.11) | 0.740 | 1.07 (0.96 to 1.18) | 0.211 |
| Heart failure | 1.37 (1.05 to 1.78) | 0.019 | 1.34 (0.99 to 1.81) | 0.057 |
| Hypertension | 0.88 (0.74 to 1.05) | 0.158 | ||
| Diabetes | 0.97 (0.77 to 1.22) | 0.778 | ||
| Stroke or TIA | 0.91 (0.69 to 1.19) | 0.472 | ||
| Vascular disease | 0.76 (0.58 to 1.00) | 0.052 | ||
| Procedure time* | 1.11 (1.01 to 1.21) | 0.023 | 1.09 (0.99 to 1.21) | 0.095 |
| Ablation time* | 1.09 (1.00 to 1.18) | 0.063 | ||
| Empirical extra-PV LA ablation* | 1.17 (0.98 to 1.40) | 0.075 | 0.98 (0.77 to 1.25) | 0.891 |
| Extra-PV triggers | 1.13 (0.83 to 1.53) | 0.448 | ||
| Class III AAD | 1.21 (1.01 to 1.45) | 0.042 | 1.19 (0.98 to 1.44) | 0.083 |
| AMD‡ | 1.23 (1.00 to 1.50) | 0.047 | ||
*Numerical data were divided by SD.
†Additional ablation lesions other than the pulmonary veins in the LA.
‡Cox regression analysis was done for the class Ic AAD group versus amiodarone group.
AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AF, atrial fibrillation; AMD, amiodarone; BSA, body surface area; E/Em, the ratio of the early diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E) to the early mitral annular velocity (Em); LA, left atrial; LV, left ventricular; PV, pulmonary vein; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Age factors
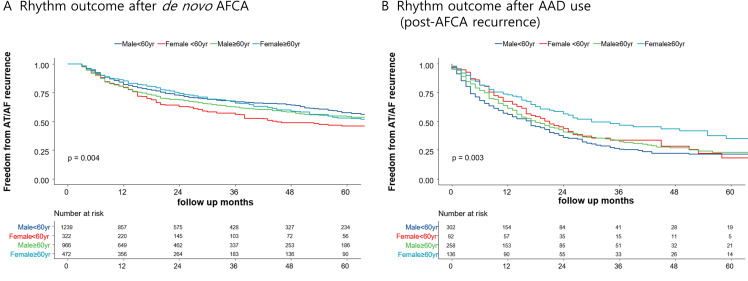
We compared rhythm outcomes depending on the median age of 60 years. AF recurrence did not differ according to age after AFCA (log-rank p=0.700, figure 2C; off-AAD log-rank p=0.080; online supplemental figure 1B) but was significantly lower in patients above 60 years of age after AAD use than their counterparts (log-rank p=0.016, figure 2D). After grouping with regard to age and sex, women younger than 60 years showed significantly poorer rhythm outcomes after de novo AFCA (log-rank p=0.004, figure 3A), whereas women older than 60 years showed significantly better rhythm outcomes after AAD use (log-rank p=0.003, figure 3B).
Figure 3.
Risk of AF recurrence after de novo AFCA (A) and AAD use (B) according to age and sex. AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AF, atrial fibrillation; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; AT, atrial tachycardia.
Sex difference in rhythm outcome after PS matching
To minimise the selection bias between men and women, we performed PS matching (online supplemental figure 2) in de novo AFCA patients (469 women and 469 men; online supplemental table 3) and patients with AAD use (140 women and 140 men; online supplemental table 4), respectively. After the PS matching, the rhythm outcome of de novo AFCA was worse in women than in men (log-rank p=0.030; online supplemental figure 3A). However, the response to AAD after recurrence was better in women than in men (log-rank p=0.011; online supplemental figure 3B). Women younger than 60 years showed poor rhythm outcomes after de novo AFCA (log-rank p=0.026; online supplemental figure 4A), but women older than 60 years showed better AAD response than other groups (log-rank p=0.015; online supplemental figure 4B).
AAD types, responsiveness and adverse effects
Although the proportions of class IC AAD prescribed at post-AFCA recurrence did not differ between women and men (table 2), AAD responses to class IC AAD were significantly better in women (log-rank p=0.009; online supplemental figure 5A) and in those over 60 years old (log-rank p=0.045; online supplemental figure 5C). Class III AAD responses did not differ depending on sex (log-rank p=0.075; online supplemental figure 5B) or age (log-rank p=0.071; online supplemental figure 5D).
Online supplemental table 5 summarises the duration and adverse effects of each AAD in women and men. The adverse effects of AADs did not differ between the two sexes. The most frequent adverse effects of AAD were sinus node dysfunction and thyroid dysfunction. By AAD type, amiodarone was more prescribed (p=0.018), and dronedarone was less prescribed (p=0.048) in women than in men.
Redo-mapping findings
In 249 patients who underwent repeat procedures 34.7±26.7 months after the de novo procedure because of repeated recurrence after AAD use, the proportions of repeat ablations were 25.9% (59/228) in women and 33.9% (190/560) in men. The PV reconnection rate was significantly lower in women than in men (62.7% vs 76.8%, p=0.048), but there was no significant difference in the existence of extra-PV triggers (37.8% vs 25.4%, p=0.169, table 5).
Table 5.
Procedural characteristics of repeat AFCA
| Repeat AFCA after AAD use (n=249) |
Female (n=59) |
Male (n=190) |
P value | |
| PV reconnection (%) | 183 (73.5) | 37 (62.7) | 146 (76.8) | 0.048 |
| 1 | 51 (20.5) | 15 (25.4) | 36 (18.9) | |
| 2 | 56 (22.5) | 10 (16.9) | 46 (24.2) | |
| 3 | 37 (14.9) | 6 (10.2) | 31 (16.3) | |
| 4 | 39 (15.7) | 6 (10.2) | 33 (17.4) | |
| Extra-PV triggers (%), n=167 | 48 (28.7) | 17 (37.8) | 31 (25.4) | 0.169 |
Variables are presented as count (percentage).
AAD, antiarrhythmic drug; AFCA, atrial fibrillation catheter ablation; PV, pulmonary vein.
Discussion
Main findings
In this single-centre retrospective cohort study with a regular rhythm follow-up protocol, we found that the AAD response after post-AFCA recurrence was significantly better in women than in men, particularly older than 60 years of age using class IC AAD. This was in contrast with the outcome of the de novo AFCA, which showed worse rhythm outcomes in women than in men. Therefore, women show opposite responsiveness to catheter ablation and AAD therapy compared with men with AF.
Sex differences in AF
The prevalence of AF is higher in men, but this progressive degenerative disease increases significantly in older women.2 AF in older women is particularly affected by haemodynamic factors. Central aortic pressure significantly increases in women with ageing, inducing left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction, generating an AF vulnerable condition.13 14 Aged women are more vulnerable to AF development and progression, and accompanying atrial structural remodelling and reduced LA appendage function are associated with a higher risk of stroke.15 In this study, although the LA size was smaller and the proportion of paroxysmal AF was higher in women than in men, the rhythm outcome of de novo AFCA was worse in women than in men, consistent to the previous studies.11 16 However, there has been no study on sex differences in AAD response in patients with post-ablation AF recurrence. In this study, although the recurrence rate after AFCA was high in women, the response to AAD was superior in women, especially in older aged women, than in men.
Mechanisms of AF recurrence and the AAD response after AFCA
Despite the diverse and positive clinical effects of AFCA,5–7 continuous AF recurrence after the procedure remains an unsolved issue. There are several potential mechanisms for AF recurrence after AFCA: first, insufficient ablation17 or PV reconnection18; second, atrial remodelling and extra-PV triggers19; third, inflammation and atrial substrate progression20; and fourth, autonomic neural imbalance.21 Durable PVI is an essential issue in AFCA, and updated catheter technology improved durable PVI by the ablation index-guided PVI.22 EAST-AFNET4 trial23 proved the importance of the early rhythm control. Shorter AF duration was associated with better rhythm outcomes of AFCA in our cohort.24 Integrated AF management of other risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, obstructive sleep apnoea, dyslipidaemia and physical factors, also improves cardiovascular outcomes.25
AAD response is better in patients with recurrent AF after AFCA than in those without intervention.10 Moreover, fewer PV reconnections result in a better response to AADs.26 Prolongation of action potential duration, reduced resting membrane potential or reduced conduction velocity by AAD has an anti-AF effect on the gaps of PV reconnection, delayed conducting substrate or extra-PV triggers.
Female AF patients have a thinner antral wall thickness, more frequent extra-PV triggers and longer time to recurrence after de novo AFCA than male patients.11 27 28 Women also show a lower PV reconnection rate and more common extra-PV triggers at repeat procedures after AF recurrence.11 29 In our study, the PV reconnection rate was lower in women than in men during the repeat procedures after AAD use. Considering these facts, we can suggest a few reasons for superior AAD response after ablation in women than in men. First, the lower rate of PV reconnections in women indicates that progressive substrate remodelling and extra-PV triggers could be the main cause of recurrence in women. Therefore, women had a better response to AAD than men. Extra-PV triggers might be related to spontaneous calcium release,30 so that AAD with beta-blocker activity might be more effective in women. Second, AAD appropriately controls extra-PV substrates or triggers that are more commonly found in women with relatively thin antral walls and well-maintained PVI. Third, the AAD blood concentration was potentially higher in women, who have a relatively lower BSA, than in men, even at the same AAD dose. Therefore, the effect of AAD on rhythm control was superior in women than in men, especially in those older than 60 years old, who experienced AF recurrence after catheter ablation.
Clinical significance
Our study is clinically meaningful in that it identified the sex difference in AAD response among patients with post-AFCA recurrence and followed up for an extended period. Women, especially those above 60 years of age, showed better AAD response than men in this patient group. Lower rate of PV reconnections, more extra-PV triggers, more atrial remodelling associated with diastolic dysfunction and lower LA voltage could explain the mechanisms of the opposite response to ablation and AAD response in women and men with AF.
Limitations
Despite these findings, this study had several limitations. First, this was a retrospective, non-randomised comparison study, and selection bias regarding the treatment could have been involved. We used PS matching to adjust some variables between the female and male groups. Second, this study was conducted at a single centre and included a relatively small number of patients; hence, the findings from this study cannot be generalised to all patients with AF. Third, the ablation lesion set was not controlled for de novo AFCA. Fourth, the type and dose of AAD were also not regulated. However, most patients used an optimal amount of AAD, and this could reduce this bias. Fifth, although we conducted a regular-based Holter follow-up, we could not evaluate the real AF burden. Sixth, with the nature of AF progression, later rhythm control might affect the rhythm outcomes. However, we could not match the index time because it was hard to determine the actual AF duration. Lastly, since patients who underwent repeat ablation were a part of patients with recurrence, it may be limited in explaining the sex difference in AAD response in recurrent patients after AFCA.
Conclusion
Although women showed worse rhythm outcomes than men after AFCA, the post-AFCA AAD response was better in older women than in men.
What is already known on this subject?
The risk of atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence after catheter ablation is higher in women than in men. However, the sex differences in antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) response among patients with recurrence after AF ablation and the mechanisms related to AAD response are unknown.
What might this study add?
The AAD response of patients with post-AF catheter ablation (AFCA) recurrence was significantly better in women than in men, particularly in those older than 60 years old. The rate of pulmonary vein reconnection was significantly lower in women than in men (62.7% vs 76.8%, p=0.048) during repeat ablation after AAD use, which might be the reason for the better AAD response in women than in men after post-AFCA recurrence.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
Women show opposite responsiveness to catheter ablation and AAD therapy compared with men with AF. In practice, some patients with postprocedural AF recurrence cannot undergo repeat ablation due to a poor general condition, advanced age or patient rejection. AAD may be an alternative for such patients.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. John Martin for his linguistic assistance
Footnotes
Correction notice: This article has been corrected since it was first published to correct a typo in Table 1.
Contributors: YJP designed the study, analysed and interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. J-WP analysed and interpreted the data. HTY, T-HK and J-SU contributed to acquiring patients’ clinical data. BJ and M-HL revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. H-NP designed the study and did the final approval of the manuscript submitted. H-NP has been the study supervisor and is the corresponding author and guarantor. All authors read and approved the manuscript before its submission.
Funding: This work was supported by a grant (HI21C0011) from the Ministry of Health and Welfare and grant (NRF-2020R1A2B5B01001695) from the Basic Science Research Programme run by the National Research Foundation of Korea, which is funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information. Data, analytic methods and study materials are available on reasonable request to other researchers who want to reproduce the results or replicated the procedure.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by The study protocol adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Yonsei University Health System (4-2014-0104). Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
- 1. Kim D, Yang P-S, Jang E, et al. 10-year nationwide trends of the incidence, prevalence, and adverse outcomes of non-valvular atrial fibrillation nationwide health insurance data covering the entire Korean population. Am Heart J 2018;202:20–6. 10.1016/j.ahj.2018.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation 2014;129:837–47. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Emdin CA, Wong CX, Hsiao AJ, et al. Atrial fibrillation as risk factor for cardiovascular disease and death in women compared with men: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ 2016;532:h7013. 10.1136/bmj.h7013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Schnabel RB, Pecen L, Ojeda FM, et al. Gender differences in clinical presentation and 1-year outcomes in atrial fibrillation. Heart 2017;103:1024–30. 10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Packer DL, Mark DB, Robb RA, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drug therapy on mortality, stroke, bleeding, and cardiac arrest among patients with atrial fibrillation: the CABANA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019;321:1261–74. 10.1001/jama.2019.0693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Kim M, HT Y, Kim J. Atrial fibrillation and the risk of ischaemic strokes or intracranial haemorrhages: comparisons of the catheter ablation, medical therapy, and non-atrial fibrillation population. EP Europace 2020. 10.1093/europace/euaa235 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Jin M-N, Kim T-H, Kang K-W, et al. Atrial fibrillation catheter ablation improves 1-year follow-up cognitive function, especially in patients with impaired cognitive function. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019;12:e007197. 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Park J-W, Yu HT, Kim T-H, et al. Trends and Outcome of Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Over 9 Years - Focus on Empirical Extra-Pulmonary Vein Ablation. Circ J 2019;83:304–12. 10.1253/circj.CJ-18-0928 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hussein AA, Saliba WI, Martin DO, et al. Natural history and long-term outcomes of ablated atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2011;4:271–8. 10.1161/CIRCEP.111.962100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Duytschaever M, Demolder A, Phlips T, et al. Pulmonary vein isolation with vs. without continued antiarrhythmic drug trEatment in subjects with recurrent atrial fibrillation (powder AF): results from a multicentre randomized trial. Eur Heart J 2018;39:1429–37. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Pak H-N, Park J-W, Yang S-Y, et al. Sex differences in mapping and rhythm outcomes of a repeat atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart 2021;107:1862–7. 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-318282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2018;20:e1–160. 10.1093/europace/eux274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lee JS, Shim CY, Wi J, et al. Left ventricular diastolic function is closely associated with mechanical function of the left atrium in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ J 2013;77:697–704. 10.1253/circj.CJ-12-1009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Shim CY, Park S, Choi D, et al. Sex differences in central hemodynamics and their relationship to left ventricular diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1226–33. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.09.067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. HT Y, Lee JS, Kim TH. Advanced left atrial remodeling and appendage contractile dysfunction in women than in men among the patients with atrial fibrillation: potential mechanism for stroke. J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5. 10.1161/JAHA.116.003361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yu HT, Yang P-S, Kim T-H, et al. Poor Rhythm Outcome of Catheter Ablation for Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Women - Mechanistic Insight. Circ J 2018;82:2259–68. 10.1253/circj.CJ-17-1358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kuck K-H, Hoffmann BA, Ernst S, et al. Impact of complete versus incomplete circumferential lines around the pulmonary veins during catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: results from the Gap-Atrial Fibrillation-German atrial fibrillation competence network 1 trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2016;9:e003337. 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Nilsson B, Chen X, Pehrson S, et al. Recurrence of pulmonary vein conduction and atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation: a randomized trial of the ostial versus the extraostial ablation strategy. Am Heart J 2006;152:537.e1–537.e8. 10.1016/j.ahj.2006.05.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Park J, Joung B, Uhm J-S, et al. High left atrial pressures are associated with advanced electroanatomical remodeling of left atrium and independent predictors for clinical recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Heart Rhythm 2014;11:953–60. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Meyre PB, Sticherling C, Spies F, et al. C-reactive protein for prediction of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2020;20:427. 10.1186/s12872-020-01711-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kang K-W, Kim TH, Park J, et al. Long-term changes in heart rate variability after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: 1-year follow-up study with irrigation tip catheter. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2014;25:693–700. 10.1111/jce.12398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hussein A, Das M, Riva S, et al. Use of ablation index-guided ablation results in high rates of durable pulmonary vein isolation and freedom from arrhythmia in persistent atrial fibrillation patients: the praise study results. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2018;11:e006576. 10.1161/CIRCEP.118.006576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kirchhof P, Camm AJ, Goette A, et al. Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1305–16. 10.1056/NEJMoa2019422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yu HT, Kim I-S, Kim T-H, et al. Persistent atrial fibrillation over 3 years is associated with higher recurrence after catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2020;31:457–64. 10.1111/jce.14345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Wijtvliet EPJP, Tieleman RG, van Gelder IC, et al. Nurse-Led vs. usual-care for atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 2020;41:634–41. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Verma A, Kilicaslan F, Pisano E, et al. Response of atrial fibrillation to pulmonary vein antrum isolation is directly related to resumption and delay of pulmonary vein conduction. Circulation 2005;112:627–35. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.533190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Park J-W, Yu HT, Kim T-H, et al. Mechanisms of long-term recurrence 3 years after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2020;6:999–1007. 10.1016/j.jacep.2020.04.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lee J-H, Kwon O-S, Shim J, et al. Left atrial wall stress and the long-term outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: an artificial Intelligence-Based prediction of atrial wall stress. Front Physiol 2021;12:686507. 10.3389/fphys.2021.686507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Kim T-H, Park J, Uhm J-S, et al. Pulmonary vein reconnection predicts good clinical outcome after second catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Europace 2017;19:961–7. 10.1093/europace/euw128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Herraiz-Martínez A, Tarifa C, Jiménez-Sábado V, et al. Influence of sex on intracellular calcium homeostasis in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 2021. 10.1093/cvr/cvab127. [Epub ahead of print: 31 Mar 2021]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
heartjnl-2021-320601supp001.pdf (385.9KB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information. Data, analytic methods and study materials are available on reasonable request to other researchers who want to reproduce the results or replicated the procedure.