Abstract
Guberan, E., Williams, M. K., Walford, Joan, and Smith, Margaret M. (1969).Brit. J. industr. Med.,26, 121-125. Circadian variation of F.E.V. in shift workers. The one-second forced expiratory volume (F.E.V.1·0), the forced vital capacity, and the oral temperature were measured in a group of men working a rotating three-shift system—2 to 10 p.m. one week, 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. the next week, and 6 a.m. to 2 p.m. the third week. The outside air temperature at the London Weather Centre was also obtained. Measurements were made on Mondays and Fridays at the beginning, middle, and end of the shift.
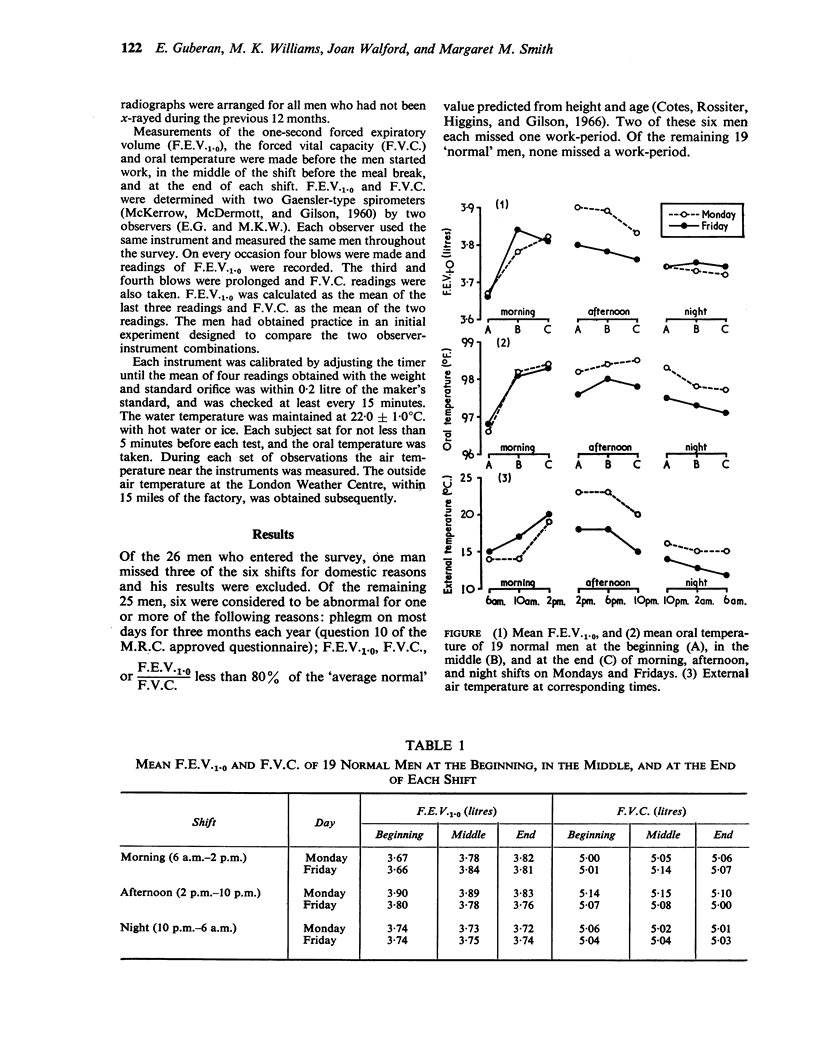
The mean F.E.V.1·0 of 19 normal men showed an increase of 0·15 litre (4·1%) between the beginning and end of both the morning shifts, a mean decrease of some 0·05 litre (1·5%) between the beginning and end of the afternoon shifts, and little change during the night shifts. This circadian variation could not be attributed to industrial fume, smoking or a learning effect.
The findings will be of practical importance when F.E.V. is measured in shift workers to determine the effects of toxic substances on ventilatory capacity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOUHUYS A., HARTOGENSIS F., KORFAGE H. J. BYSSINOSIS PREVALENCE AND FLAX PROCESSING. Br J Ind Med. 1963 Oct;20:320–323. doi: 10.1136/oem.20.4.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Rossiter C. E., Higgins I. T., Gilson J. C. Average normal values for the forced expiratory volume in white Caucasian males. Br Med J. 1966 Apr 23;1(5494):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5494.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWINSOHN H. C., CAPEL L. H., SMART J. Changes in forced expiratory volumes throughout the day. Br Med J. 1960 Feb 13;1(5171):462–464. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5171.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKERROW C. B., McDERMOTT M., GILSON J. C., SCHILLING R. S. Respiratory function during the day in cotton workers: a study in byssinosis. Br J Ind Med. 1958 Apr;15(2):75–83. doi: 10.1136/oem.15.2.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford J., Lammers B., Schilling R. S., Hoven van Genderen D., van der Veen Y. G. Diurnal variation in ventilatory capacity. An epidemiological study of cotton and other factory workers employed on shift work. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):142–148. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


