Abstract
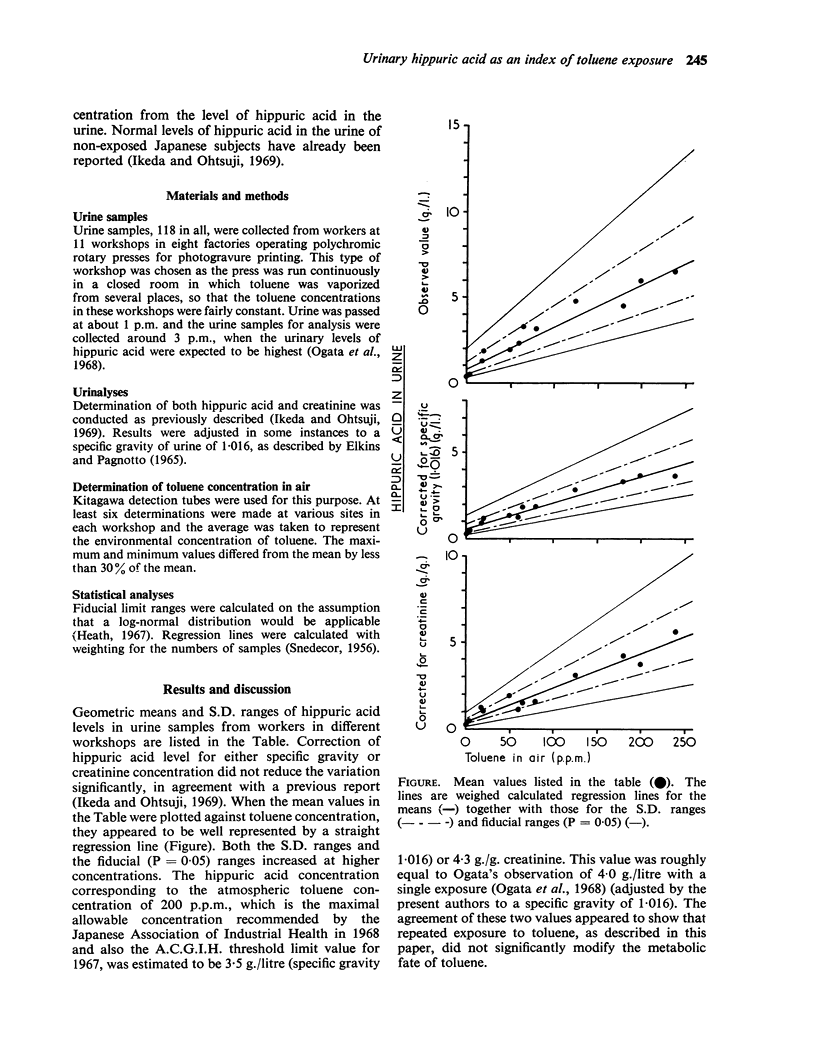
Ikeda, Masayuki, and Ohtsuji, Hatsue (1969).Brit. J. industr. Med.,26, 244-246. Significance of urinary hippuric acid determination as an index of toluene exposure. Urine samples from 118 male workers in photogravure printing factories were analysed for hippuric acid. The urinary levels of hippuric acid were proportional to the environmental concentrations of toluene, although within wide variations. The urinary concentration of hippuric acid corresponding to 200 p.p.m. of toluene was 3·5 g./litre (specific gravity 1·016) or 4·3 g./g. creatinine.
Full text
PDF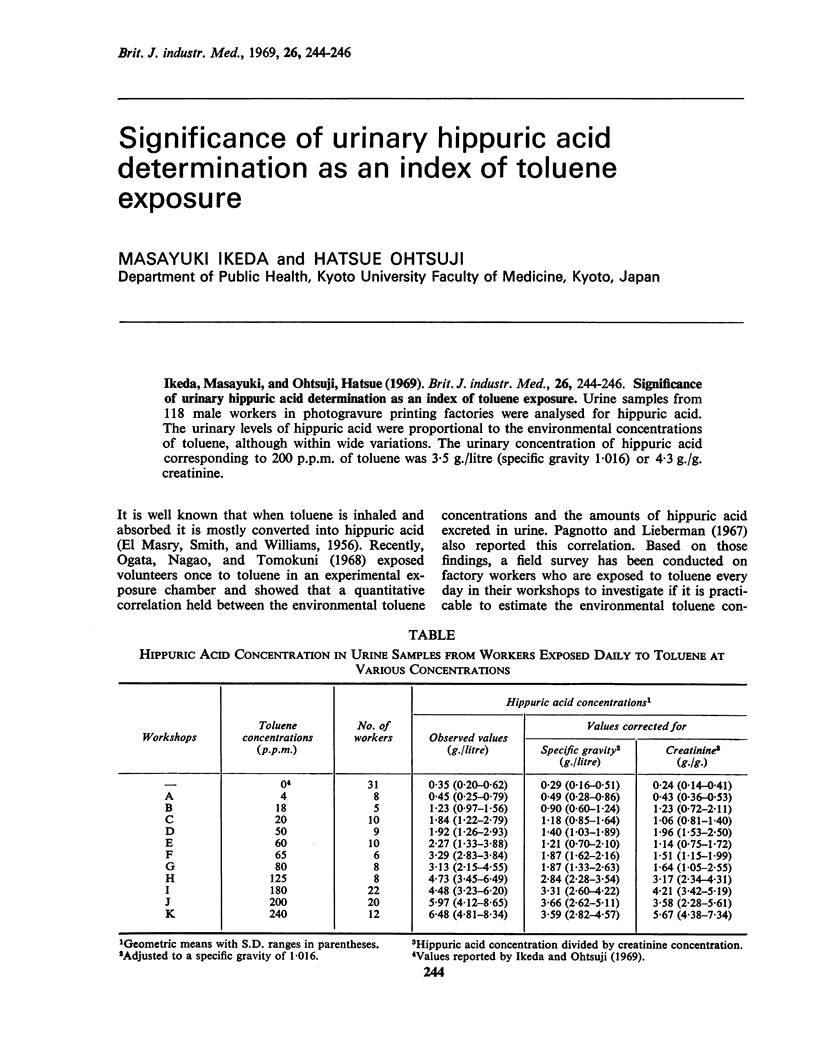

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EL MASRY A. M., SMITH J. N., WILLIAMS R. T. Studies in detoxication. 69. The metabolism of alkylbenzenes: n-propylbenzene and n-butylbenzene with further observations on ethylbenzene. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):50–56. doi: 10.1042/bj0640050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins H. B., Pagnotto L. D. Is the 24-hour urine sample a fallacy? Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1965 Sep-Oct;26(5):456–460. doi: 10.1080/00028896509342757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Ohtsuji H. Hippuric acid, phenol, and trichloroacetic acid levels in the urine of Japanese subjects with no known exposure to organic solvents. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Apr;26(2):162–164. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnotto L. D., Lieberman L. M. Urinary hippuric acid excretion as an index of toluene exposure. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1967 Mar-Apr;28(2):129–134. doi: 10.1080/00028896709342496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


