Summary
Belantamab mafodotin, an immuno‐conjugate targeting B‐cell maturation antigen, showed single‐agent activity in phase 1 and 2 studies, and was recently approved for heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) patients. Real‐world data and long‐term follow‐up are scarce. We conducted a multisite retrospective study aimed to assess safety and efficacy of belantamab mafodotin monotherapy administered via the GSK expanded access compassionate care programme. One‐hundred and six RRMM patients were treated with belantamab mafodotin between July 2019 and March 2021. The median age was 69.4 years. Patients were heavily pretreated with a median of six (range 2–11) prior therapy lines. Major adverse effects included ocular toxicity (keratopathy 68.4%, grade ≥3: 40.5%; blurred vision 36.8%, grade ≥3: 6.3%), thrombocytopenia (27.4%, grade ≥3: 17.9%) and infections (11.3%, grade ≥3: 7.5%). Median follow‐up time was 11.9 [95% confidence interval (CI) 10.0–13.8] months. Overall response rate was 45.5%. Median progression‐free survival was 4.7 (95% CI 3.5–5.9) months in the entire cohort and 8.8 (95% CI 6.6–10.9) months among responders. Median overall survival was 14.5 (95% CI 9.5–19.6) months, and not reached for responders. To conclude, in a real‐world setting, belantamab mafodotin monotherapy showed efficacy comparable with the prospective clinical trials, with a tolerable toxicity profile.
Keywords: immunotherapy, multiple myeloma, myeloma therapy
Abbreviations
- AE
adverse event
- AKI
acute kidney injury
- ASCT
autologous stem‐cell transplantation
- BCMA
B‐cell maturation antigen
- CI
confidence interval
- CMV
cytomegalovirus
- DOR
duration of response
- EMD
extramedullary disease
- FISH
fluorescence in‐situ hybridization
- HDM
high‐dose melphalan
- IMiD
immunomodulatory drug
- ISS
international staging system
- MM
multiple myeloma
- MoAb
monoclonal antibody
- ORR
overall response rate
- OS
overall survival
- PFS
progression‐free survival
- PI
proteasome inhibitor
- PR
partial response
- rISS
revised international staging system
- RRMM
relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
- TLS
tumour lysis syndrome
- TTNT
time to next treatment
INTRODUCTION
Despite the advances in management of multiple myeloma (MM), outcome remains poor for triple‐class‐refractory patients, i.e., patients who are refractory to immunomodulatory agents (IMiDs; lenalidomide or pomalidomide), proteasome inhibitors (PI; bortezomib, carfilzomib or ixazomib) and anti‐CD38 monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs; daratumumab or isatuximab). In a large retrospective study, the median overall survival (OS) rate of such patients was 9.2 months. 1 Prognosis is even worse for penta‐refractory patients (patients refractory to two PIs, three IMiDs and an anti‐CD 38 MoAb), with a median OS of less than 6 months. 1 This population represents an unmet need, and a search for new targeted therapy is ongoing. B‐cell maturation antigen (BCMA) expression was previously shown to be associated with longer survival time of plasma cells. 2 Patients with relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM) have higher levels of BCMA expression. 3 Therefore, BCMA is being extensively studied as a target for anti‐myeloma therapy in various modalities, including chimaeric antibody‐receptor T cells, 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 T‐cell redirecting bispecific antibodies 8 , 9 , 10 and antibody–drug conjugates. 11 , 12 Belantamab mafodotin is a first‐in‐class anti‐BCMA immunoconjugate, recently approved for the treatment of advanced RRMM after four treatment lines in the United States (for triple‐exposed patients) and Europe (triple‐refractory patients). In the first‐in‐human DREAMM1 study, 11 35 heavily pretreated (five median prior therapy lines) RRMM patients who received belantamab mafodotin monotherapy had an overall response rate (ORR) of 60% with a median progression‐free survival (PFS) of 12.0 months and median duration of response (DOR) of 14.3 months in the entire cohort, but only 6.2 month in patients refractory to IMiDs and PIs, and exposed to anti‐CD 38 MoABs. Treatment was well tolerated with thrombocytopenia and corneal toxicity being the major adverse events (AEs). 11 The DREAMM2 phase 2 study randomized 196 heavily pretreated RRMM patients (median number of prior lines: six) to receive belantamab mafodotin either in 3.4 or 2.5 mg/kg dose. 12 The ORR was 31% and 34% for the 2.5 and 3.4 mg/kg doses, respectively. Median PFS was 2.8 months. In a recent update, DOR for the 2.5 mg/kg dosing was reported to be 13.1 months for patients achieving at least partial response (PR) and 11.7 months for patients achieving at least minimal response. 13 Keratopathy was observed in 72% of the patients (24% of the grade ≥3), resulting in treatment discontinuation in four (2%) patients. 12
Prospective trials show encouraging outcomes, yet, clinical trials, in particular registration pivotal trials, tend to apply highly selective eligibility criteria, excluding patients with significant comorbidities such as recent active coronary disease, advanced heart failure, renal failure or any serious or unstable medical condition or lab abnormality or poor performance function. Specific populations tend to be under‐represented in clinical trials, namely frail patients, and patients with aggressive and rapidly progressing disease. 14 Thus, while trial data are essential for establishing the safety and efficacy of drug combinations in a rigorous and unbiased methodology, there is increasing recognition of the complimentary role of real‐world evidence, in understanding the effectiveness of treatment regimens in broader settings, and guiding treatment selection among the multiple alternatives. This is of particular importance with a novel therapy such as belantamab, which presents a new challenge of managing ocular toxicity in collaboration with ophthalmologists. So far, three real‐world experience series were published, describing 39, 15 36 16 and 28 17 very heavily pretreated patients. Response rates were 27%, 33% and 46%, respectively. Median PFS was 1.8, 2.0 and 4.7 months respectively; median OS was 9.2, 6.5 and 7.4 months, respectively. Patients were treated with belantamab mafodotin as monotherapy (95% of the patients in Becnel et al. 15 and 83% in Vaxman et al. 16 ), or in combination with corticosteroids. 17
In this study, we aimed to analyse real‐world outcomes of belantamab mafodotin therapy among a multisite Israeli cohort treated with belantamab mafodotin via the GSK compassionate access programme, and to assess whether clinical trial results are compatible with outcomes in the real‐world setting.
METHODS
This was a retrospective, multisite study, conducted in 12 hospitals throughout Israel. All consecutive RRMM patients aged 18 years or older who received more than a single dose of belantamab mafodotin as monotherapy or in combination with corticosteroids under GSK expanded access compassionate care, from 1 May 2019 through 1 March 2021, were included. Exclusion criteria are mentioned in Appendix S1.
The study was approved by institutional review boards (IRBs) of the participating centres. Data were extracted by review of electronic medical charts and abstracted using the REDCAP electronic data capture tool. 18
High‐risk cytogenetics were defined as the presence of any of the following aberrations: t(4, 14), t(14; 16), del(17p), or 1q21 gain or amplification.
Patients received belantamab mafodotin at an initial dose of 3.4 mg/kg, which was reduced to 2.5 mg/kg in September 2019, according to GSK guidance following DREAMM2 trial 12 results. No premedication was given routinely. Patients received corticosteroids eye‐drops until November 2019, when they were withheld according to GSK instructions. Artificial tears and eye cooling during belantamab mafodotin administration were applied according to the treating physician's decision. Belantamab mafodotin was administered every 21 days unless deemed ineligible due to AEs, in which case dosing was delayed until recovery of toxicity to grade 1 or better.
Patients were considered refractory to a drug in the prior anti‐myeloma regimens if a documented relapse or progression according to the international myeloma working group (IMWG) criteria occurred during, or within 60 days of, drug administration. 19
The primary end‐point was ORR according to IMWG criteria, 19 as reported by the investigator. Secondary outcomes included PFS, OS, DOR, and time to next treatment (TTNT).
Dose delay was defined as doses given beyond 25 days following the preceding dose. Length of delay was defined as number of days from last dose minus 25. Proportion of delayed doses was calculated as the cumulative number of days of each delay, divided by total number of doses beyond first dose, for each patient.
Non‐ocular AEs were assessed using Common Terminology Criteria for AEs version 5.0 (CTCAE v5.0) 20 Ocular side effects were assessed at the beginning of each cycle, and as needed, by an ophthalmologist, and were recorded on a designated form as part of the access programme requirements.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were compared with the use of Fisher's exact test or the chi‐squared test. Continuous variables were analysed using the Mann–Whitney test for independent samples. Survival probabilities were estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method. All tests were two‐sided, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Multivariate analysis was carried out using a logistic regression model and included variables reaching statistical significance (p < 0.05). All analyses were obtained using the statistical software IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25 (IBM Corporation, 2017).
RESULTS
A total of 106 patients (60 males, 56.6%) who received more than one dose of belantamab mafodotin between May 2019 and March 2021 were included. Three patients were excluded as they received a single dose (none of them discontinued therapy due to AEs). Patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. The median age was 69.4 (range 36.3–88.0) years. Patients were heavily pretreated with a median of six (range 2–11) previous treatment lines.
TABLE 1.
Patient characteristics.
| No. of patients with available data | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age: median (range) | 69.4 (36.3–88.0) | 106 |
| Age >70, n (%) | 52 (49) | |
| Male sex n, (%) | 60 (56.6) | 106 |
| ISS at diagnosis, % 1/2/3 | 43/30/26 | 76 |
| rISS at diagnosis | 33/51/15 | 54 |
| Cytogenetics, n % | 63 | |
| High‐risk a | 27 (42.8) | |
| Double‐hit b | 5 (7.9) | |
| del17p | 12 (19.0) | |
| t 4;14 | 1 (1.6) | |
| t 14;16 | 1 (1.6) | |
| +1q21 | 18 (28.5) | |
| t 11;14 | 15 (25.3) | |
| EMD n (%) | 12 (21.4) | 57 |
| Previous lines of therapy median, n (range) | 6 (2–11) | 106 |
| Previous exposure, n (%) | 106 | |
| PIs | ||
| Bortezomib | 103 (97.1) | |
| Carfilzomib | 77 (72.6) | |
| IMiDs | ||
| Lenalidomide | 97 (91.5) | |
| Pomalidomide | 82 (77.3) | |
| Daratumumab | 101 (95.2) | |
| HDM/ASCT | 62 (58.5) | |
| Refractoriness, n (%) | ||
| PIs | ||
| Bortezomib | 58 (58.0) | |
| Carfilzomib | 68 (64.5) | |
| IMiDs | ||
| Lenalidomide | 79 (74.5) | |
| Pomalidomide | 67 (63.2) | |
| Daratumumab | 85 (80.1) | |
| IMiD + PI refractory | 85 (80.2) | 106 |
| Triple‐refractory | 77 (72.6) | 106 |
| Penta‐refractory | 34 (32.0) | 106 |
| Refractory to last line of therapy | 82 (91.1) | 90 |
Abbreviations: EMD, extramedullary disease; HDM/ASCT, high‐dose melphalan/autologous stem cell transplantation; IMiDs, immunomudolators; ISS, international staging system; PIs, proteasome inhibitors; rISS, revised international staging system.
High‐risk cytogenetics defined as: t(4; 14), t(14; 16), del(17p), or +1q21.
Double‐hit: two high‐risk cytogenetic aberrations.
Exposure rates to bortezomib, lenalidomide and daratumumab were 97.1%, 91.5% and 95.2%, respectively. Seventy‐seven patients (72.6%) were triple‐refractory, and 34 patients (32.0%) were penta‐refractory. Sixty‐two (58.5%) patients were post autologous transplant. Twenty‐seven patients (42.8% of patients with available cytogenetic data) had high‐risk fluorescence in‐situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetic aberrations. Extramedullary disease (EMD) was present in 21.4% of evaluable patients, mostly paraskeletal (15.8%) and skin (3.5%).
The initial belantamab mafodotin dose was 2.5 mg/kg for 82 (80%) patients and 3.4 mg/kg for 20 (20%) patients. The median number of cycles administered was four (range 2–17) and five (range 2–17) cycles for the entire cohort and responding patients (patients achieving PR or better) respectively.
Efficacy
Response
The ORR was 45.5% (46/101); five patients could not be evaluated for response due to non‐secretory disease (bone marrow biopsy and/or imaging were unavailable). Rates of complete response, very good partial response and PR were 4.0%, 13.9% and 27.7% respectively. ORR rates were similar regardless of initial dose (47.4% for 2.5 mg/kg and 42.1% for 3.4 mg/kg, p = 0.1). Triple‐refractory and penta‐refractory patients responded similarly to the ORR of the entire cohort (Table 2). By univariate analysis, no significant association was found between age, sex, triple‐/penta‐refractoriness, international staging system (ISS), revised ISS, high‐risk cytogenetics and EMD to ORR. The proportional length of delayed cycles did not correlate with treatment outcomes (as detailed below). Ocular toxicity after the first dose did not affect response rate (ORR 8/20, 40%). The median time to first and best response was 23 (range 23–119) and 42 (range 7–152) days respectively.
TABLE 2.
Response rates, PFS and OS.
| N | ORR, % | Median PFS, months (95% CI) | Median OS, months (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire cohort | 106 | 45.5 a | 4.7 (3.5–5.9) | 14.5 (9.5–19.6) |
| Responders | 46 | 8.8 (6.6–10.9) | NR b | |
| Triple‐refractory | 77 | 43.0 c | 5.3 (3.6–6.9) | 14.5 (8.8–20.2) |
| Penta‐refractory | 34 | 45.4 d | 4.7 (3.2–6.2) | 13.8 (9.2–18.3) |
| Initial BELA dose 2.5 mg/kg | 82 e | 47.4 f | 5.1 (3.9–6.4) | 14.5 (11.3–17.7) |
| Initial BELA dose 3.4 mg/kg | 20 | 42.1 | 1.6 (0–4.2) | 9.5 (3.4–15.7) |
Abbreviations: BELA, belantamab mafodotin; CI, confidence interval; NR, not reached; ORR, overall response rate; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression‐free survival.
Response could be assessed in 101 patients.
There were not enough events to estimate a standard error for the median survival time.
Response could be assessed in 72 patients.
Response could be assessed in 33 patients.
Four patients had missing data regarding their initial dose.
Response could be assessed in 78 patients.
PFS, TTNT, DOR, and OS
The median follow‐up was 11.9 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 10.0–13.8]. Median PFS was 4.7 months (95% CI 3.5–5.9) for the entire cohort and 8.8 months (95% CI 6.6–10.9) for responders (Figure 1). TTNT was 5.4 months (95% CI 4–6.8). Median DOR was 8.1 months (95% CI 5.7–10.5). The median PFS was not different in the triple‐refractory patients [5.3 months (95% CI 3.6–6.9), p = 0.382] (Figure 2) and penta‐refractory patients [4.7 months (95% CI 3.2–6.2), p = 0.977]. Similarly, no difference in PFS was found between patient with and without high‐risk cytogenetics (p = 0.46). No statistically significant difference in PFS was found between patients starting at the 3.4 mg/kg dose [median PFS: 1.6 months (95% CI 0–4.2)] and 2.5 mg/kg dose [median PFS 5.1 months (95% CI 3.9–6.4)], p = 0.328 (Table 2). Median DOR for responders was also not different between patients receiving an initial dose of 3.4 mg/kg [6.4 months (95% CI 3.9–10.3)] and 2.5 mg/kg [8.1 months (95% CI 6.7–10.3)], p = 0.53.
FIGURE 1.
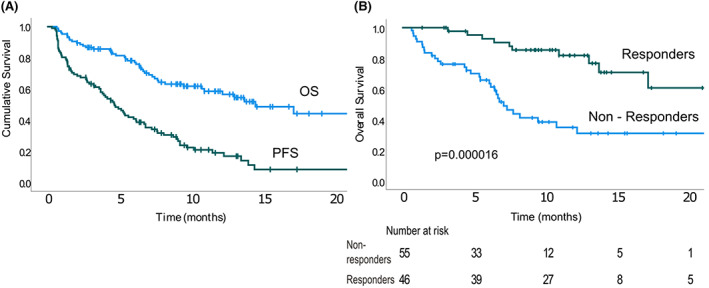
(A) Progression‐free survival and overall survival. (B) Overall survival was significantly longer among patients achieving partial response or better. OS, overall survival; PFS, progression‐free survival. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
FIGURE 2.
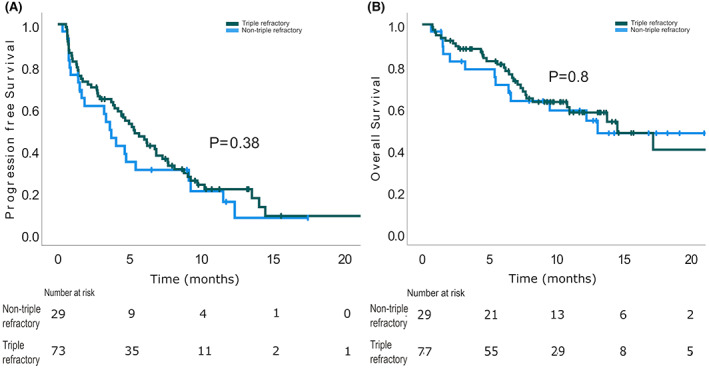
Progression‐free survival (A) and overall survival (B) were not statistically different among triple‐refractory and non‐triple‐refractory patients. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
The median OS was 14.5 months (95% CI 9.5–19.6). Patients achieving PR or better had a statistically significant longer OS [not reached (NR) for responders vs. 7.1 for non‐responders]. At 12 months the OS was 81.9% ± 6.3% versus 35.0% ± 7.5% in responders versus non‐responders (Figure 1) (p = 0.000016). This finding was consistent within the triple‐refractory patients [median OS NR for responders vs. 7.3 months (95% CI 6–8.6) for non‐responders, p = 0.0003]. The median OS was similar in the triple‐refractory patients and the non‐triple‐refractory cohort (14.5 months for triple‐refractory vs. 13.1 months for non‐triple‐refractory patients, respectively; p = 0.80) (Figure 2). At 12‐months, the OS for triple‐refractory was 57.8% ± 6.5%. Median OS for penta‐refractory patients was 13.8 months (95% CI 9.2–18.8) and was similar to that for the non‐penta‐refractory cohort (14.5 months, p = 0.768). The 12‐months OS for penta‐refractory was 61.7 ± 9.7% (Table 2). No difference was found in the OS of patients with and without high‐risk cytogenetics (p = 0.31).
Safety
Ocular toxicity
Data regarding ocular toxicity were available for 95 (89.6%) patients. Sixty‐five patients (68.4%) experienced keratopathy. Maximal grade of keratopathy reached grade 1, 2, 3 and 4 in 11.6%, 16.8%, 38.9% and 1.1% of patients, respectively. Of the 52 patients who experienced grade 2–4 corneal toxicity with available data, 33 (63.4%) had resolution to grade 1 or less during the follow‐up period. Thirteen (25.0%) and six (11.5%) patients remained with grade 2 and 3 keratopathy respectively. None of the patients had grade 4 keratopathy at the end of the follow‐up period. Blurred vision was reported in 36.8% (35/95) of patients with available data. Grade of blurred vision was 1, 2, 3, 4 in 13.7%, 16.9%, 5.3% and 1.0%, respectively. Of the 20 patients with grade 2 or worse blurred vision with available data, resolution to grade 1 or less was observed in 16 (75%) and four (25%) remained with grade 2, at time of data cut‐off. Four patients (3.8%) discontinued treatment due to ocular toxicity. These patients had a median PFS of 7.5 (range 5.7–21.7) months and median OS of 12.6 (range 7.5–21.7) months, respectively. Blurred vision significantly correlated with slit‐lamp findings: keratopathy grade 2 or more was associated with blurred vision (any grade); hazard ratio 14.5 (95% CI 4.0–53.2). No association was found between starting dose and keratopathy (p = 0.42) nor blurred vision (p = 0.49).
Non‐ocular toxicity
Safety data for non‐ocular AEs were reported for all patients. Most AEs were haematological. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 27.4% (grade ≥3: 17.9%; one major bleeding) of the patients, anaemia in 11.3% (grade ≥3: 3.8%) and neutropenia in 7.5% (grade ≥3: 4.7%). Other frequent (≥5%) AEs were infection (11.3%, grade ≥3: 3.8%) and hypersensitivity/infusion reaction (7.5%; grade ≥3: 2.8%). Two patients (1.9%) experienced hepatitis B virus reactivation. Two patients (1.9%) experienced tumour lysis syndrome; both had a high disease burden prior to belantamab mafodotin treatment initiation. Treatment‐related mortality was 1.9% (2/106). Both of these patients died from infections (pneumonia and sepsis). Reported non‐ocular AEs are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3.
Treatment‐emergent adverse events (non‐ocular).
| All grades n (%) | Grade 3–5 a n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia | 29 (27.4) | 19 (17.9) |
| Infection | 12 (11.3) | 8 (7.5) |
| Anaemia | 12 (11.3) | 4 (3.8) |
| Hypersensitivity/infusion reaction | 8 (7.5) | 3 (2.8) |
| Neutropenia | 8 (7.5) | 5 (4.7) |
| Transaminitis | 5 (4.7) | 1 (0.9) |
| Dry eyes | 5 (4.7) | 0 |
| Fever | 4 (3.8) | 1 (0.9) |
| TLS | 2 (1.9) | 1 (0.9) |
| Cholangitis/elevated bilirubin | 2 (1.9) | 2 (1.9) |
| CMV reactivation | 2 (1.9) | 2 (1.9) |
| AKI | 2 (1.9) | 1 (0.9) |
| Nausea/vomiting | 2 (1.9) | 1 (0.9) |
| Diarrhoea | 2 (1.9) | 1 (0.9) |
| Confusion | 2 (1.9) | 0 |
| Hepatitis B reactivation | 2 (1.9) | 0 |
| Dermatitis | 1 (0.9) | 0 |
| Other b | 11 (10.3) | 6 (5.6) |
Abbreviations: AKI, acute kidney injury; CMV, cytomegalovirus; TLS, tumour lysis syndrome.
Two grade 5 adverse events were reported (pneumonia and sepsis).
Other adverse effects included (one event each): cough, fatigue, gastritis, general deterioration, gamma glutamyl transferase increase, hypotension, impaired hearing, listeria cerebritis, peripheral neuropathy, pneumonitis, sialadenitis.
Dose delays
In all, 524 doses were recorded. Of 97 patients with available data, 54 (55.6%) experienced dose delays. Of the 418 doses given beyond the first dose, 116 doses were delayed (27.8%). Dose were delayed due to ocular toxicity in 82 cases (70.7%), haematological toxicity in 11 cases (9.5%) and infections in four (3.5%) cases. Nineteen cases of delay had other reason. The median duration of delay (per dose) was 31 days (range: 1–153 days). First delay occurred in the second, third, fourth or fifth cycle in 10.3%, 29.3%, 15.2% and 14.5%, respectively (percentages are calculated from the number of patients receiving this cycle). Five patients (out of 36, 13.8%) had their first delay beyond the fifth cycle. Out of 33 patients who had dose delay because of ocular toxicity and received subsequent doses, 26 (78.8%) had at least 1 more dose delay secondary to ocular toxicity. Proportion of dose delays, calculated as cumulative number of days of delay divided by number of cycles (see the “Methods” section) did not correlate significantly with response rates, as mentioned earlier.
DISCUSSION
We present real‐world data on 106 RRMM patients treated in Israel between 2019 and 2021with belantamab mafodotin with or without corticosteroids under the GSK compassionate programme. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest belantamab mafodotin real‐world series reported to date. This was a heavily pretreated population of patients, who has a dismal prognosis and represent an urgent unmet need for new therapeutic options. In our cohort, belantamab mafodotin monotherapy resulted in an encouraging response rate, as well as OS and PFS, considerably higher than expected in this patient population. 1 These findings were obtained in a real‐world compassionate programme setting, with a broad patient population, excluding mostly patients with severe renal failure and very low cytopenia. A comparison between clinical trials cohorts and our cohort is presented in Table 4. Notably, our cohort population was older (with almost one quarter of patients older than 75 years) and had similar rates of multidrug‐refractory patients to the DREAMM2 cohort and higher compared to DREAMM1. Yet, response rates were 45% (exceeding response rates in DREAMM2). The PFS was 4.7 months, and DOR 8.1 months. OS was relatively favourable with a median of 14.5 ± 2.5 months. A highly significant difference was noticed in PFS and OS among responders versus non‐responders, suggesting the improved OS is likely attributable to belantamab mafodotin therapy. The PFS and OS of responders in our study are comparable to the results published for the 2.5 mg/kg cohort of the DREAMM2 study, with a median estimated PFS and OS of 6.2 months and 13.7 months for responders respectively. 13 Another encouraging finding was that response rates, PFS and OS were not inferior for triple‐ and penta‐refractory patients. Efficacy and safety outcomes did not differ in patients receiving an initial dose of 3.4 or 2.5 mg/kg.
TABLE 4.
Comparison between phase 1 and phase 2 clinical trial and study cohort
| DREAMM1 11 | DREAMM2 12 | Real‐world a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 mg/kg | 3.4 mg/kg | |||
| Patients, n | 35 | 97 | 96 | 106 |
| Age, years; median (range) | 60 (46–75) | 65 (60–70) | 67 (61–72) | 69 (36–88) |
| >75 years, n (%) | NR | 13 (13) | 17 (17) | 24 (23) |
| ISS 1/2/3, % | 54/17/11 | 22/34/43 | 18/51/30 | 43/30/26 |
| High‐risk cytogenetics, n(%) | ||||
| del17p | 6 (17) | 16 (16) | 22 (22) | 12 (19) |
| t 4;14 | 3 (9) | 11 (11) | 11 (11) | 1 (1.6) |
| t 14;16 | 1 (3) | 7 (7) | 2 (2) | 1 (1.6) |
| +1q gain/amp | 3 (9) | 25 (26) | 30 (30) | 18 (28) |
| Extra‐medullary disease | NR | 22 (23) | 18 (18) | 12 (21) |
| Number of previous lines, n (range) | 5 (1–10+) | 7 (3–21) | 6 (3–21) | 6 (2–11) |
| Exposure/refractoriness to anti‐myeloma drugs; (%/%) | ||||
| PIs | ||||
| Bortezomib | 100/97 | 98/76 | 98/75 | 97/58 |
| Carfilzomib | NR | 76/65 | 65/58 | 72/64 |
| IMiDs | ||||
| Lenalidomide | 83/77 | 100/90 | 100/89 | 92/74 |
| Pomalidomide | 100/94 | 92/87 | 85/78 | 77/63 |
| Daratumumab | NR | 100/100 | 97/92 | 95/80 |
| Triple refractory, % | 63/63 | 100 | 100 | 73 |
| Penta‐refractory, n (%) | 40/40 | 32 | ||
Abbreviations: IMiD, immunomodulatory drug; ISS, international staging system; NR, not reached; PI, proteasome inhibitor.
Percentages in real‐world cohort are computed from number of patients with available data.
Toxicity, mainly ocular toxicity, is associated with belantamab mafodotin therapy in the real‐world setting, comparable to the findings observed in clinical trials. Among patients, 69% experienced keratopathy, 41% of them grade ≥3, very similar to the DREAMM2 13‐months follow‐up update. 13 High rates (36.8%) of blurred vision were recorded, consistent with the results of the clinical trials (25%–34%), and similarly, only a minority (6.3%) of these cases was high‐grade (grade 3–4). 11 , 13 Keratopathy and blurred vision were reversible in the majority of patients. Although a significant portion remained with some degree of ocular toxicity at the time of data cut‐off, follow‐up time was short and thus, improvement could have occurred later. All of the above‐mentioned findings regarding ocular toxicity are in concordance with the clinical trials results 11 , 13 and no new safety signals were noted. Not surprisingly, keratopathy grade 2 or more significantly correlated with blurred vision. Abeykoon et al. recently published their analysis of a real‐world RRMM cohort treated with belantamab mafodotin, focusing on ocular toxicity and its consequences. 21 They found a similar rate of ocular toxicity (75%) but a higher rate of treatment discontinuation secondary to this toxicity (14%). Interestingly, they found ocular toxicity after the first dose to be a significant predictor of response. The authors concluded that keratopathy significantly complicates belantamab mafodotin therapy and mitigates its full potential. 21 Compromised efficacy due to treatment discontinuation and/or delays, and association between toxicity after the first cycle and response rates, were not found in our current study. Further analysis of real‐world cohorts may contribute to further clarification of this important issue.
Haematological toxicity was manageable, although concern for thrombocytopenic bleeds remains a challenge in the ambulatory setting in some patients. Infectious complications were not uncommon, highlighting the need for close surveillance and early intervention as needed. The two cases of hepatitis B reactivation are worrisome, and repeated testing prior to initiation of treatment should be considered. We report two cases of tumour lysis syndrome, not previously reported in clinical trials but reported by Vaxman et al. 16 in the real‐world setting, highlighting the need for risk assessment and appropriate prophylactic and supportive measures in high‐risk patients.
Our study has several limitations. First, due to its retrospective nature, not all data were available. Second, exclusion of three patients receiving only one dose may have caused overestimation of response rates, PFS and OS; however, the small number could not skew the results significantly. Importantly, none of these patients discontinued therapy beyond first dose because of AEs. Third, the compassionate access programme did have exclusion criteria (see the “Methods” section) and may not fully represent all real‐life patients.
To conclude, belantamab mafodotin efficacy was confirmed in a real‐world setting, in patients with advanced RRMM. Response rate, duration of response and toxicity profile appear to be comparable to those observed in prospective trial settings. Ocular toxicity remains a major challenge due to the high percentage of keratopathy, dose reduction and delays. Nevertheless, these findings support the role of belantamab mafodotin as a benificial treatment option for heavily pretreated RRMM patients.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Tamir Shragai and Yael C. Cohen designed the study, collected the data and wrote the manuscript. Efrat Luttwak performed the statistical analyses and also wrote the manuscript. Tamir Shragai, Hila Magen, Noa Lavi, Moshe Gatt, Svetlana Trestman, Miri Zektser, Chezi Ganzel, Osnat Jarchowsky, Tamar Berger, Tamar Tadmor, Merav Leiba, Katrin Hertzog‐Tzarfaty, Netanel Horowitz, Michael Shapira, Irit Avivi, Efrat Luttwak and Yael C. Cohen contributed patients. David Varssano, Yoav Berger, Shahar Frenkel and Mark Krauthammer performed the ophthalmologic testing. All authors had access to the study data, proofread the manuscript, agreed with the content, and approved its submission.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no competing interests. Yael C. Cohen received honoraria from GSK, unrelated to this research. All other authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Supporting information
Appendix S1
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The Israeli Belantamab Mafodotin compassionate care programme was supported by GSK. The authors wish to thank Claire Wardel D.Phil and the GSK Israel Belantamab Mafodotin expanded compassionate programme for their collaboration. The authors wish to thank Mr Nathan Melamed from the haematology institute, Tel‐Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, for his technical support preparing the figures.
Shragai T, Magen H, Lavi N, Gatt M, Trestman S, Zektser M, et al. Real‐world experience with belantamab mafodotin therapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: A multicentre retrospective study. Br J Haematol. 2023;200(1):45–53. 10.1111/bjh.18479
Tamir Shragai and Hila Magen share equal contribution.
Local EC number: 0362‐18.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
For the original data, please contact the corresponding author at tamirsh@tlvmc.gov.il.
REFERENCES
- 1. Gandhi UH, Cornell RF, Lakshman A, Gahvari ZJ, McGehee E, Jagosky MH, et al. Outcomes of patients with multiple myeloma refractory to CD38‐targeted monoclonal antibody therapy. Leukemia. 2019. Sep 1;33(9):2266–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. O'Connor BP, Raman VS, Erickson LD, Cook WJ, Weaver LK, Ahonen C, et al. BCMA is essential for the survival of long‐lived bone marrow plasma cells. J Exp Med. 2004. Jan 5;199(1):91–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Sanchez E, Li M, Kitto A, Li J, Wang CS, Kirk DT, et al. Serum B‐cell maturation antigen is elevated in multiple myeloma and correlates with disease status and survival. Br J Haematol. 2012. Sep;158(6):727–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Cohen YC, Cohen AD, Delforge M, Hillengass J, Goldschmidt H, Weisel K, et al. Efficacy and safety of Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel (Cilta‐cel), a B‐cell maturation antigen (BCMA)‐directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T‐cell therapy, in lenalidomide‐refractory patients with progressive multiple myeloma after 1‐3 prior lines of therapy: updated results from CARTITUDE‐2. Blood. 2021. Nov 23;138(Suppl 1):3866–6. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Berdeja JG, Madduri D, Usmani SZ, Jakubowiak A, Agha M, Cohen AD, et al. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a B‐cell maturation antigen‐directed chimeric antigen receptor T‐cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CARTITUDE‐1): a phase 1b/2 open‐label study. Lancet. 2021. Jul 24;398(10297):314–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Raje N, Berdeja J, Lin Y, Siegel D, Jagannath S, Madduri D, et al. Anti‐BCMA CAR T‐cell therapy bb2121 in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2019. May 2;380(18):1726–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Munshi NC, Anderson LD, Shah N, Madduri D, Berdeja J, Lonial S, et al. Idecabtagene vicleucel in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021. Feb 25;384(8):705–16. 10.1056/NEJMoa2024850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Topp MS, Duell J, Zugmaier G, Attal M, Moreau P, Langer C, et al. Anti‐B‐cell maturation antigen BiTE molecule AMG 420 induces responses in multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2020. Mar 10;38(8):775–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Moreau P. Updated results from MajesTEC‐1: phase 1/2 study of teclistamab, a B‐cell maturation antigen × CD3 bispecific antibody, in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. ASH. 2021;138:896. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Usmani SZ, Garfall AL, van de Donk NWCJ, Nahi H, San‐Miguel JF, Oriol A, et al. Teclistamab, a B‐cell maturation antigen × CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (MajesTEC‐1): a multicentre, open‐label, single‐arm, phase 1 study. Lancet (London, England). 2021. Aug 21;398(10301):665–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Trudel S, Lendvai N, Popat R, Voorhees PM, Reeves B, Libby EN, et al. Targeting B‐cell maturation antigen with GSK2857916 antibody‐drug conjugate in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (BMA117159): a dose escalation and expansion phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018. Dec 1;19(12):1641–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lonial S, Lee HC, Badros A, Trudel S, Nooka AK, Chari A, et al. Belantamab mafodotin for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (DREAMM‐2): a two‐arm, randomised, open‐label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019 Dec 2019 Dec [cited 2020 Jan 6]; Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1470204519307880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lonial S, Lee HC, Badros A, Trudel S, Nooka AK, Chari A, et al. Longer term outcomes with single‐agent belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: 13‐month follow‐up from the pivotal DREAMM‐2 study. Cancer. 2021. Nov 15;127(22):4198–212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chari A, Romanus D, Palumbo A, Blazer M, Farrelly E, Raju A, et al. Randomized clinical trial representativeness and outcomes in real‐world patients: comparison of 6 Hallmark randomized clinical trials of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020. Jan 1;20(1):8–17.e16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Becnel M, Ferreri CJ, Feng L, Richards TA, Horowitz SB, Patel N, et al. Retrospective, single‐center, real‐world experience of belantamab mafodotin in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2022. Jun 2;40(16_suppl):8060. 10.1200/JCO20224016_suppl8060 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Vaxman I, Abeykoon J, Dispenzieri A, Kumar SK, Buadi F, Lacy MQ, et al. “Real‐life” data of the efficacy and safety of belantamab mafodotin in relapsed multiple myeloma—the Mayo Clinic experience. Blood Cancer J. 2021. Dec 7;11(12):196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Atieh T, Atrash S, Mohan M, Shune L, Mahmoudjafari Z, Quick J, et al. Belantamab in combination with dexamethasone in patients with triple‐class relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood. 2021. Nov 23;138(Suppl 1):1642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)‐a metadata‐driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009. Apr 1;42(2):377–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Kumar S, Paiva B, Anderson KC, Durie B, Landgren O, Moreau P, et al. International myeloma working group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:e328–e346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. National Cancer Institute . Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 [Internet]. 2017. [cited 2022 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.meddra.org/
- 21. Abeykoon JP, Vaxman J, Patel SV, Kumar S, Malave GC, Young KS, et al. Impact of belantamab mafodotin‐induced ocular toxicity on outcomes of patients with advanced multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2022. 10.1111/bjh.18298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix S1
Data Availability Statement
For the original data, please contact the corresponding author at tamirsh@tlvmc.gov.il.


