Abstract
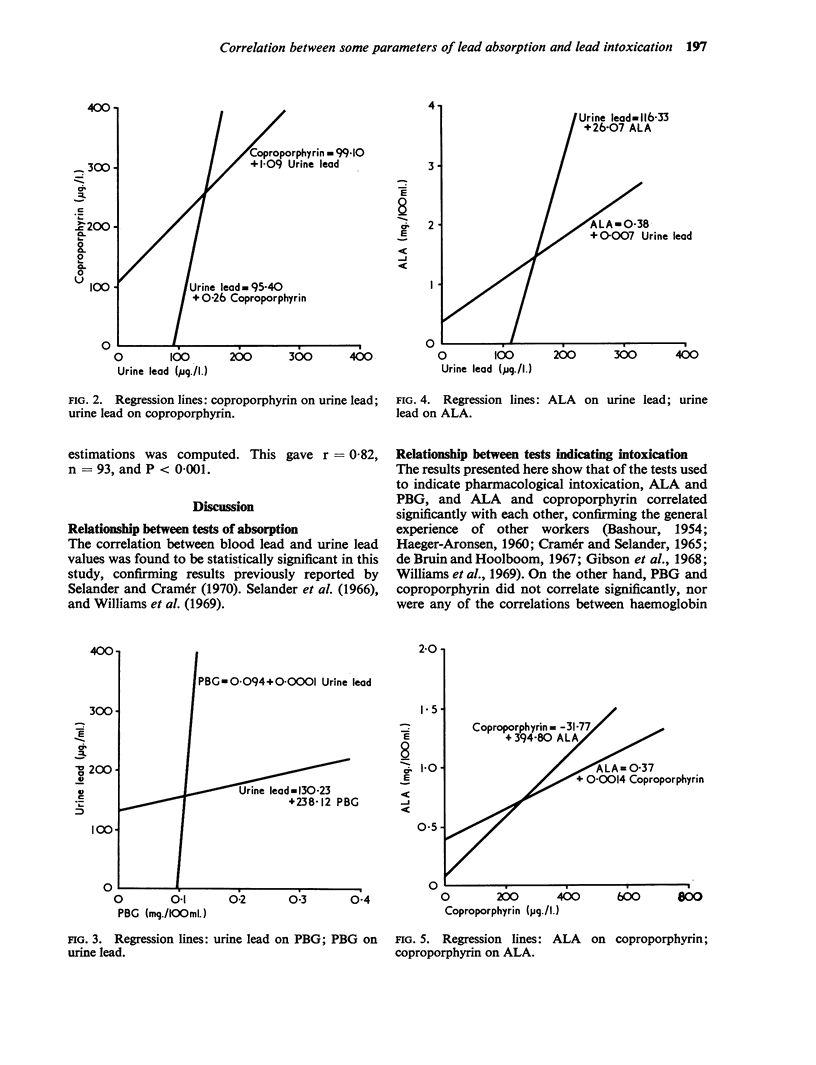
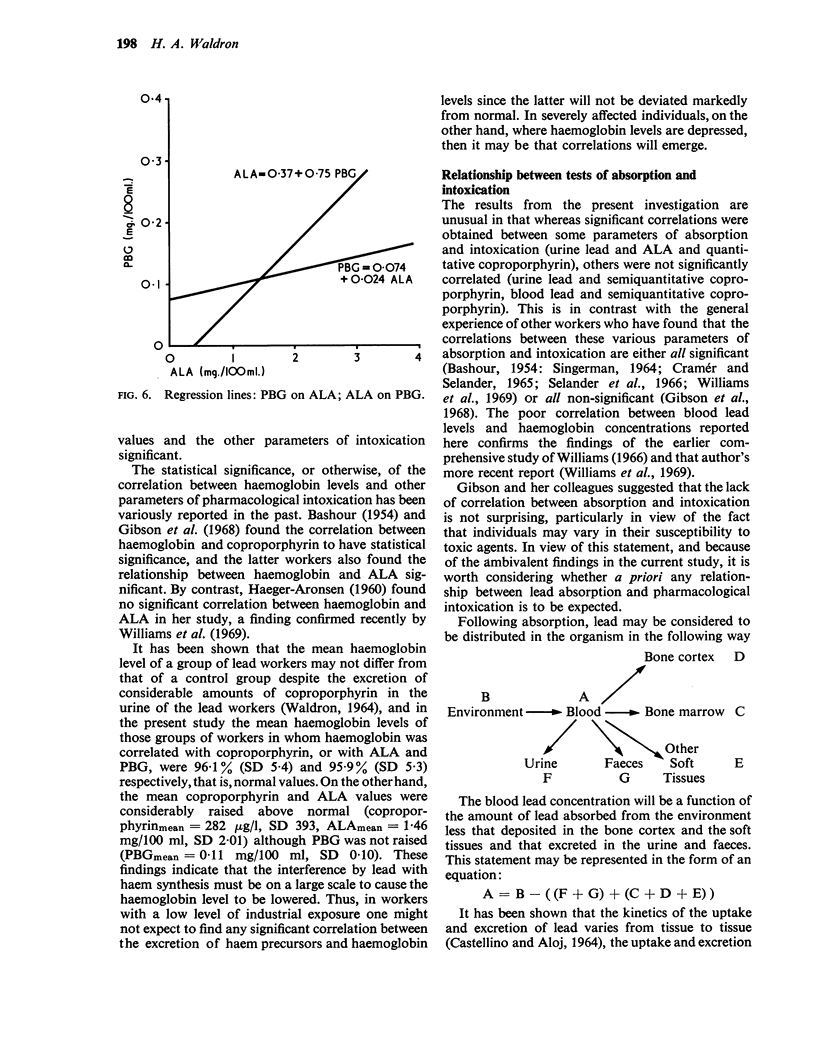
Waldron, H. A. (1971).Brit. J. industr. Med.,28, 195-199. Correlation between some parameters of lead absorption and lead intoxication. Use has been made of data collected over a number of years from workers exposed to a lead hazard in a motor-car factory. The correlations between various parameters of lead absorption and lead intoxication were computed, including blood and urine lead concentrations, urinary coproporphyrin, ALA and PBG concentrations, and haemoglobin concentration. In all, 15 correlation coefficients were calculated, of which only six showed a statistically significant result (i.e., P<0·05). These six were blood lead and urine lead (r = 0·38, P<0·001), urine lead and coproporphyrin (r = 0·42, P<0·001), urine lead and ALA (r = 0·43, P<0·001), coproporphyrin and ALA (r = 0·75, P<0·001), ALA and PBG (r = 0·49, P<0·001), and urine lead and PBG (r = 0·19, P<0·05).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS A. L. An appraisal of a urinary porphyrin test in detection of lead absorption. Ind Med Surg. 1951 Sep;20(9):390–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTELLINO N., ALOJ S. KINETICS OF THE DISTRIBUTION AND EXCRETION OF LEAD IN THE RAT. Br J Ind Med. 1964 Oct;21:308–314. doi: 10.1136/oem.21.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramér K., Selander S. Studies in lead poisoning. Comparison between different laboratory tests. Br J Ind Med. 1965 Oct;22(4):311–314. doi: 10.1136/oem.22.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE KRETSER A. J., WALDRON H. A. Urinary delta aminolaevulinic acid and porphobilinogen in lead-exposed workers. Br J Ind Med. 1963 Jan;20:35–40. doi: 10.1136/oem.20.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin A., Hoolboom H. Early signs of lead-exposure. A comparative study of laboratory tests. Br J Ind Med. 1967 Jul;24(3):203–212. doi: 10.1136/oem.24.3.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W. Urinary screening tests to detect excessive lead absorption. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Oct;23(4):263–281. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. L., Mackenzie J. C., Goldberg A. The diagnosis of industrial lead poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Jan;25(1):40–51. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLYNEUX M. K. USE OF SINGLE URINE SAMPLES FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF LEAD ABSORPTION. Br J Ind Med. 1964 Jul;21:203–209. doi: 10.1136/oem.21.3.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGERMAN A. STUDIES ON LEAD POISONING IN ARGENTINA. Arch Environ Health. 1964 Oct;9:464–472. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1964.10663866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander S., Cramér K., Hallberg L. Studies in lead poisoning. Oral therapy with penicillamine: relationship between lead in blood and other laboratory tests. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Oct;23(4):282–291. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.4.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander S., Cramér K. Interrelationships between lead in blood, lead in urine, and ALA in urine during lead work. Br J Ind Med. 1970 Jan;27(1):28–39. doi: 10.1136/oem.27.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDRON H. A. PLASMA PORPHYRINS IN LEAD WORKERS. Br J Ind Med. 1964 Oct;21:315–317. doi: 10.1136/oem.21.4.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman M. P., Pfitzer E., Ellis L. D., Jensen W. N. Concentrations of lead in bone in plumbism. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 2;273(23):1246–1250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512022732304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. K. Blood lead and haemoglobin in lead absorption. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. K., King E., Walford J. An investigation of lead absorption in an electric accumulator factory with the use of personal samplers. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Jul;26(3):202–216. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.3.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


