Abstract
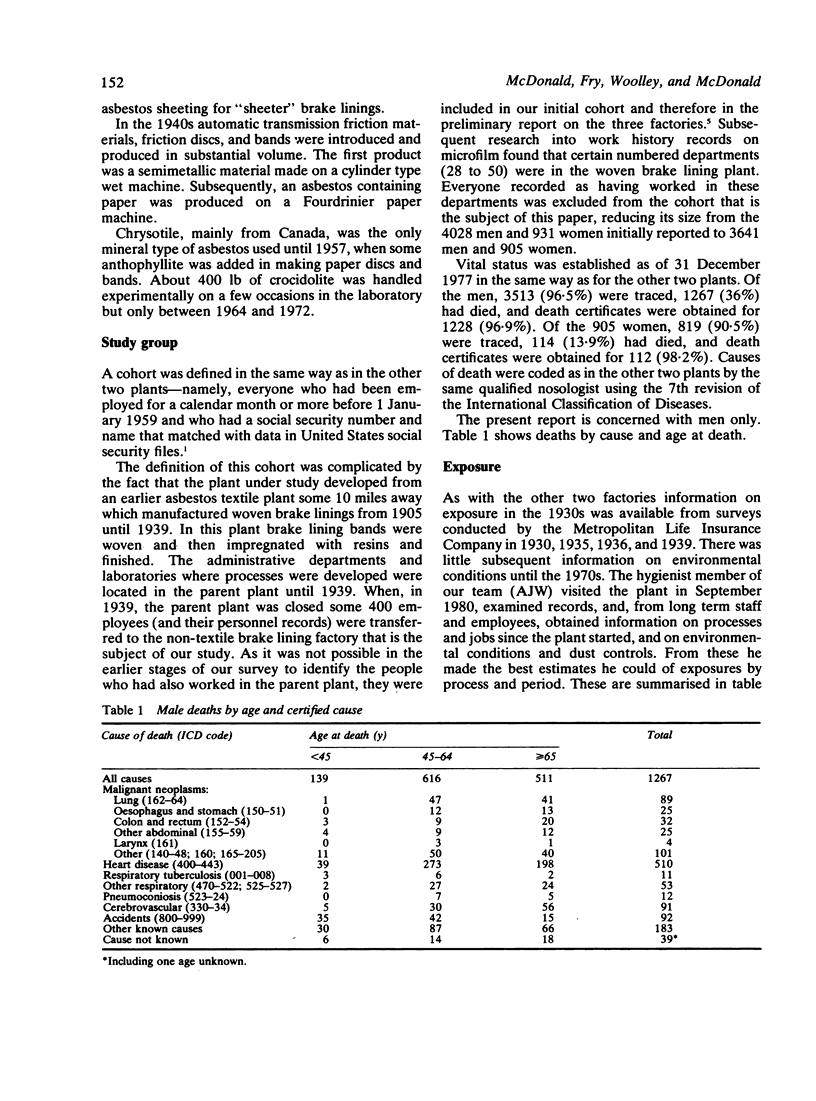
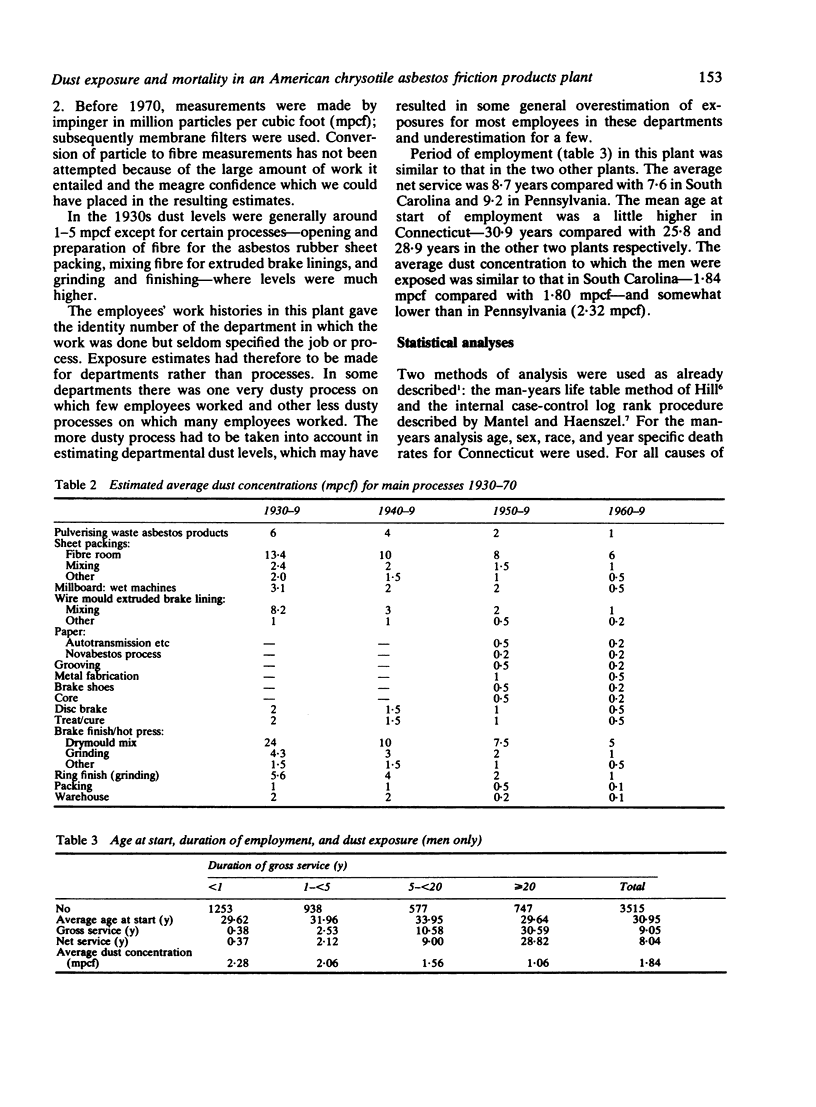
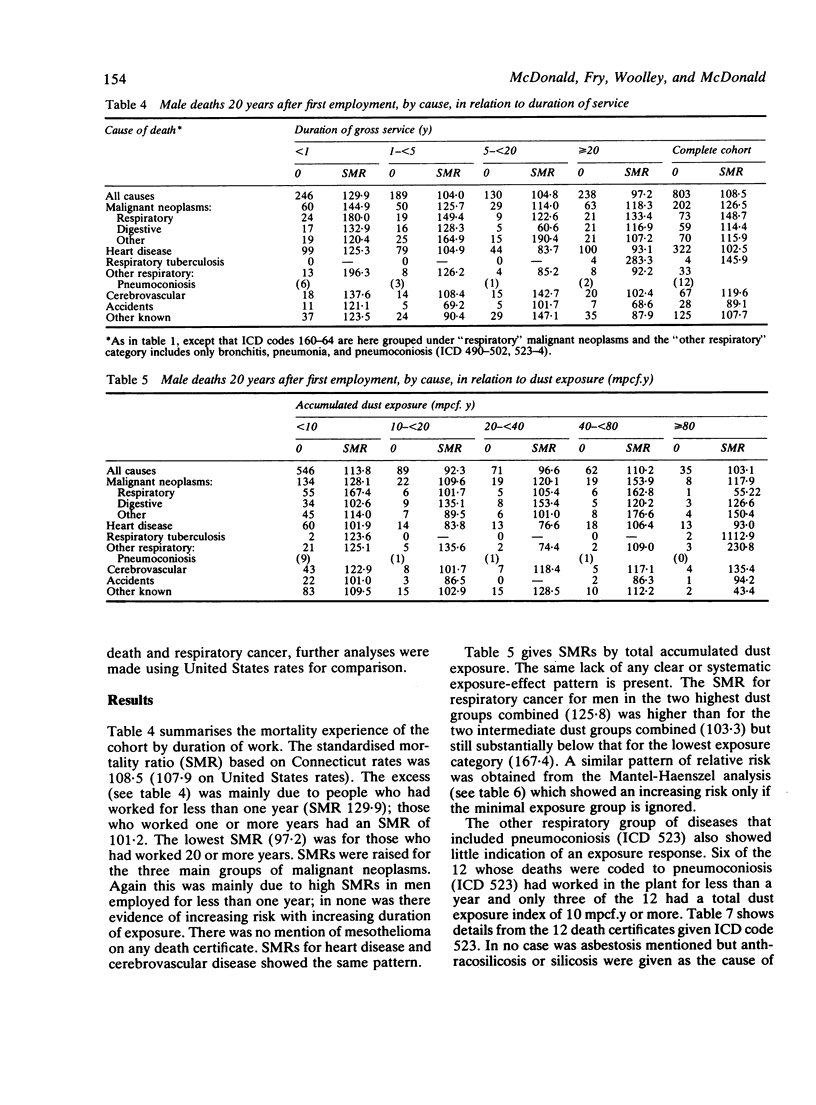
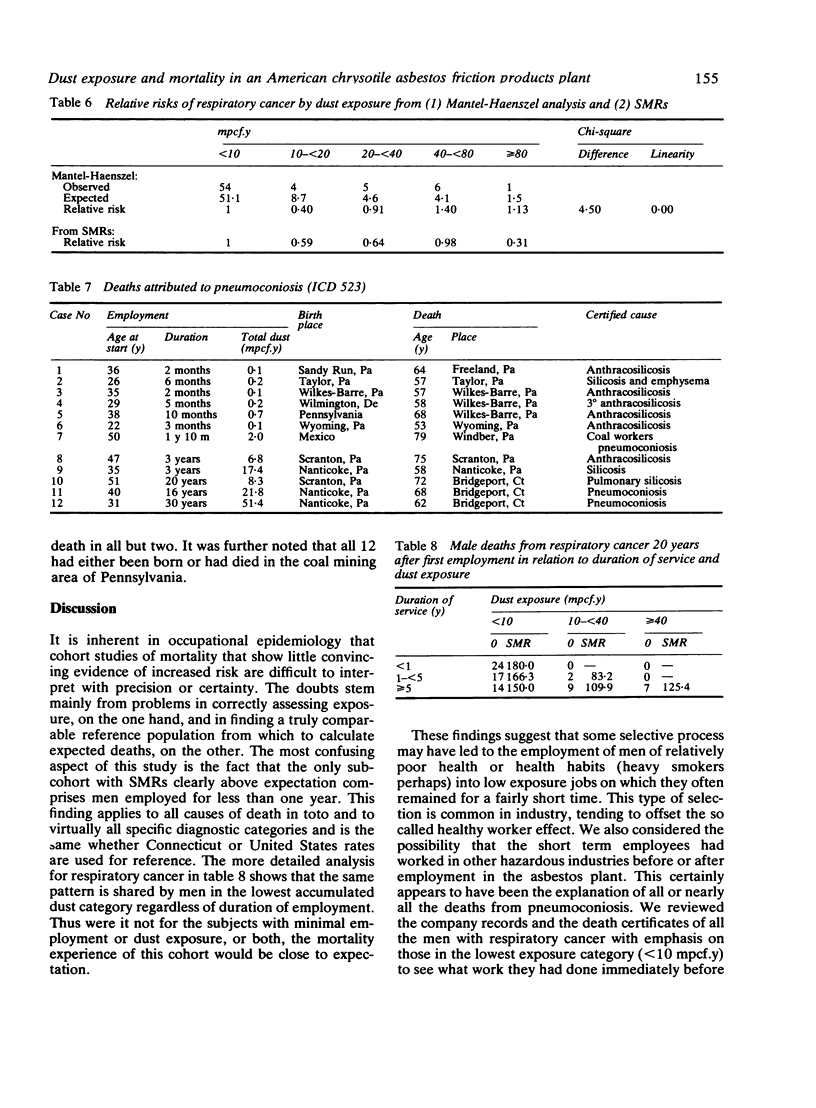
Cohort studies in three American asbestos factories were undertaken to investigate the effect of fibre type and manufacturing process on lung cancer, mesothelioma, and asbestosis. Reports have been published on a chrysotile textile plant in South Carolina and a mainly textile plant in Pennsylvania, which also used amphiboles. In the third plant in Connecticut friction products and packings were made from chrysotile only. In a cohort of 3641 men employed for one month or more, 1938-58, 3513 (96.5%) were traced, 1267 (36%) had died, and death certificates were obtained for 1228 (96.9%). Individual exposures were estimated (in mcpf . years) from impinger measurements. Life table analyses using Connecticut mortality rates gave an SMR for all causes of 108.5 (USA 107.9). The SMR (all causes) for men who had worked for less than a year was 129.9 and for those who had worked for a year or more, 101.2. The equivalent SMRs for respiratory cancer were 167.4 and 136.7 respectively. Excluding men who had worked for less than a year, there was possible evidence of some increase in risk of lung cancer with increasing exposure, supported also by a "log-rank" (case-control) analysis, of the same order as that observed in chrysotile mining and milling. These findings may be compared with chrysotile textile manufacture where the risk of lung cancer was some 50-fold greater. It is suggested that the differences in risk are perhaps related to the higher proportion of submicroscopic fibres in textile manufacture that may result from the traumatic carding , spinning, and weaving processes. No case of mesothelioma was found, consistent with a much lower risk of this tumour with chrysotile than with amphiboles. Twelve deaths (nine in men with very short and low asbestos exposure) were given ICD code 523 (pneumoconiosis); all but two were ascribed to anthracosilicosis or silicosis and none to asbestosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry G., Newhouse M. L. Mortality of workers manufacturing friction materials using asbestos. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Feb;40(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
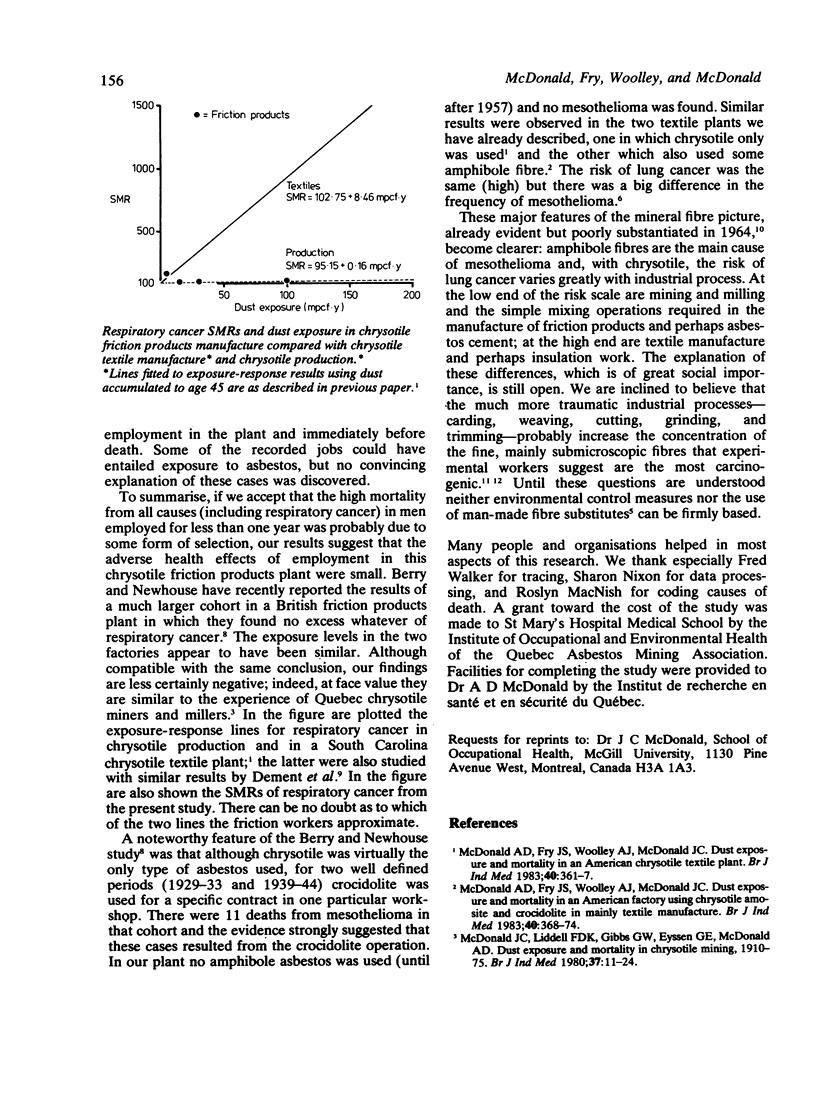
- Dement J. M., Harris R. L., Jr, Symons M. J., Shy C. Estimates of dose-response for respiratory cancer among chrysotile asbestos textile workers. Ann Occup Hyg. 1982;26(1-4):869–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill I. D. Computing man years at risk. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1972 May;26(2):132–134. doi: 10.1136/jech.26.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. D., Fry J. S. Mesothelioma and the fiber type in three American asbestos factories - preliminary report. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1982;8 (Suppl 1):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. D., Fry J. S., Woolley A. J., McDonald J. C. Dust exposure and mortality in an American factory using chrysotile, amosite, and crocidolite in mainly textile manufacture. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Nov;40(4):368–374. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.4.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. D., Fry J. S., Woolley A. J., McDonald J. Dust exposure and mortality in an American chrysotile textile plant. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Nov;40(4):361–367. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. C., Liddell F. D., Gibbs G. W., Eyssen G. E., McDonald A. D. Dust exposure and mortality in chrysotile mining, 1910-75. Br J Ind Med. 1980 Feb;37(1):11–24. doi: 10.1136/oem.37.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


