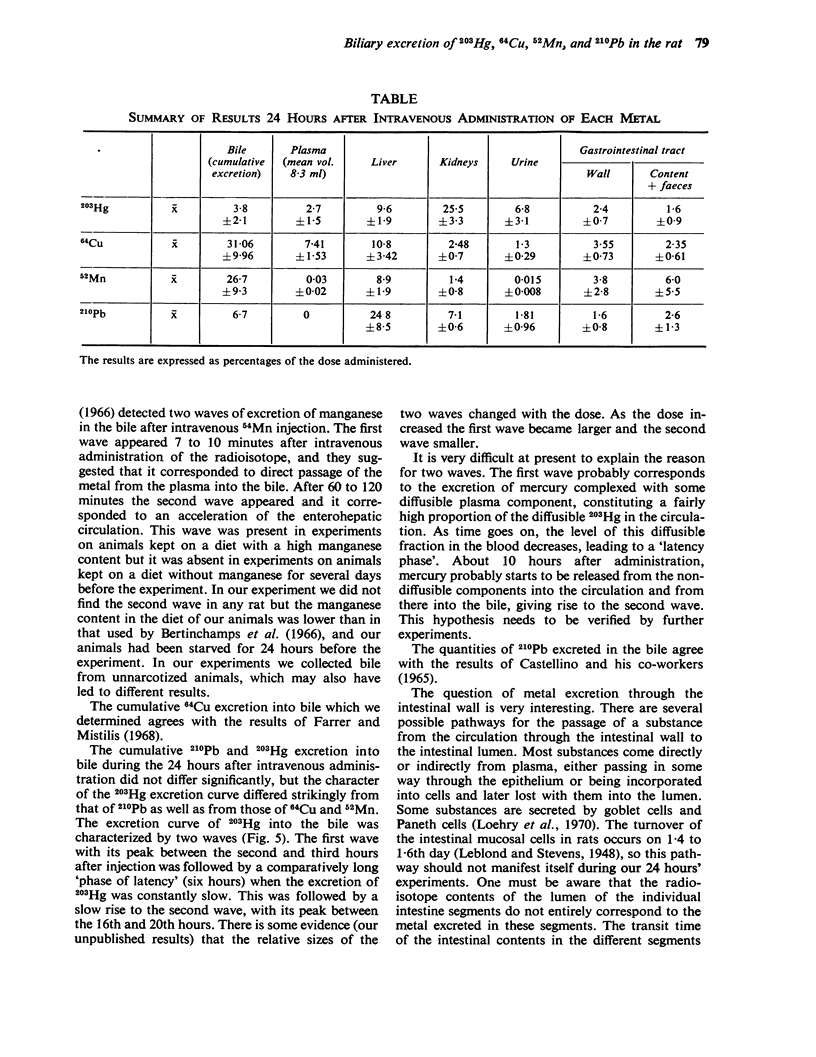
Abstract
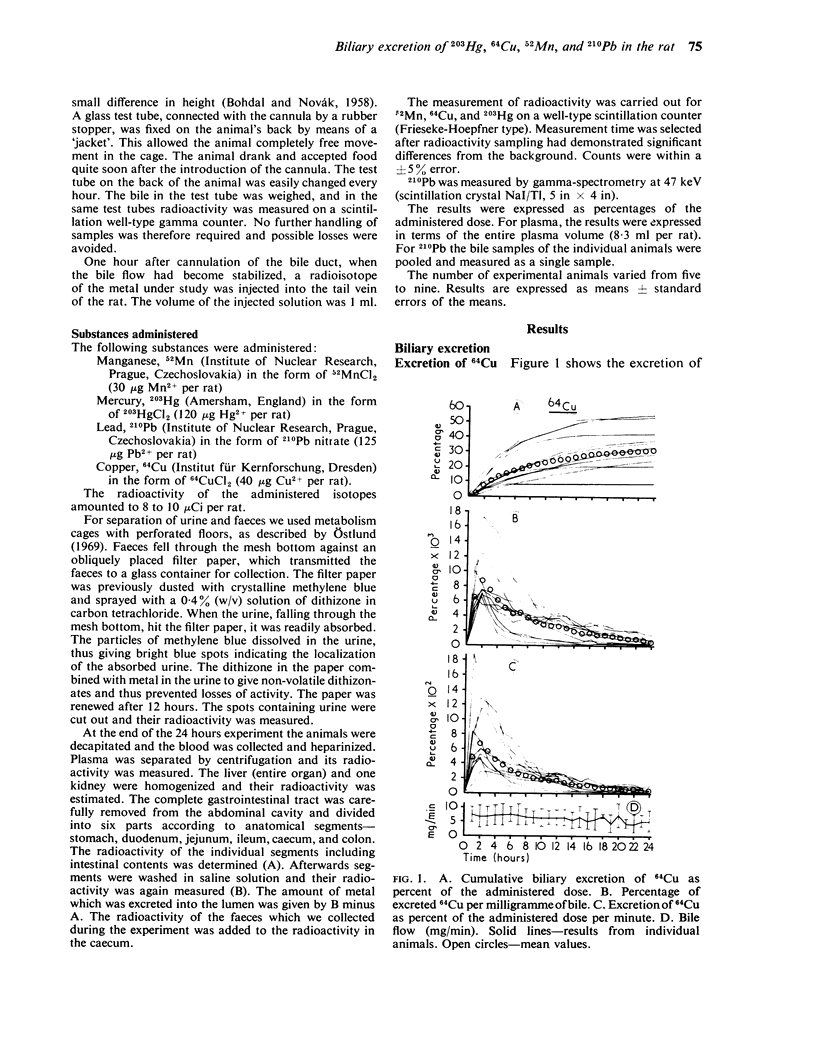
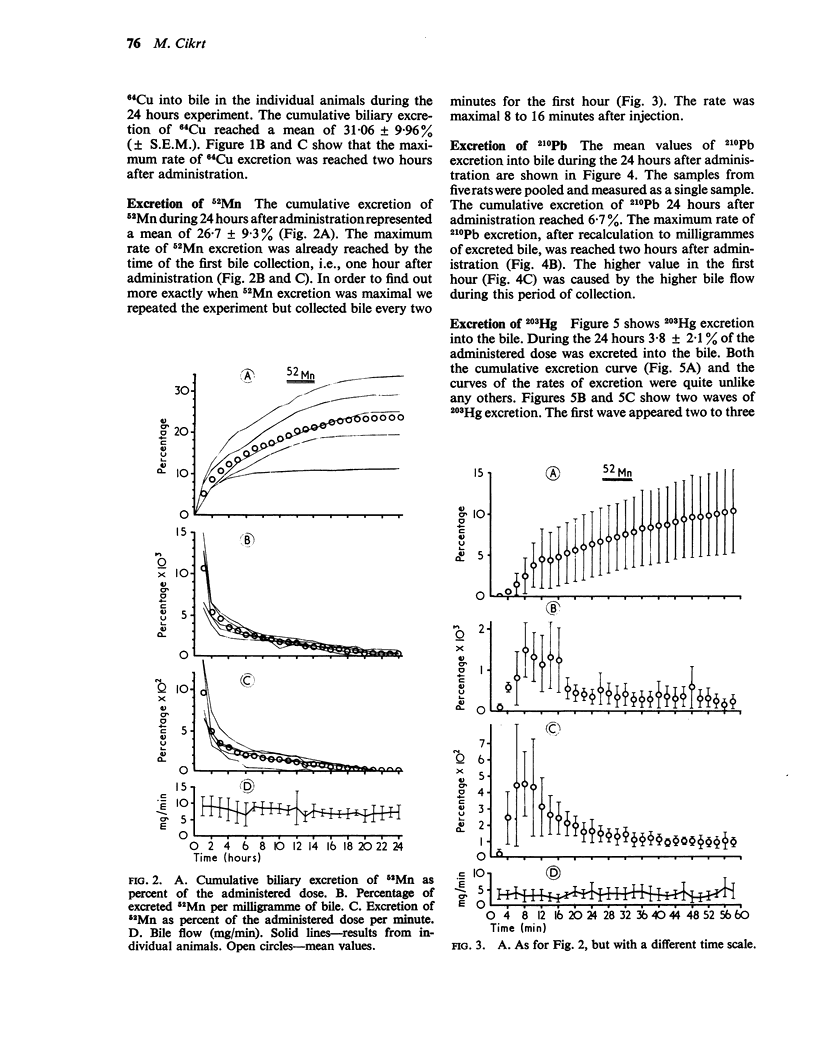
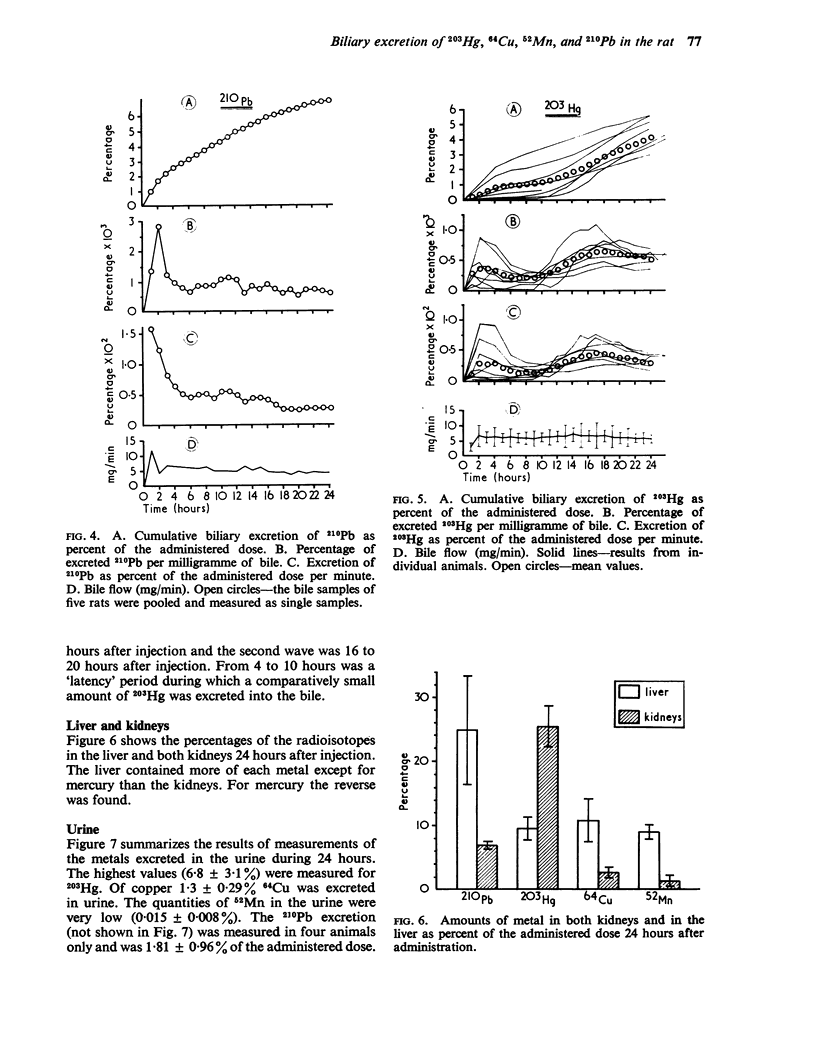
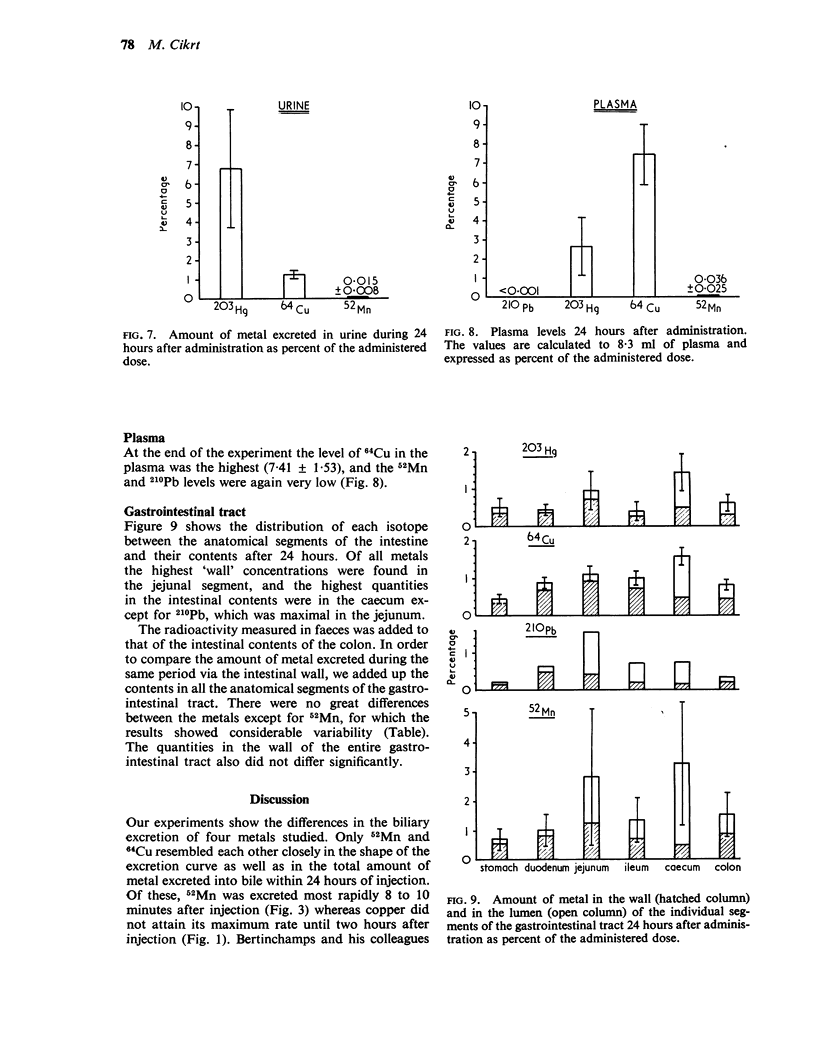
Cikrt, M. (1972).Brit. J. industr. Med.,29, 74-80. Biliary excretion of 203Hg, 64Cu, 52Mn, and 210Pb in the rat. The biliary excretion of 52Mn, 64Cu, 203Hg, and 210Pb after intravenous adminstration of 52MnCl2, 64CuCl2, 203HgCl2, and 210Pb (NO3)2 in non-toxic doses was studied in rats. Cumulative biliary excretion reached by 24 hours after administration in the case of 64Cu 31·06%, of 52Mn 26·7%, of 203Hg 3·8%, and of 210Pb 6·7% of the administered dose. The excretion curve for 203Hg differed significantly from those of the other three metals. The maximum rate of excretion was reached at different periods after administration for each metal. The excretion of the metals via the wall of the gastrointestinal tract during 24 hours after administration was also studied. The excretion into faeces occurred mainly via the bile; to a lesser extent there was excretion through the wall, probably chiefly of the upper segments of the digestive tract.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertinchamps A. J., Miller S. T., Cotzias G. C. Interdependence of routes excreting manganese. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):217–224. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cikrt M. The uptake of Hg203, Cu64, Mn52, and Pb212 by the intestinal wall of the duodenal and ileal segment in vitro. Int Z Klin Pharmakol Ther Toxikol. 1970 Oct;3(4):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIBERG L. Studies on the accumulation, metabolism and excretion of inorganic mercury (Hg203) after prolonged subcutaneous administration to rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1956;12(4):411–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1956.tb01402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN M. I. Pancreatic secretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1958 Sep;194(3):535–539. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.3.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaballah S. S., Abood L. G., Caleel G. T., Kapsalis A. Uptake and biliary excretion of Cu64 in rabbits in relation to blood ceruloplasmin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):733–735. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehry C. A., Axon A. T., Hilton P. J., Hider R. C., Creamer B. Permeability of the small intestine to substances of different molecular weight. Gut. 1970 Jun;11(6):466–470. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.6.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS C. S., LENGEMANN F. W. Use of radioyttrium to study food movement in the small intestine of the rat. J Nutr. 1962 Feb;76:179–182. doi: 10.1093/jn/76.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau N., Aspin N., Sass-Kortsak A. Absorption of copper 64 from gastrointestinal tract of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Feb;218(2):377–383. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistilis S. P., Farrer P. A. The absorption of biliary and non-biliary radiocopper in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(6):586–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN C. A., Jr ABSORPTION AND EXCRETION OF CU64-LABELED COPPER BY THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Dec;207:1203–1206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou P. S., Miller S. T., Cotzias G. C. Role of liver in regulating distribution and excretion of manganese. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):211–216. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITSCHI H. P. TIEREXPERIMENTELLE UNTERSUCHUNGEN ZUR ENTERALEN BLEIAUSSCHEIDUNG. Int Arch Gewerbepathol Gewerbehyg. 1964 May 12;20:449–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


