Abstract
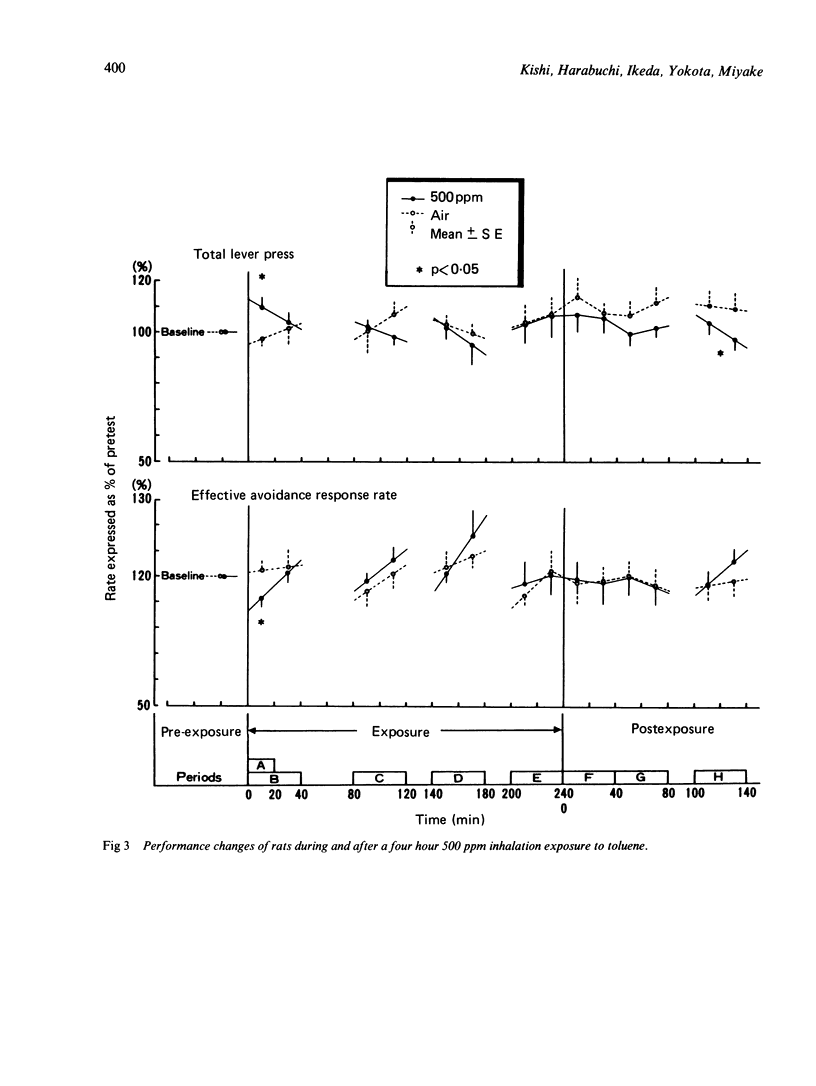
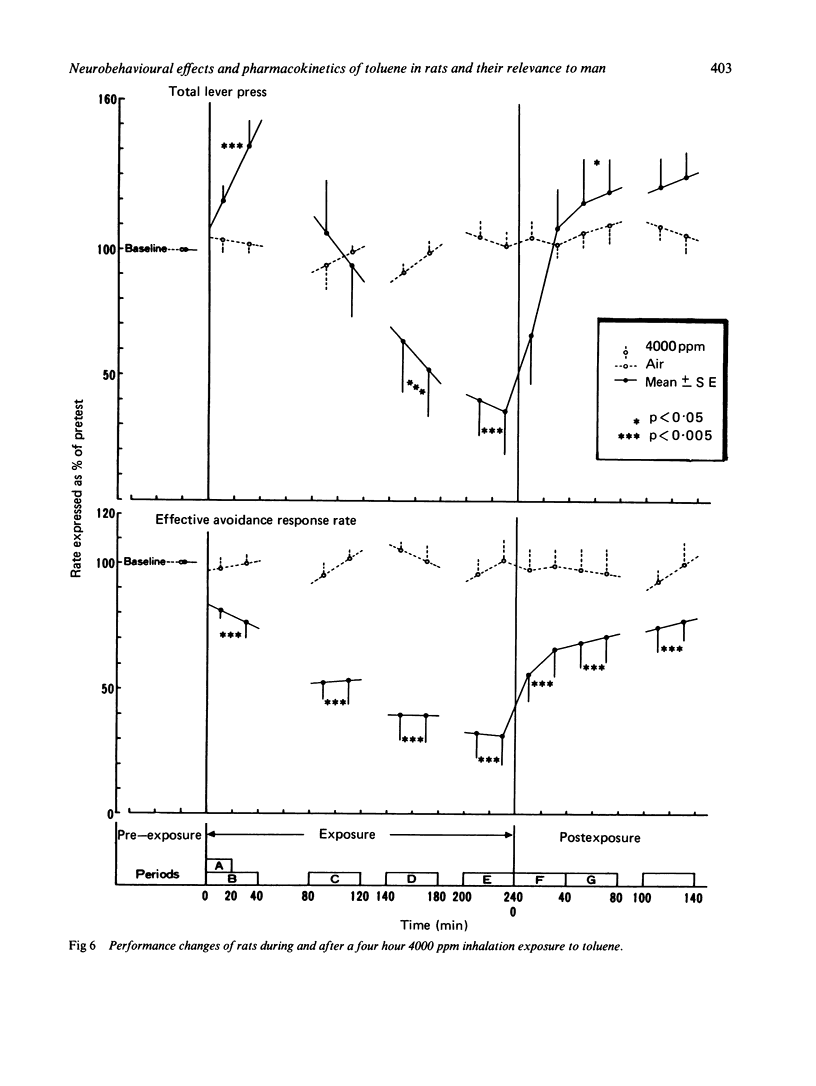
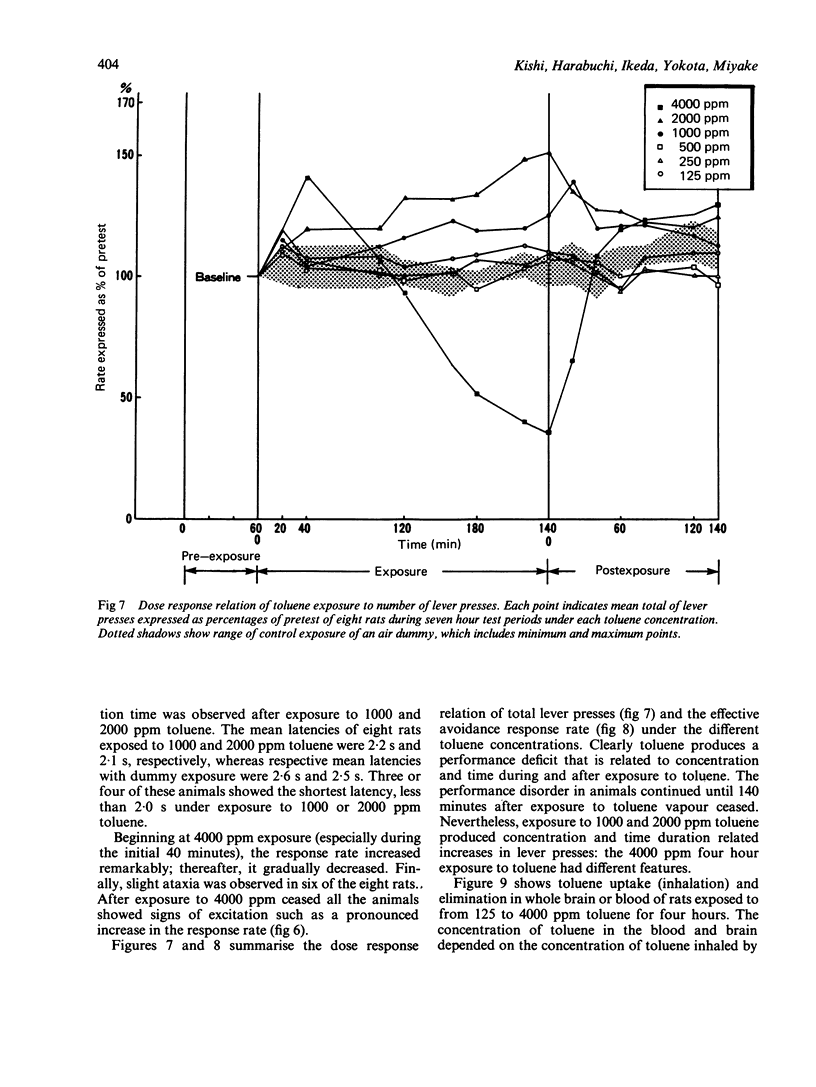
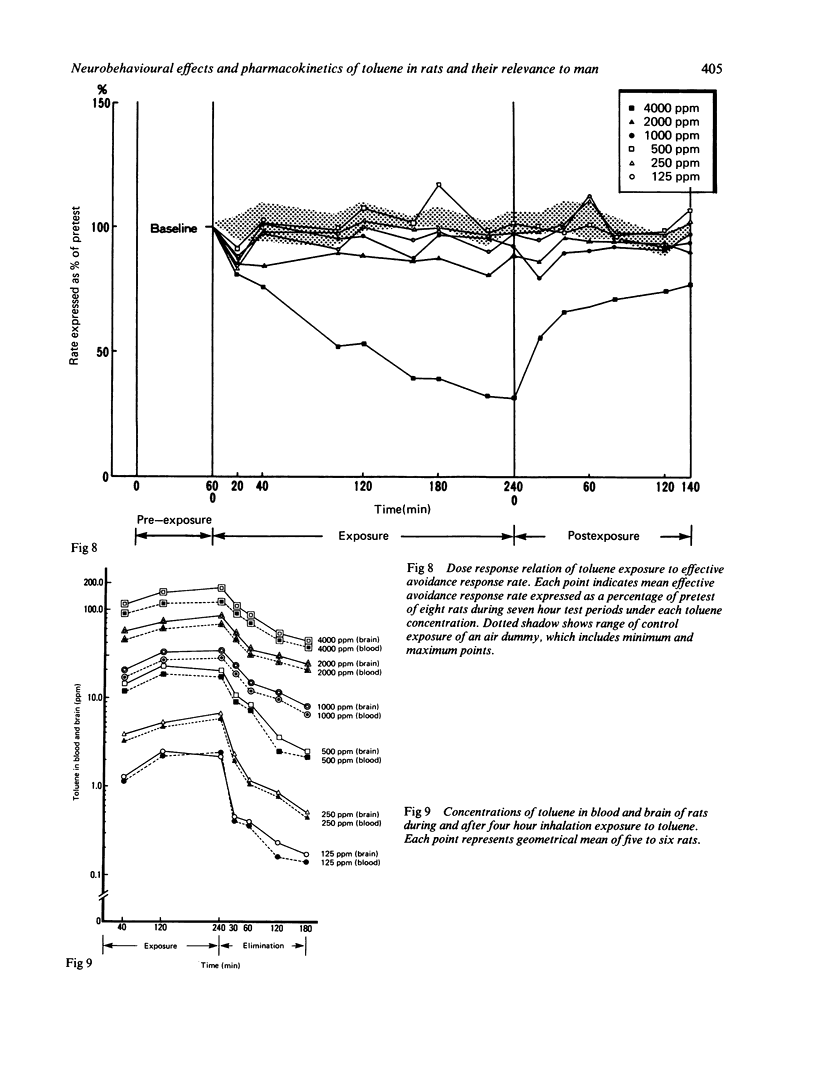
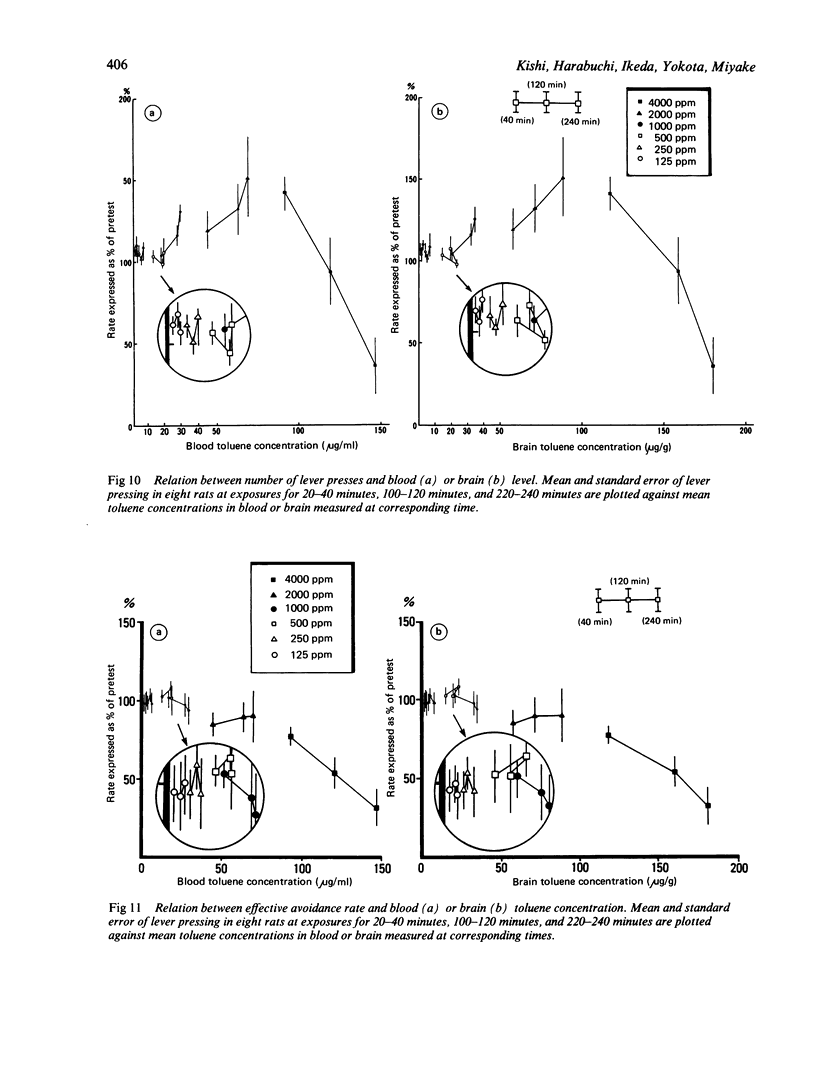
The present study was designed to determine the critical concentrations in blood and brain associated with specific behavioural changes during and after exposure to toluene. The effects of a single four hour exposure to toluene on signalled bar press shock avoidance in rats were tested. Rats exposed to 125, 250, and 500 ppm toluene showed a decline in conditioned avoidance responses at 20 minutes exposure compared with the pre-exposure baseline, although they recovered to almost the same level of performance as that before exposure. Exposure to 1000 ppm toluene for about four hours and 2000 ppm for two hours produced a concentration related increase in incorrect responses, acceleration of the reaction time, and decreases in the effective avoidance response rate. Beginning at 4000 ppm toluene exposure, the response rate increased; thereafter, it gradually decreased and finally slight ataxia was observed. After 4000 ppm exposure, all rats showed signs of excitation such as a pronounced increase in response rate. From analysis of the temporal courses of the blood and brain toluene concentrations during and after each exposure, excitative performance decrements were noticed in rats with blood and brain concentrations about 27 micrograms/ml blood and 32 micrograms/g respectively. Anaesthetic performance decrements were seen when the blood toluene concentration increased to 120 micrograms/ml and that of the brain reached about 160 micrograms/g. According to our results, the effects on the central nervous system are considered to be a function of both the exposure concentration and its duration, which are closely related to the increase of brain and blood toluene concentration.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baelum J., Andersen I. B., Lundqvist G. R., Mølhave L., Pedersen O. F., Vaeth M., Wyon D. P. Response of solvent-exposed printers and unexposed controls to six-hour toluene exposure. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Aug;11(4):271–280. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benignus V. A., Muller K. E., Barton C. N., Bittikofer J. A. Toluene levels in blood and brain of rats during and after respiratory exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;61(3):326–334. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benignus V. A. Neurobehavioral effects of toluene: a review. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1981 Winter;3(4):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick R. B., Setzer J. V., Wait R., Hayden M. B., Taylor B. J., Tolos B., Putz-Anderson V. Effects of acute exposure of toluene and methyl ethyl ketone on psychomotor performance. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1984;54(2):91–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00378512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harabuchi I., Kishi R., Ikeda T., Kiyosawa H., Miyake H. [A chronobiological study on toluene anesthesia in mice]. Sangyo Igaku. 1984 Jul;26(4):279–282. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.26.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashima T., Fukui M., Masuda Y., Wakasugi C., Hayama R. [Report of five cases where an ordinary vinyl bag was used for suicidal purpose. (Suffocation, CO-poisoning and "thinner"-poisoning)]. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 1969 May;23(3):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake H., Ikeda T., Maehara N., Harabuchi I., Kishi R., Yokota H. Slow learning in rats due to long-term inhalation of toluene. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser V. C., Balster R. L. Acute motor and lethal effects of inhaled toluene, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, halothane, and ethanol in mice: effects of exposure duration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;77(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama K., Nomiyama H. Three fetal cases of thinner-sniffing, and experimental exposure to toluene in human and animals. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1978 Jan 27;41(1):55–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00377799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., Wood R. W., McCormick J. P., Cox C. Toxicokinetics of toluene in the rat. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Aug;11(4):301–306. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nakajima T., Fujiwara Y. Determination of benzene and toluene in blood by means of a syringe-equilibration method using a small amount of blood. Br J Ind Med. 1975 Aug;32(3):210–214. doi: 10.1136/oem.32.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. D., Evans H. L. Effects of toluene inhalation on behavior and expired carbon dioxide in macaque monkeys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 30;80(3):487–495. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A., Cherry N., Johnston J. D. The effects of ethanol on blood toluene concentrations. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;51(4):365–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00378350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron H. A., Cherry N., Johnston J. D. The effects of ethanol on blood toluene concentrations. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;51(4):365–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00378350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Wood R. W., Macys D. A. Behavioral toxicology of carbon disulfide and toluene. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Jun;30:39–45. doi: 10.1289/ehp.793039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


