Abstract
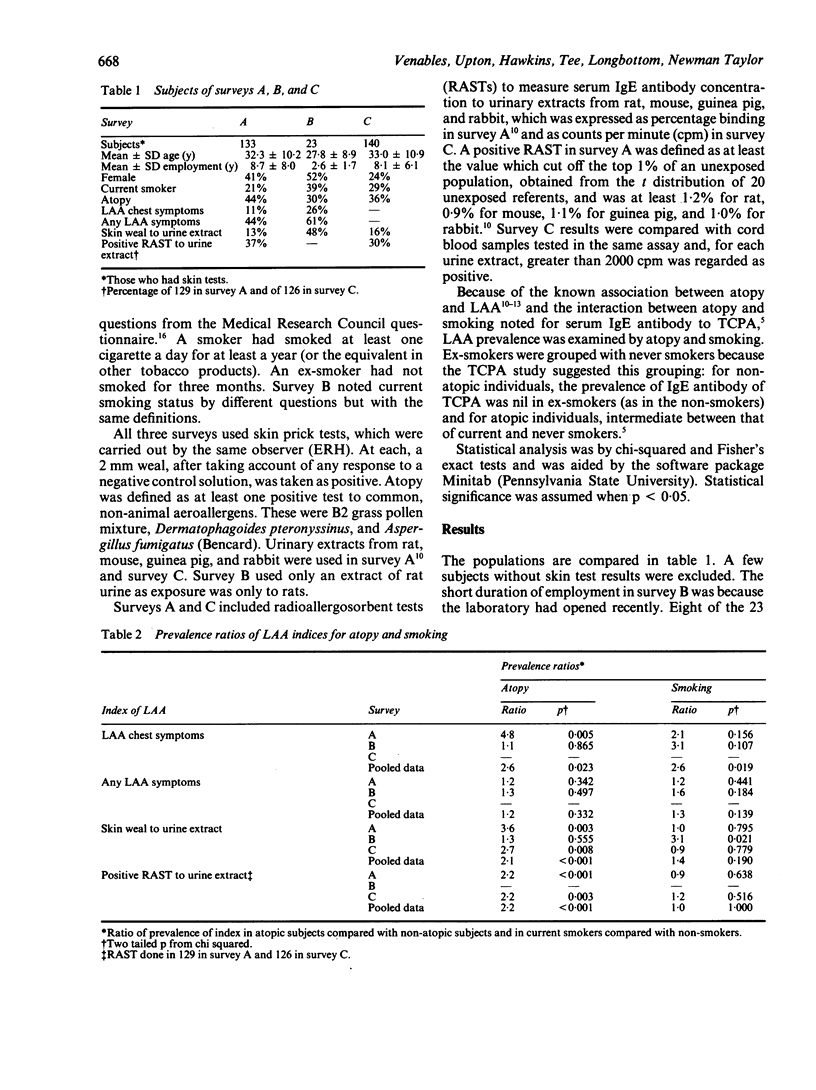
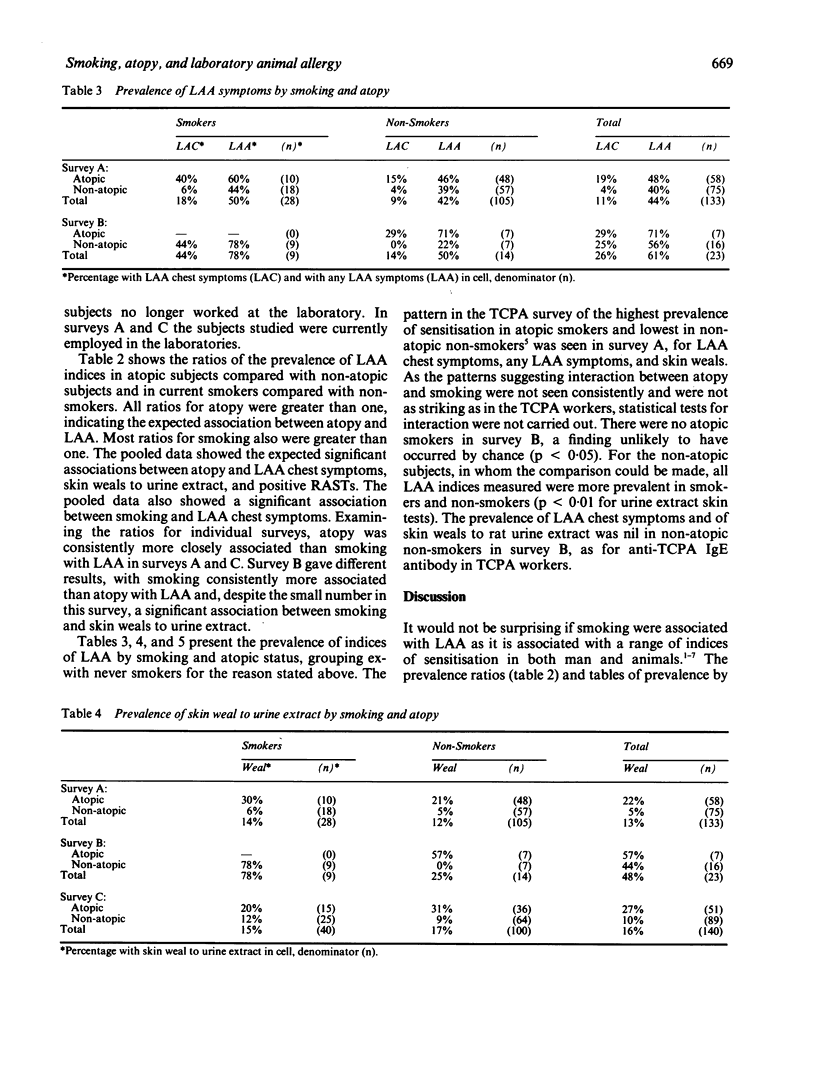
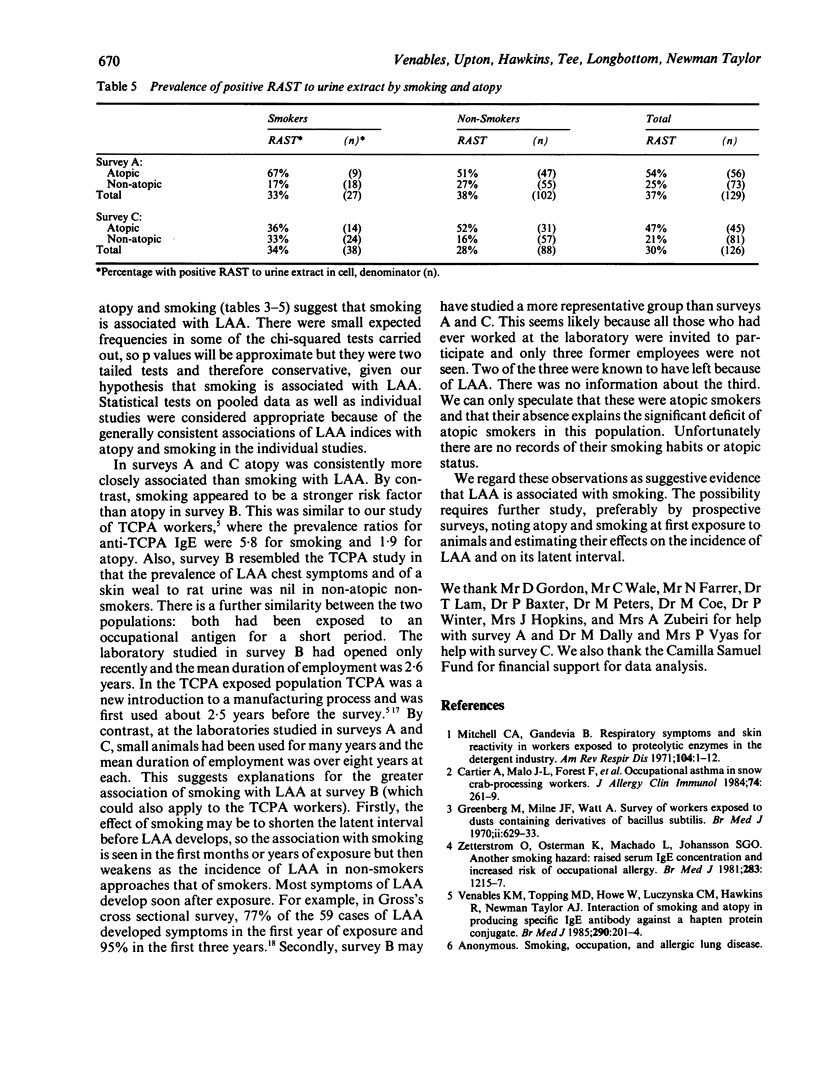
This study examined data from three cross sectional surveys of 296 laboratory workers exposed to small mammals. Four indices of laboratory animal allergy were studied: symptoms suggestive of occupational asthma, symptoms suggestive of any occupational allergy, skin weals to animal urine extracts, and serum binding in radioallergosorbent tests with urine extracts. Pooled data from the three surveys showed an association between smoking and all indices except radioallergosorbent tests; the association was significant for symptoms of occupational asthma. One of the three surveys consistently showed a stronger association of allergy indices with smoking than with atopy (defined on skin tests with non-animal aeroallergens). Associations with smoking persisted after stratifying by atopic status, suggesting that smoking may be a risk factor for laboratory animal allergy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beeson M. F., Dewdney J. M., Edwards R. G., Lee D., Orr R. G. Prevalence and diagnosis of laboratory animal allergy. Clin Allergy. 1983 Sep;13(5):433–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1983.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagini R. E., Moorman W. J., Lewis T. R., Bernstein I. L. Ozone enhancement of platinum asthma in a primate model. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Oct;134(4):719–725. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartier A., Malo J. L., Forest F., Lafrance M., Pineau L., St-Aubin J. J., Dubois J. Y. Occupational asthma in snow crab-processing workers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;74(3 Pt 1):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft A., Edwards J., McCarthy P., Andersson N. Allergy in laboratory animal workers. Lancet. 1981 Apr 11;1(8224):827–830. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92693-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M., Milne J. F., Watt A. Survey of workers exposed to dusts containing derivatives of Bacillus subtilis. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 13;2(5710):629–633. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5710.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Allergy to laboratory animals: epidemiologic, clinical, and physiologic aspects, and a trial of cromolyn in its management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Aug;66(2):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe W., Venables K. M., Topping M. D., Dally M. B., Hawkins R., Law J. S., Taylor A. J. Tetrachlorophthalic anhydride asthma: evidence for specific IgE antibody. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Jan;71(1 Pt 1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y. The effects of ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide on the experimentally induced allergic respiratory disorder in guinea pigs. I. The effect on sensitization with albumin through the airway. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Sep;102(3):430–437. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. A., Gandevia B. Respiratory symptoms and skin reactivity in workers exposed to proteolytic enzymes in the detergent industry. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jul;104(1):1–12. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovak A. J., Hill R. N. Laboratory animal allergy: a clinical survey of an exposed population. Br J Ind Med. 1981 Feb;38(1):38–41. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soter N. A., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Cold urticaria: release into the circulation of histamine and eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis during cold challenge. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 25;294(13):687–690. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603252941302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables K. M., Tee R. D., Hawkins E. R., Gordon D. J., Wale C. J., Farrer N. M., Lam T. H., Baxter P. J., Newman Taylor A. J. Laboratory animal allergy in a pharmaceutical company. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Oct;45(10):660–666. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.10.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables K. M., Topping M. D., Howe W., Luczynska C. M., Hawkins R., Taylor A. J. Interaction of smoking and atopy in producing specific IgE antibody against a hapten protein conjugate. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jan 19;290(6463):201–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6463.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström O., Nordvall S. L., Björkstén B., Ahlstedt S., Stelander M. Increased IgE antibody responses in rats exposed to tobacco smoke. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 May;75(5):594–598. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström O., Osterman K., Machado L., Johansson S. G. Another smoking hazard: raised serum IgE concentration and increased risk of occupational allergy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Nov 7;283(6301):1215–1217. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6301.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


