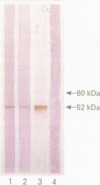
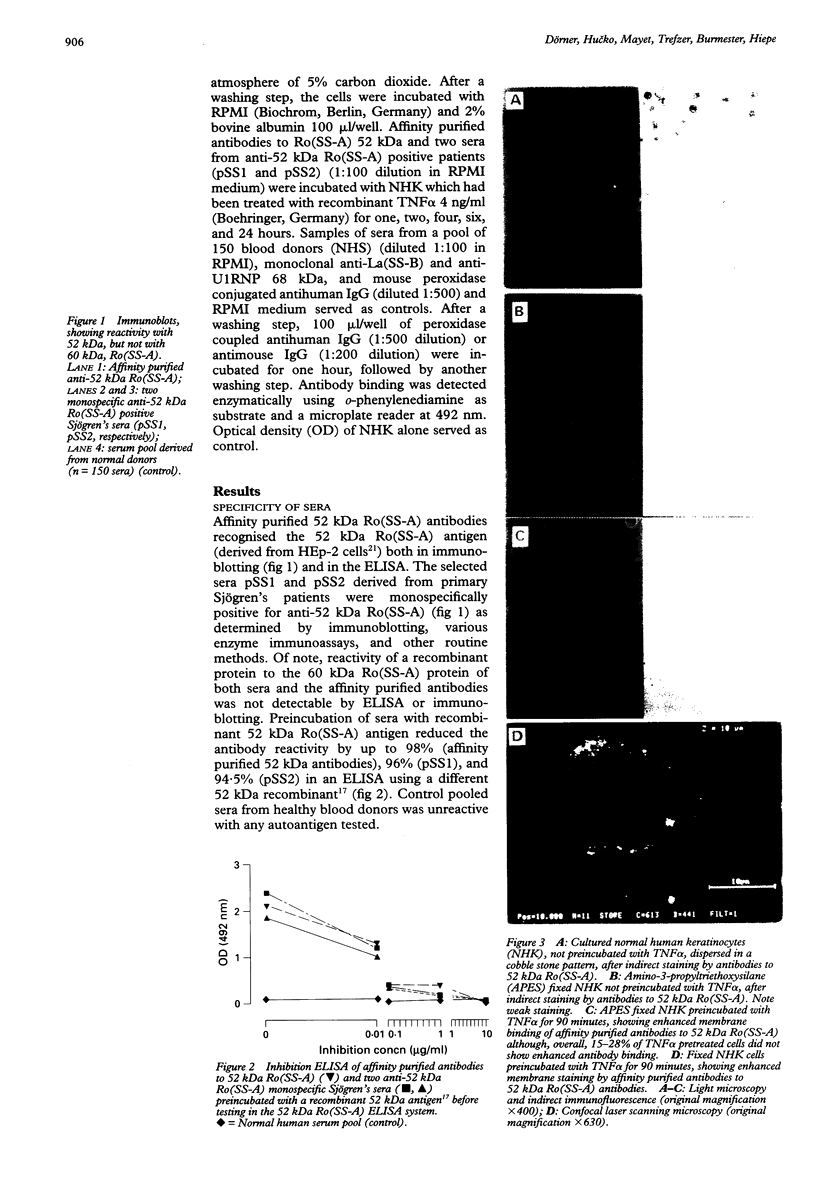
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To investigate the membrane expression of the 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) and La(SS-B) antigens in human keratinocytes under the influence of an important mediator of inflammation, TNF alpha. METHODS--Keratinocytes, isolated from human skins obtained at circumcision and identified using monoclonal antibodies, were treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and incubated with antibodies to 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) isolated and purified from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or Sjögren's syndrome, with mouse monoclonal antibody to La(SS-B), and (as controls) with sera from normal healthy blood donors and a mouse monoclonal antibody to U1RNP 68 kDa. Membrane expression of the 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) and La(SS-B) antigens was detected using cyto enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), laser scanning microscopy, and indirect immunofluorescence. RESULTS--After the incubation with TNF alpha, cyto ELISA revealed a significantly increased membrane binding of 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) antibodies, with a maximum after two hours, followed by enhanced 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) expression during the subsequent 24 hours. The La(SS-B) antigen was expressed rapidly after TNF alpha treatment (within one hour), with a fast decrease to the preincubation value within three hours. Indirect immunofluorescence with fixed normal human keratinocytes confirmed increased 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) and La(SS-B) antigen expression after the incubation with TNF alpha. CONCLUSIONS--TNF alpha mediates 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) and La(SS-B) autoantigen surface expression on human keratinocytes, and may be an important factor both in antibody induction and in the initiation of immunopathogenic processes which occur after antibody binding in autoimmune dermatitis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E. L., Provost T. T. Cutaneous manifestations of primary Sjögren's syndrome: a reflection of vasculitis and association with anti-Ro(SSA) antibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 May;80(5):386–391. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12552002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baboonian C., Venables P. J., Booth J., Williams D. G., Roffe L. M., Maini R. N. Virus infection induces redistribution and membrane localization of the nuclear antigen La (SS-B): a possible mechanism for autoimmunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):454–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Zaubitzer T., Müller W. E. The autoantigen La/SSB: detection on and uptake by mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Aug;201(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90288-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Chetrit E., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. A 52-kD protein is a novel component of the SS-A/Ro antigenic particle. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1560–1571. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Anhalt G., Rosen A. Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1317–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Miller D. K., Anhalt G. J., Rosen A. Specific cleavage of the 70-kDa protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is a characteristic biochemical feature of apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30757–30760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Hamel J. C., Buyon J. P., Tan E. M. Molecular definition and sequence motifs of the 52-kD component of human SS-A/Ro autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):68–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI115003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. Expression of Ro/SS-A antigen in human skin and heart. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):412–416. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton G., Jayne D. R., Perry G. J., Lockwood C. M., Cameron J. S. Autoantibodies to endothelial cells and neutrophil cytoplasmic antigens in systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa F., Kashihara-Sawami M., Lyons M. B., Norris D. A. Binding of antibodies to the extractable nuclear antigens SS-A/Ro and SS-B/La is induced on the surface of human keratinocytes by ultraviolet light (UVL): implications for the pathogenesis of photosensitive cutaneous lupus. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jan;94(1):77–85. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12873930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa F., Lyons M. B., Lee L. A., Coulter S. N., Norris D. A. Estradiol enhances binding to cultured human keratinocytes of antibodies specific for SS-A/Ro and SS-B/La. Another possible mechanism for estradiol influence of lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1480–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan T. D., Elkon K. B., Gharavi A. E., Krueger J. G. Enhanced membrane binding of autoantibodies to cultured keratinocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus patients after ultraviolet B/ultraviolet A irradiation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1172/JCI115922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell M., Zimmermann G., Hülser D., Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P. TNF receptors TR60 and TR80 can mediate apoptosis via induction of distinct signal pathways. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 1;153(5):1963–1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., de Rooij D. J., Salden M. H., Verhagen A. P., van Eekelen C. A., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. Antibodies against distinct nuclear matrix proteins are characteristic for mixed connective tissue disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G., Harley J. B., Bias W. B., Roebber M., Reichlin M., Hochberg M. C., Arnett F. C. Two Ro (SS-A) autoantibody responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Correlation of HLA-DR/DQ specificities with quantitative expression of Ro (SS-A) autoantibody. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Apr;31(4):496–505. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Sestak A. L., Willis L. G., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A., Reichlin M. A model for disease heterogeneity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationships between histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies, and lymphopenia or renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):826–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon C. E., Deng J. S., Peebles C. L., Tan E. M. The importance of tissue substrate in the SS-A/Ro antigen-antibody system. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):166–173. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. K. The effects of hormonal and other stimuli on cell-surface Ro/SSA antigen expression by human keratinocytes in vitro: their possible role in the induction of cutaneous lupus lesions. Br J Dermatol. 1992 Jun;126(6):554–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb00099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Sasakawa H., Suzuki S., Shirako M., Tashiro F., Nishioka K., Yamamoto K. Autoepitopes of the 52-kd SS-A/Ro molecule. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jul;38(7):990–998. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Wright S. C. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3215–3223. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2172061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFeber W. P., Norris D. A., Ryan S. R., Huff J. C., Lee L. A., Kubo M., Boyce S. T., Kotzin B. L., Weston W. L. Ultraviolet light induces binding of antibodies to selected nuclear antigens on cultured human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1545–1551. doi: 10.1172/JCI111569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. A., Weston W. L., Krueger G. G., Emam M., Reichlin M., Stevens J. O., Surbrugg S. K., Vasil A., Norris D. A. An animal model of antibody binding in cutaneous lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):782–788. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayet W. J., Csernok E., Szymkowiak C., Gross W. L., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Human endothelial cells express proteinase 3, the target antigen of anticytoplasmic antibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1221–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina R., Provost T. T., Alexander E. L. Two types of inflammatory vascular disease in Sjögren's syndrome. Differential association with seroreactivity to rheumatoid factor and antibodies to Ro (SS-A) and with hypocomplementemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Nov;28(11):1251–1258. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond C. B., Peterson M. G., Rothfield N. F. Correlation of anti-Ro antibody with photosensitivity rash in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;32(2):202–204. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mécheri S., Dannecker G., Dennig D., Poncet P., Hoffmann M. K. Anti-histone autoantibodies react specifically with the B cell surface. Mol Immunol. 1993 Apr;30(6):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90029-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Allaway G. P., Srinivasappa J., Notkins A. L. Cell surface expression of the 70-kD component of Ku, a DNA-binding nuclear autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1301–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI114838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):331–343. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(75)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber M., Urbina C., Rieber M. S. DNA on membrane receptors: a target for monoclonal anti-DNA antibody induced by a nucleoprotein shed in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robaye B., Mosselmans R., Fiers W., Dumont J. E., Galand P. Tumor necrosis factor induces apoptosis (programmed cell death) in normal endothelial cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):447–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario M. O., Fox O. F., Koren E., Harley J. B. Anti-Ro (SS-A) antibodies from Ro (SS-A)-immunized mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Feb;31(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobbe R. L., Pluk W., van Venrooij W. J., Pruijn G. J. Ro ribonucleoprotein assembly in vitro. Identification of RNA-protein and protein-protein interactions. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90890-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Morimoto C., Steinberg A. D., Wolf A., Schlossman S. F., Steinberg R. T., Penner E., Reinherz E., Reichlin M., Chused T. M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: delineation of subpopulations by clinical, serologic, and T cell subset analysis. Am J Med Sci. 1985 Apr;289(4):139–147. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198504000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trefzer U., Brockhaus M., Lötscher H., Parlow F., Budnik A., Grewe M., Christoph H., Kapp A., Schöpf E., Luger T. A. The 55-kD tumor necrosis factor receptor on human keratinocytes is regulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and by ultraviolet B radiation. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):462–470. doi: 10.1172/JCI116589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasicek C. A., Reichlin M. Clinical and serological differences between systemic lupus erythematosus patients with antibodies to Ro versus patients with antibodies to Ro and La. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):835–843. doi: 10.1172/JCI110523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]