Abstract
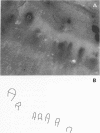
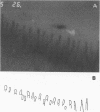
OBJECTIVES--To evaluate an objective and quantitative method for assessment of capillary abnormalities in systemic sclerosis (SSc). METHODS--Nailfold capillaries were investigated by capillary microscopy and photographed in 17 consecutive SSc patients (five with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dSSc) and 12 with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (lSSc)) and in 17 healthy controls. Investigators having no access to clinical data made drawings from magnified projections of coded photographs and analysed them using a computer program. Capillary density (capillary loops/mm in the distal row) and median capillary loop area were calculated. Presence of functional or organic arterial changes was evaluated by measurement of finger pressure with finger cooling. Plasma concentration of von Willebrand factor (VWF) was analysed using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS--In 16 of 17 SSc patients and 13 of 17 controls the technical quality of the photographs was sufficient for computer analysis. Capillary density was decreased in dSSc (median 6.9 loops/mm) and in lSSc (median 3.8 loops/mm) compared with healthy controls (8.9 loops/mm) and median capillary loop area was increased in dSSc (7.3 x 10(-3) mm2) and in lSSc (8.5 x 10(-3) mm2) compared with healthy controls (5.0 x 10(-3) mm2). An inverse relation was found between capillary density and median capillary loop area in SSc patients. Plasma VWF was increased in patients (median 401 IE/l in dSSc and 409 IE/l in lSSc) compared with controls matched for age and sex (median 276 IE/l). Computer based analysis showed capillary density below the control range and median capillary loop area above the control range in 14 of 16 SSc patients. Measurement of finger pressure with finger cooling showed organic vascular changes in nine of 13 SSc patients. CONCLUSION--Computer based quantitative analysis has low interobserver variability and is a quantitative and sensitive method of assessing capillary abnormalities in SSc.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arneklo-Nobin B., Johansen K., Sjöberg T. The objective diagnosis of vibration-induced vascular injury. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1987 Aug;13(4):337–342. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D. von Willebrand factor, exercise, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Mar;52(3):245–245. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.3.245-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A., Jayson M. I., Pope M. H., Kaigle A. M., Wilder D., Weinstein J. N. Postural variation in von Willebrand factor antigen. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jan;52(1):82–82. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.1.82-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier P. H., Maricq H. R. Microvasculature in systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):75–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. O., Wacher T., Cairns D., Conners G., McGrath M. Nailfold capillary circulation in osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Dec;32(12):1062–1065. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.12.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell A. J., Williams R. B., Stevens C. R., Lawrie A. S., Cox N. L., Blake D. R. Exercise induced release of von Willebrand factor: evidence for hypoxic reperfusion microvascular injury in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Oct;51(10):1117–1122. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.10.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houtman P. M., Kallenberg C. G., Fidler V., Wouda A. A. Diagnostic significance of nailfold capillary patterns in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. An analysis of patterns discriminating patients with and without connective tissue disease. J Rheumatol. 1986 Jun;13(3):556–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B. Vascular disease in scleroderma. Endothelial T lymphocyte-fibroblast interactions. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):53–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy E. C., Black C., Fleischmajer R., Jablonska S., Krieg T., Medsger T. A., Jr, Rowell N., Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Feb;15(2):202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Leung F. Y., Alderdice C., Armstrong S. K. Nailfold capillary microscopy in the connective tissue diseases: a semiquantitative assessment. J Rheumatol. 1983 Dec;10(6):930–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Sarkozi J., Bookman A. A., Keystone E. C., Armstrong S. K. Digital blood flow and nailfold capillary microscopy in Raynaud's phenomenon. J Rheumatol. 1986 Jun;13(3):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford F., Edwards J. C. Nailfold capillary microscopy in connective tissue disease: a quantitative morphological analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):741–749. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovy M., MacCarter D., Steigerwald J. C. Relationship between nailfold capillary abnormalities and organ involvement in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 May;28(5):496–501. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq H. R. Comparison of quantitative and semiquantitative estimates of nailfold capillary abnormalities in scleroderma spectrum disorders. Microvasc Res. 1986 Sep;32(2):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(86)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq H. R., LeRoy E. C., D'Angelo W. A., Medsger T. A., Jr, Rodnan G. P., Sharp G. C., Wolfe J. F. Diagnostic potential of in vivo capillary microscopy in scleroderma and related disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq H. R., LeRoy E. C. Patterns of finger capillary abnormalities in connective tissue disease by "wide-field" microscopy. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Sep-Oct;16(5):619–628. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq H. R., Spencer-Green G., LeRoy E. C. Skin capillary abnormalities as indicators of organ involvement in scleroderma (systemic sclerosis), Raynaud's syndrome and dermatomyositis. Am J Med. 1976 Dec;61(6):862–870. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90410-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):581–590. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheja A., Eskilsson J., Akesson A., Wollheim F. A. Inverse relation between plasma concentration of von Willebrand factor and CrEDTA clearance in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1994 Apr;21(4):639–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statham B. N., Rowell N. R. Quantification of the nail fold capillary abnormalities in systemic sclerosis and Raynaud's syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66(2):139–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerer R. G., Tashkin D. P., Furst D., Clements P. J., Gong H., Jr, Bein M., Smith J. W., Roberts N., Cabeen W. Prevalence and clinical correlates of pulmonary arterial hypertension in progressive systemic sclerosis. Am J Med. 1983 Jul;75(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zufferey P., Depairon M., Chamot A. M., Monti M. Prognostic significance of nailfold capillary microscopy in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon and scleroderma-pattern abnormalities. A six-year follow-up study. Clin Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;11(4):536–541. doi: 10.1007/BF02283115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Sabbagh M. R., Steen V. D., Zee B. C., Nalesnik M., Trostle D. C., Bedetti C. D., Medsger T. A., Jr Pulmonary arterial histology and morphometry in systemic sclerosis: a case-control autopsy study. J Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;16(8):1038–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]