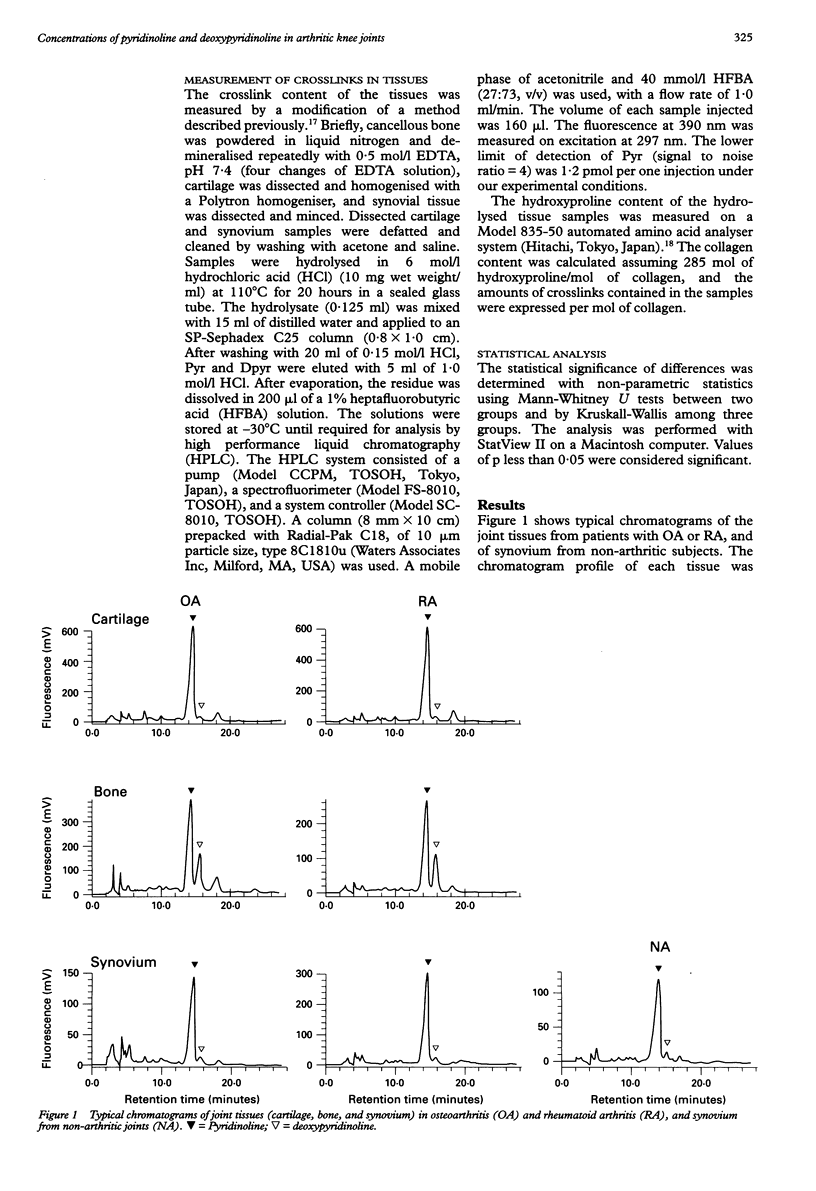
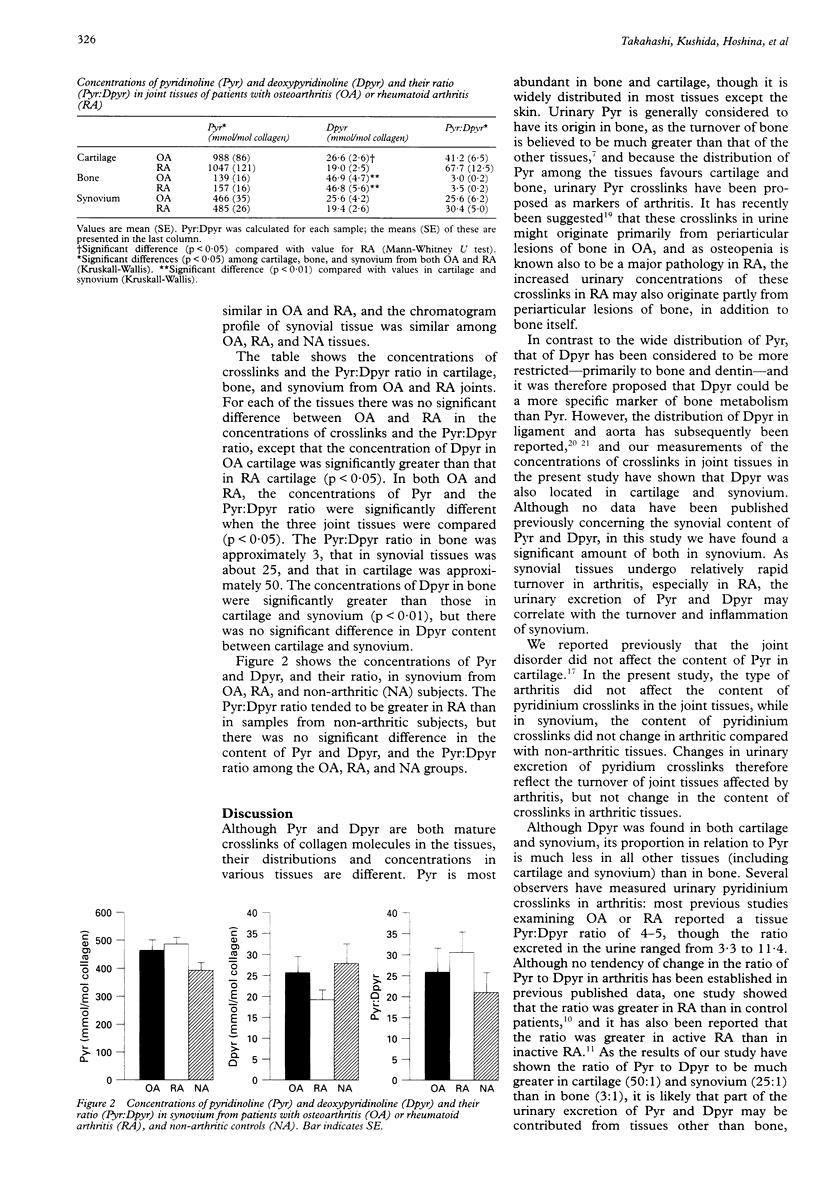
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To assess the usefulness of pyridinoline (Pyr) and deoxypyridinoline (Dpyr), intermolecular crosslinks of collagen, as markers in the evaluation of arthritis, by studying their distribution in tissues from knee joints. METHODS: Joint tissues (cartilage, bone, synovium) were obtained during operation from 10 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and 10 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Synovium was also obtained from 10 non-arthritic (NA) subjects. Hydroxyproline was measured in hydrolysed tissue samples and converted to an equivalent collagen content. The amounts of Pyr and Dpyr crosslinks measured in the hydrolysed samples using a fluorescence technique were expressed as mumol/mol of collagen. RESULTS: Pyr and Dpyr were distributed in all three tissues, but in different amounts. The ratio of the contents of Pyr and (Pyr:Dpyr) was 50:1 in cartilage, 3:1 in bone, and 25:1 in synovium. OA cartilage had a greater Dpyr content than the RA cartilage, but there was no other significant difference in the contents of Pyr and Dpyr and the ratio Pyr:Dpyr in the joint tissues from patients with OA or RA. In synovium, there was no significant difference between the contents of Pyr and Dpyr and the Pyr:Dpyr ratio among OA, RA, and NA tissues. CONCLUSION: Both Pyr and Dpyr were located in cartilage, bone, and synovium. A significant amount of Pyr and Dpyr in these joint tissues, especially in synovium, may contribute to the urinary excretion of those crosslinks that is observed in arthritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D., Marabani M., Sturrock R. D., Robins S. P. Urinary excretion of the hydroxypyridinium cross links of collagen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Aug;48(8):641–644. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.8.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Koob T. J., Van Ness K. P. Quantitation of hydroxypyridinium crosslinks in collagen by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson C., Duncan A., Robins S. P. The effects of copper deficiency on the pyridinium crosslinks of mature collagen in the rat skeleton and cardiovascular system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Nov;192(2):166–171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-192-42973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D. Isolation and characterization of a fluorescent material in bovine achilles tendon collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90972-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D., Moriguchi T. Pyridinoline, a non-reducible crosslink of collagen. Quantitative determination, distribution, and isolation of a crosslinked peptide. J Biochem. 1978 Mar;83(3):863–867. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D., Suzuki M., Uchiyama A., Miyamoto S., Inoue T. Analysis of pyridinoline, a cross-linking compound of collagen fibers, in human urine. J Biochem. 1983 Oct;94(4):1133–1136. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough A. K., Peel N. F., Eastell R., Holder R. L., Lilley J., Emery P. Excretion of pyridinium crosslinks correlates with disease activity and appendicular bone loss in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):14–17. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino H., Takahashi M., Kushida K., Ohishi T., Kawana K., Inoue T. Quantitation of the crosslinks, pyridinoline, deoxypyridinoline and pentosidine, in human aorta with dystrophic calcification. Atherosclerosis. 1995 Jan 6;112(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)05395-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollerup G., Hansen M., Hørslev-Petersen K. Urinary hydroxypyridinium cross-links of collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. Relation to disease activity and effects of methylprednisolone. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;33(9):816–820. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.9.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A. G., McHenry P., Robins S. P., Reid D. M. Relationship of urinary pyridinium crosslinks to disease extent and activity in osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Jan;33(1):16–19. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Ono T., Tsuda M., Kawanishi Y. A novel fluor in insoluble collagen: a crosslinking moiety in collagen molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1252–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth M. W., Martinez D. A., Cook M. E., Vailas A. C. Nonreducible crosslink formation in tibial dyschondroplastic growth plate cartilage from broiler chicks fed homocysteine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1582–1586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91754-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P. An enzyme-linked immunoassay for the collagen cross-link pyridinoline. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2070617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibel M. J., Duncan A., Robins S. P. Urinary hydroxy-pyridinium crosslinks provide indices of cartilage and bone involvement in arthritic diseases. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jul;16(7):964–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. D., James I. T., Hall G. M., Thompson P. W., Perrett D., Hart D. J. Increased levels of urinary collagen crosslinks in females with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1993 Jun;12(2):240–244. doi: 10.1007/BF02231535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Kushida K., Ohishi T., Kawana K., Hoshino H., Uchiyama A., Inoue T. Quantitative analysis of crosslinks pyridinoline and pentosidine in articular cartilage of patients with bone and joint disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):724–728. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. W., Spector T. D., James I. T., Henderson E., Hart D. J. Urinary collagen crosslinks reflect the radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;31(11):759–761. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.11.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama A., Ohishi T., Takahashi M., Kushida K., Inoue T., Fujie M., Horiuchi K. Fluorophores from aging human articular cartilage. J Biochem. 1991 Nov;110(5):714–718. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



