Graphical abstract
Keywords: Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm, Endocarditis, Ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm, Echocardiogram, Continuous-wave Doppler flow
Highlights
-
•
Ruptured SVA into LA is a rare disorder and has high mortality.
-
•
Wide pulse pressure without severe AR is concerning for SVA rupture.
-
•
Continuous turbulent Doppler flow by echo can identify the rupture of SVA.
-
•
Severe MR without structural valve abnormality raises the possibility of SVA rupture.
Introduction
Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SVA) is a rare disorder. Ruptured SVA has high morbidity and in-hospital death. Early identification of ruptured SVA is crucial in patient outcome. Here we present a 93-year-old man with left coronary SVA rupture into the left atrium (LA) and describe echocardiographic features for diagnosing rupture of SVA.
Case Presentation
A 93-year-old man with asymptomatic moderate aortic stenosis (AS; aortic valve area [AVA] = 1.5 cm2 by echocardiogram) presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath on exertion 10 days after being discharged from the hospital, where the patient received a course of antibiotics for bacteremia of unknown primary source. Patient denied any chest pain, cough, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache, or vision changes. The patient's vitals were 36.3 °C, blood pressure 135/40 mm Hg, pulse 87 beats/min, and resting oxygen saturation 91% on room air. Significant physical examination findings included a systolic and holodiastolic murmur and jugular venous pulse at 9 cm H2O.
Medical History
The patient had significant hypertension, dyslipidemia, deep vein thrombosis, and carotid artery stenosis status post-–carotid endarterectomy. Patient was followed closely by cardiology for asymptomatic moderate AS with normal left ventricular (LV) systolic function with an estimated LV ejection fraction (LVEF) of 79% by the biplane method of disks. The patient was recently hospitalized for Escherichia coli bacteremia and has finished cefpodoxime treatment.
Differential diagnosis includes acute coronary syndrome, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and new-onset heart failure. Given a history of bacteremia and wide pulse pressure, endocarditis resulting in valve destruction causing worsening aortic regurgitation should also be considered.
Investigations
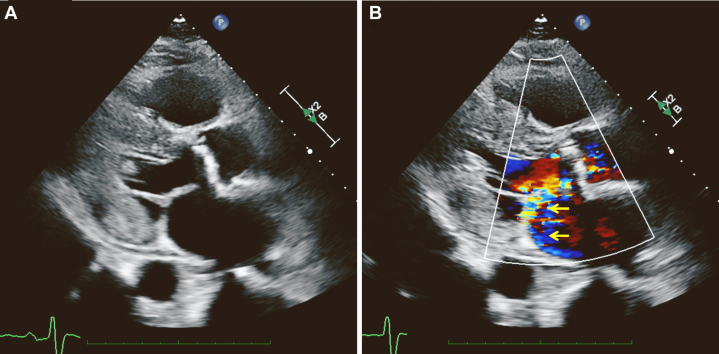
To rule out worsening AS or heart failure, a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) was performed that demonstrated moderate mitral regurgitation (MR) with posteriorly directed jet reaching the pulmonary vein that was newly onset compared with 2 months earlier (Figure 1, Video 1). The LVEF was 66% using the biplane method of disks.
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis view, early systolic phase without (A) and with (B) color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow toward the posterior of the LA, which was initially interpreted to be MR (arrows).
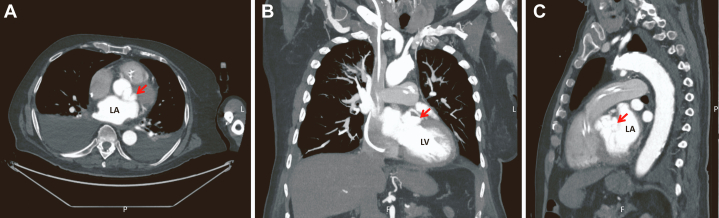
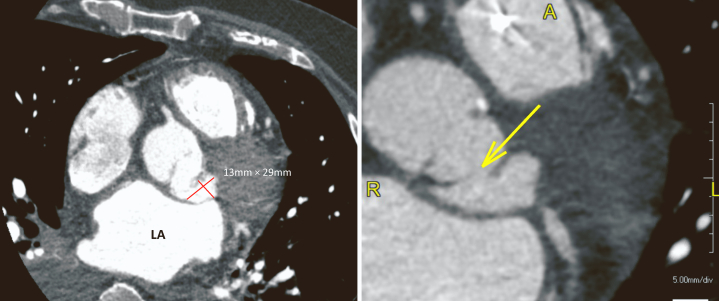
Right and left heart catheterization revealed no coronary obstruction and an AVA of 0.97 cm2 by the Fick method. Aortic pressure was 101/42 mm Hg (mean, 62 mm Hg), LV pressure 125/30 mm Hg, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure 30 mm Hg, and V-wave 33 mm Hg. Cardiac output and cardiac index were 2.6 L/min and 1.21 L/min/m2 by thermodilution and 4.11 L/min and 1.91 L/min/m2 by the Fick method, respectively. Patient was diagnosed with severe AS by catheterization. Cardiac computed tomography (CCT) was performed as workup for transcatheter aortic valve implantation for severe AS. Pseudoaneurysm arising from the left coronary sinus measuring 1.3 × 2.9 × 2.4 cm was observed on CCT (Figures 2 and 3).
Figure 2.
Cardiac computed tomography images demonstrated a pseudoaneurysm arising from the left coronary sinus (arrows) shown in the axial (A), coronal (B), and sagittal (C) displays.
Figure 3.
Cardiac computed tomography, zoomed axial display, demonstrates a pseudoaneurysm arising from the left coronary sinus measuring 13 × 29 mm (left). With a highly magnified image and contrast adjustment of the window/levels, the site of the SVA rupture can be seen (arrow).
N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and troponin were 8,648 pg/mL and 119 ng/L, respectively. Lactate was 3.88 mmol/L. Gram-positive cocci, Staphylococcus epidermidis, was detected in the blood.
Repeat Echocardiogram
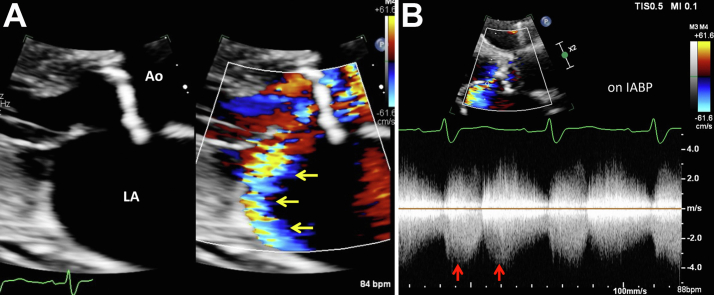
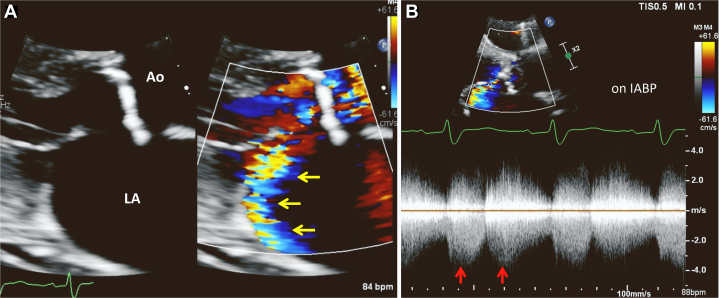
Due to worsening heart failure and cardiogenic shock, the patient received inopressors including dobutamine and dopamine, with escalation of care including an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Repeat echocardiogram performed after IABP revealed turbulent flow from the left coronary sinus into the LA that resembled posteriorly directed MR in the parasternal long-axis view (Figure 4A, Video 2). This turbulent flow showed continuous flow with a peak pressure gradient of 100 mm Hg at systole (Figure 4B). In addition, the left coronary sinus appeared to be damaged, with an indistinct border as seen in the apical 5-chamber view, which was not present in previous echocardiograms (Figure 5, Videos 3 and 4).
Figure 4.
(A) Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis, systolic phase zoom image of the aorta (Ao) and LA without (left) and with (right) color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow from the left coronary sinus into the LA that resembled posteriorly directed MR (yellow arrows). (B) Continuous-wave Doppler spectrum of this turbulent flow demonstrates a double-peak continuous flow pattern (due to the IABP) with a peak pressure gradient of 100 mm Hg (red arrows).
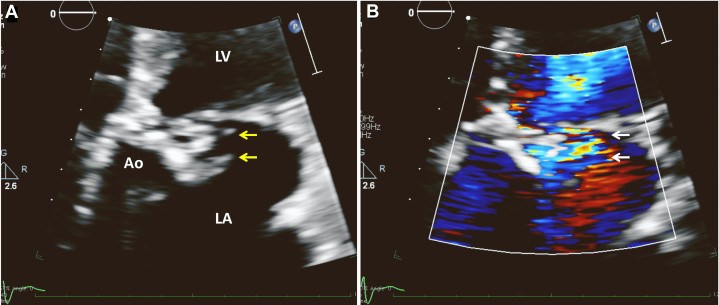
Figure 5.
Two-dimensional TTE, apical 5-chamber zoomed view without (A) and with (B) color flow Doppler demonstrates that the aortic valve or sinus is damaged with indistinct tissue borders (yellow arrows) and is associated with turbulent flow from a fistula (white arrows).
Follow-Up
After IABP placement, the patient was weaned from bilevel positive airway pressure and inopressors with improvement of mixed venous oxygen saturation. The patient had no chest pain, and the shortness of breath improved. However, our patient was not a candidate for definitive surgical or percutaneous interventions to correct the fistula. Due to advanced age and comorbidities as well as the patient’s wishes, the patient was transitioned to comfort care and deceased 7 days after admission.
Discussion
We presented a case of left coronary SVA with rupture into the LA. Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm is uncommon. An aneurysm is often seen in patients with congenital cardiac anomalies such as ventricular septal defect and those with endocarditis or atherosclerosis.1,2 Most SVAs are located at the right coronary sinus. Ruptured aneurysm occurs in the right coronary sinus (67%), the noncoronary sinus (30%), or left coronary sinus (3%).3 Also, most fistulas develop between the right coronary sinus and right ventricle or noncoronary sinus and right atrium. Left coronary SVA with rupture into the LA was identified in only 1 out of 149 cases in a previous study.3 Surgical treatment may improve outcome. However, mortality and in-hospital death are high in patients with concurrent sepsis and bacterial endocarditis.3
In the present case, a fistula between the LA and aorta was not readily apparent, but the patient had several findings on physical exam, echocardiogram, and catheterization that were inconsistent with one another. The patient presented with shortness of breath and was in cardiogenic shock, although the patient’s LV function was grossly normal. The patient had wide pulse pressure, but the echocardiogram did not show any aortic regurgitation, and the patient was not septic. Furthermore, the initial echocardiogram showed possible moderate to severe MR; however, the mitral valve morphology was normal and there was no prolapse or tethering of the valve. The supposed MR was actually continuous forward flow from the aorta to LA via left coronary sinus fistula. Due to the enormous pressure difference between the aorta and LA, this flow appeared to be moderate to severe MR with a “Coanda effect,” a phenomenon whereby turbulent flow follows the curvature of the LA wall. Usually, the fistula flow pattern is monophasic and continuous, which reflects the pressure gradient between the aorta and the LA. However, a double-peak continuous flow in the fistula was seen in our patient, who had an IABP at the time of echocardiogram. The IABP inflates during diastole to raise diastolic pressure to promote coronary artery flow. Thus, the pressure gradient between the aorta and the LA was also augmented during diastole, which may create the double-peak continuous flow, one during systole and another during diastole.
Finally, catheterization showed an AVA suggestive of severe AS, although this was not replicated by echocardiogram, possibly due to interference of pressure measurement from aortic to LA flow. Nevertheless, a CCT was performed as part of transcatheter aortic valve implantation workup and revealed coronary sinus aneurysm, prompting a second echocardiogram that showed the fistula flow in more complete detail. It is possible that despite good LV function, a significant portion of the patient’s cardiac output flowed into the LA via the fistula, causing organ hypoperfusion and shock. A fistula between the sinus of Valsalva and LA should be part of a differential diagnosis with relevant clinical information when there are (1) continuous turbulent Doppler flow in the aortic sinus, (2) an abnormal border between the aortic valve and sinus-aortic annulus, (3) deformity of the aortic valve sinus, and (4) new severe MR without concurrent mitral valve annular dilation or structural mitral leaflet abnormality or flail (or tethering). Multiple echo views or three-dimensional imaging may be helpful for diagnosing with the rupture of SVA.
Conclusion
Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm is a rare condition. However, once rupture occurs or a fistula forms between the aortic valve sinus and adjacent structures, the patient is at high risk of cardiovascular decompensation and death. Therefore, a patient with SVA may require frequent echocardiogram monitoring, and rupture should be considered in cases of cardiogenic shock.
Ethics Statement
The authors declare that the work described has been carried out in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for experiments involving humans.
Consent Statement
The authors declare that since this was a non-interventional, retrospective, observational study utilizing de-identified data, informed consent was not required from the patient under an IRB exemption status.
Funding Statement
The authors declare that this report did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Disclosure Statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.case.2022.11.004.
Supplementary Data
Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis view with color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow toward the posterior of the LA, which was initially interpreted to be MR.
Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis zoom image of the aorta and LA without (left) and with (right) color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow from the left coronary sinus into LA, which resembled posteriorly directed MR.
Two-dimensional TTE, apical 5-chamber zoomed view demonstrates that the aortic valve or sinus is damaged with indistinct tissue borders.
Two-dimensional TTE, apical 5-chamber zoomed view with color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow from the aortic valve or sinus with indistinct tissue borders and suggests a fistula to the LA.
References
- 1.Vural K.M., Sener E., Taşdemir O., Bayazit K. Approach to sinus of Valsalva aneurysms: a review of 53 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001;20:71–76. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(01)00758-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Park S.H., Jung H.S., Yu M., Min S.K., Ahn J.H., Kim Y. Left valsalva sinus aneurysm rupture into left atrium and aortic valve prolapse confirmed with transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20:1010.e3–1010.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2007.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takach T.J., Reul G.J., Duncan J.M., Cooley D.A., Livesay J.J., Ott D.A., et al. Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm or fistula: management and outcome. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68:1573–1577. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(99)01045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis view with color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow toward the posterior of the LA, which was initially interpreted to be MR.
Two-dimensional TTE, parasternal long-axis zoom image of the aorta and LA without (left) and with (right) color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow from the left coronary sinus into LA, which resembled posteriorly directed MR.
Two-dimensional TTE, apical 5-chamber zoomed view demonstrates that the aortic valve or sinus is damaged with indistinct tissue borders.
Two-dimensional TTE, apical 5-chamber zoomed view with color flow Doppler demonstrates turbulent flow from the aortic valve or sinus with indistinct tissue borders and suggests a fistula to the LA.