Abstract
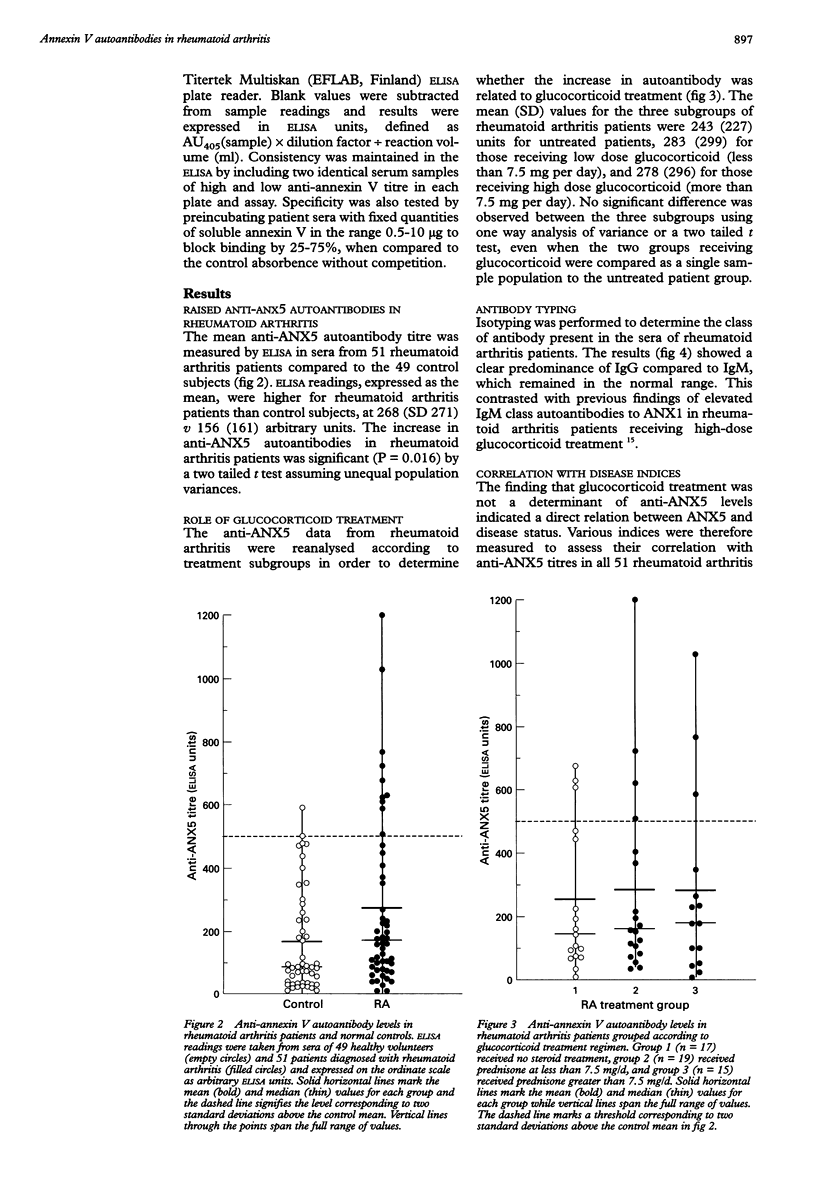
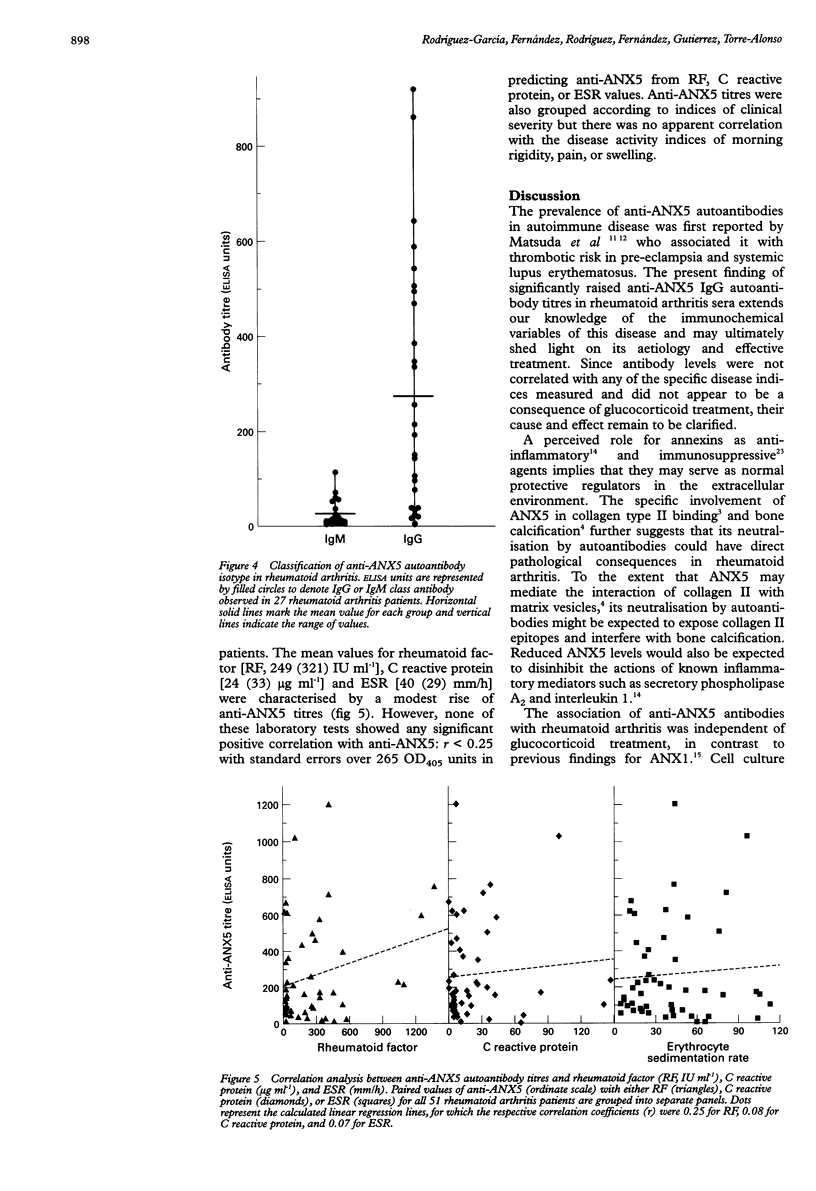
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the occurrence of anti-annexin V autoantibodies in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis to assess involvement with the disease and any relation to glucocorticoid treatment. METHODS: Anti-annexin V antibodies were measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) which used the purified human recombinant protein as antigen. RESULTS: Concentrations of anti-annexin V autoantibodies, predominantly of the IgG class, were significantly raised in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to normal controls. This was not correlated with other indices of disease activity such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C reactive protein and was unrelated to glucocorticoid treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Extracellular annexin V provides an antigenic stimulus for autoantibody production and its in vivo expression is independent of glucocorticoid control. Such autoantibodies may have a detrimental role in the arthritic condition by interfering with putative functions of annexin V, including collagen type II binding, inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity, and Fc receptor activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Ochs B., Abel K. J. Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger A., Berendes R., Voges D., Huber R., Demange P. A rapid and efficient purification method for recombinant annexin V for biophysical studies. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 23;329(1-2):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80185-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. F., Podgorski M. R., Goulding N. J., Godolphin J. L., Sharland P. R., O'Connor B., Flower R. J., Barnes P. J. Circulating autoantibodies to recombinant lipocortin-1 in asthma. Respir Med. 1991 Mar;85(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(06)80289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois T., Bisagni-Faure A., Coste J., Mavoungou E., Menkes C. J., Russo-Marie F., Rothhut B. High levels of antibodies to annexins V and VI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1995 Jul;22(7):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández M. P., Fernández M. R., Morgan R. O. Structure of the gene encoding anchorin CII (chick annexin V). Gene. 1994 Apr 20;141(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández M. P., Morgan R. O., Fernández M. R., Carcedo M. T. The gene encoding human annexin V has a TATA-less promoter with a high G+C content. Gene. 1994 Nov 18;149(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Rothwell N. J. Lipocortin-1: cellular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding N. J., Guyre P. M. Lipocortin 1 binding to human leukocytes correlates with its ability to inhibit IgG interactions with Fc gamma receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):351–358. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding N. J., Podgorski M. R., Hall N. D., Flower R. J., Browning J. L., Pepinsky R. B., Maddison P. J. Autoantibodies to recombinant lipocortin-1 in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Oct;48(10):843–850. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.10.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikai K., Shimizu K., Kanauchi H., Ando Y., Furukawa F., Imamura S. The presence of autoantibody to lipocortin-I in autoimmune-prone MRL mice. Autoimmunity. 1992;12(3):239–239. doi: 10.3109/08916939209148464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karopoulos C., Rowley M. J., Handley C. J. Intrasynovial levels of sulphated glycosaminoglycans and autoantibodies to type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis: a correlative analysis. Rheumatol Int. 1993;13(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00290329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. M., Kim D. K., Park Y. M., Kim C. K., Na D. S. Annexin-I inhibits phospholipase A2 by specific interaction, not by substrate depletion. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 2;343(3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch T., Wuthier R. E. Stimulation of calcification of growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles by binding to type II and X collagens. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11462–11469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacic R. T., Tizard R., Cate R. L., Frey A. Z., Wallner B. P. Correlation of gene and protein structure of rat and human lipocortin I. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 17;30(37):9015–9021. doi: 10.1021/bi00101a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersen E. K., Ulvestad E., Bjørge L., Aarli A., Matre R. Fc gamma-receptor activity of placental annexin II. Scand J Immunol. 1994 Aug;40(2):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. L., Lin Y. C., Mochitate K., Grinnell F. Stress-relaxation of fibroblasts in collagen matrices triggers ectocytosis of plasma membrane vesicles containing actin, annexins II and VI, and beta 1 integrin receptors. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):167–177. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J., Gotoh M., Saitoh N., Gohchi K., Tsukamoto M., Yamamoto T. Anti-annexin antibody in the sera of patients with habitual fetal loss or preeclampsia. Thromb Res. 1994 Jul 1;75(1):105–106. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J., Saitoh N., Gohchi K., Gotoh M., Tsukamoto M. Anti-annexin V antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with lupus anticoagulant and/or anticardiolipin antibody. Am J Hematol. 1994 Sep;47(1):56–58. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830470112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misaki Y., Van Venrooij W. J., Pruijn G. J. Prevalence and characteristics of anti-56K/annexin XI autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases. J Rheumatol. 1995 Jan;22(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer J., Bee J. A., Lizarbe M. A., von der Mark K. Role of anchorin CII, a 31,000-mol-wt membrane protein, in the interaction of chondrocytes with type II collagen. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1572–1579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morand E. F., Jefferiss C. M., Dixey J., Mitra D., Goulding N. J. Impaired glucocorticoid induction of mononuclear leukocyte lipocortin-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):207–211. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers S. H., Smillie F., Elderfield A. J., Flower R. J. Glucocorticoid-and non-glucocorticoid induction of lipocortins (annexins) 1 and 2 in rat peritoneal leucocytes in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):66–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podgorski M. R., Goulding N. J., Hall N. D., Flower R. J., Maddison P. J. Autoantibodies to lipocortin-1 are associated with impaired glucocorticoid responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1668–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Goulding N. J., Flower R. J., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Goodman P. J., Scott K. F., Vadas P. Circulating group II phospholipase A2 activity and antilipocortin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Correlative study with disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1994 Feb;21(2):252–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal P., Pollard H. B. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 5;1197(1):63–93. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers J. K., Podgorski M. R., Goulding N. J., Wong E., McGrath J. A., Flower R. J., Greaves M. W. The presence of autoantibody to recombinant lipocortin-I in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Br J Dermatol. 1990 Nov;123(5):569–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., Iwagami S., Tsuruta Y., Suzuki S., Suzuki R. Study of natural lipocortin I. A potent mediator for macrophage-mediated immunosuppression in tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4964–4972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez F., Rothhut B., Comera C., Touqui L., Marie F. R., Silve C. Expression of annexin I, II, V, and VI by rat osteoblasts in primary culture: stimulation of annexin I expression by dexamethasone. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Oct;8(10):1201–1210. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650081007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]