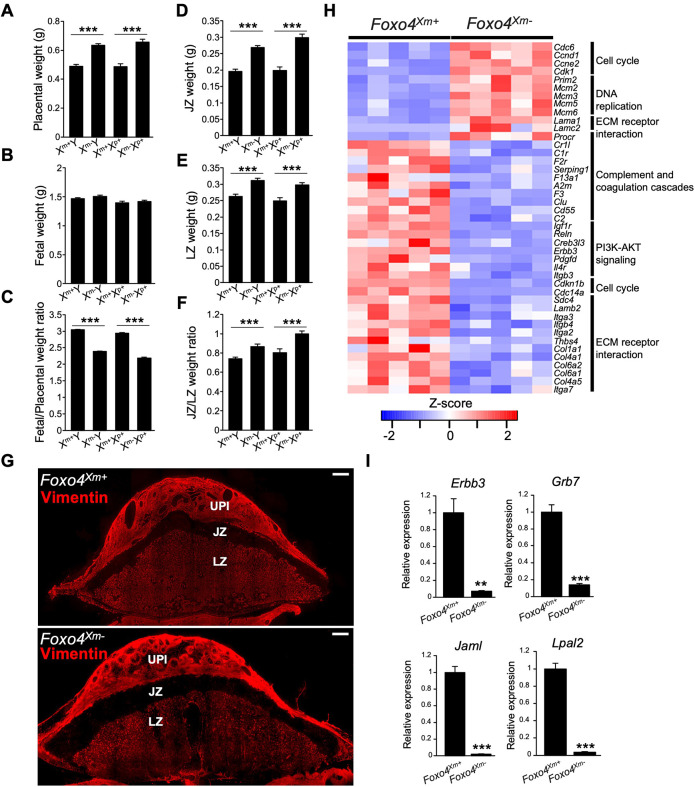
Fig. 6.
Foxo4 hemizygous null and Foxo4 maternally inherited heterozygous conceptuses exhibit placental overgrowth, and FOXO4 deficiency alters the transcriptomes of the junctional zone. (A-C) Placentas (A) and fetuses (B) were dissected from Foxo4 heterozygous females mated with wild-type males at gd 18.5 and weighed; the fetus/placenta ratio is shown in C. (D-F) Placentas were then separated into junctional zone (JZ; D) and labyrinth zone (LZ; E) compartments and weighed; the JZ/LZ weight ratio is shown in F. Graphs represent mean±s.e.m. Xm+Y, n=25; Xm−Y, n=31; Xm+Xp+, n=14; Xm−Xp+, n=22 from 8 dams. Asterisks denote statistical differences (***P<0.001) as determined by unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. (G) Vimentin immunostaining of gd 18.5 Foxo4Xm+ and Foxo4Xm placentation sites. The junctional zone (JZ) is negative for vimentin immunostaining, whereas the uterine-placental interface (UPI) and labyrinth zone (LZ) stain positive for vimentin. Images are representative of five samples. Scale bars: 1000 μm. (H) Heat maps depicting differentially expressed genes in Foxo4Xm+ versus Foxo4Xm−junctional zones. The heatmap color keys represent z-scores of TPM values. (I) RT-qPCR validation of RNA-seq results (n=6/group). Graphs represent mean±s.e.m. Asterisks denote statistical difference (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001) as determined by unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test.