Figure 7. Neuronal-specific induction of G34R results in neurodegeneration and cortical atrophy.
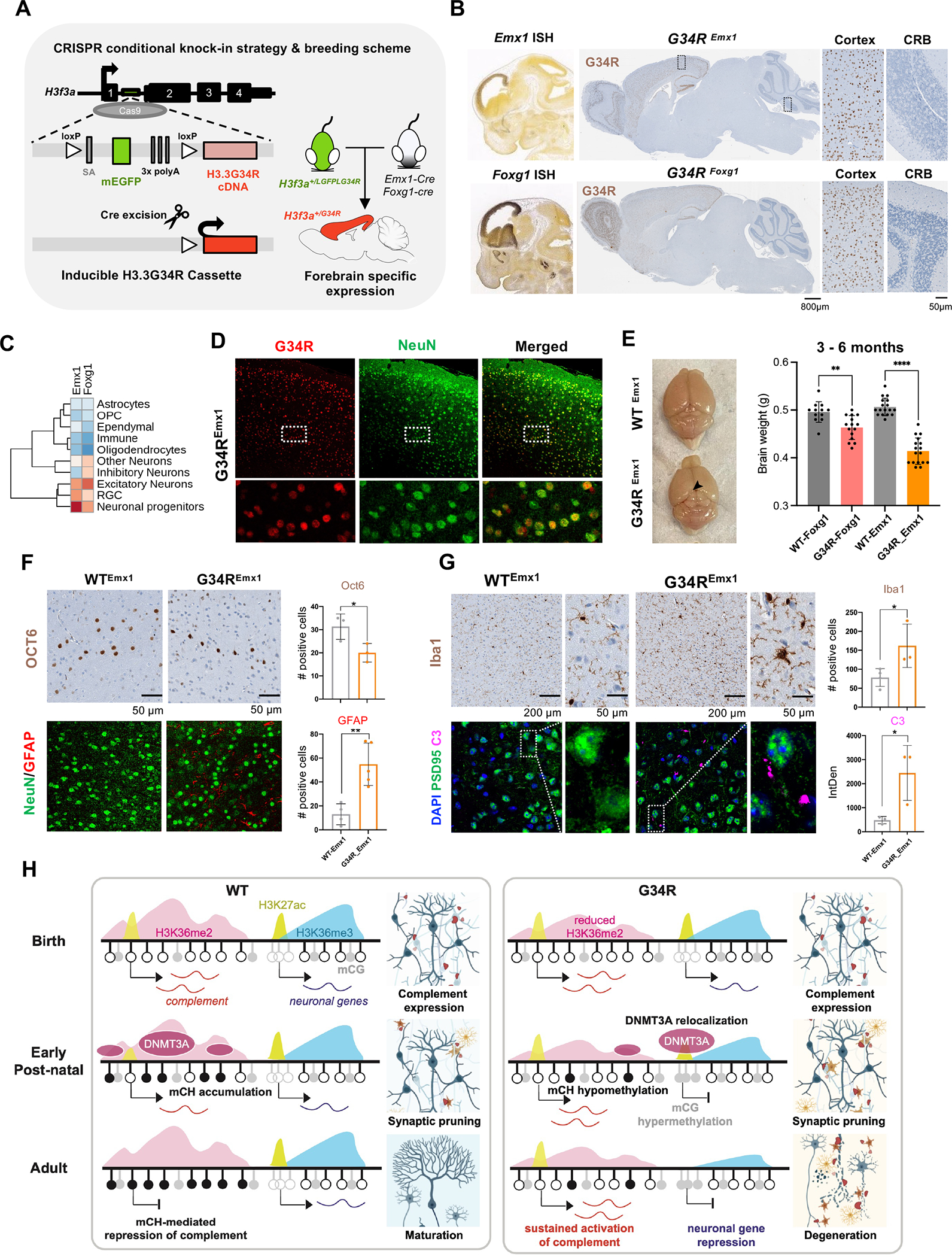
A. Schematic representation of the CRISPR G34R-conditional knock-in strategy. An inducible transgene cassette targeting exon 1 of the H3f3a gene was inserted using Cas9:gRNA approach. Loxp sites flanked an adenovirus splice-acceptor (SA), mEGFP, and 3x polyA sequences, followed by the H3.3G34R cDNA. Carrier H3f3a+/LGFPLG34R mice were crossed with Emx1-Cre or Foxg1-Cre mice to generate heterozygous H3f3a+/G34R mice with cortical-specific expression of G34R. B. In situ hybridization of Emx1 and Foxg1 genes (Allen Brain Atlas). H3.3G34R IHC staining for representative sagittal section of adult mouse brain from G34REmx1 and G34RFoxg1. CRB: cerebellum. C. Expression levels of Emx1 and Foxg1 in murine developing brain atlas. D. Immunofluorescent co-staining of neuronal marker NeuN (green) and G34R (red) in G34REmx1 adult mouse brain (20x). E. G34REmx1 shows cortex atrophy. Representative image and brain weights (means ± SE) of WTEmx1 and the reduced cortical region (arrow) of G34REmx1 mice. Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001. F. Immunohistochemical staining of layer V neuronal marker (Oct6) (top), neurons (NeuN), and astrocytes (GFAP) (bottom) in WTEmx1 and G34REmx1 (20x). Related quantifications, Oct6 (n = 3) and GFAP (n ≥ 4), means ± SD. Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. G. Immunohistochemical staining of microglial marker (Iba1), neuronal postsynaptic protein PSD95, and complement C3 in adult WTEmx1 and G34REmx1 mice (63x). Related quantifications, Iba1 (n ≥ 3) and C3 (n = 3), means ± SD. Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05. H. Model to illustrate dysregulation of epigenetic reprogramming in the postnatal G34R brain, which may account for neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration.
