Abstract
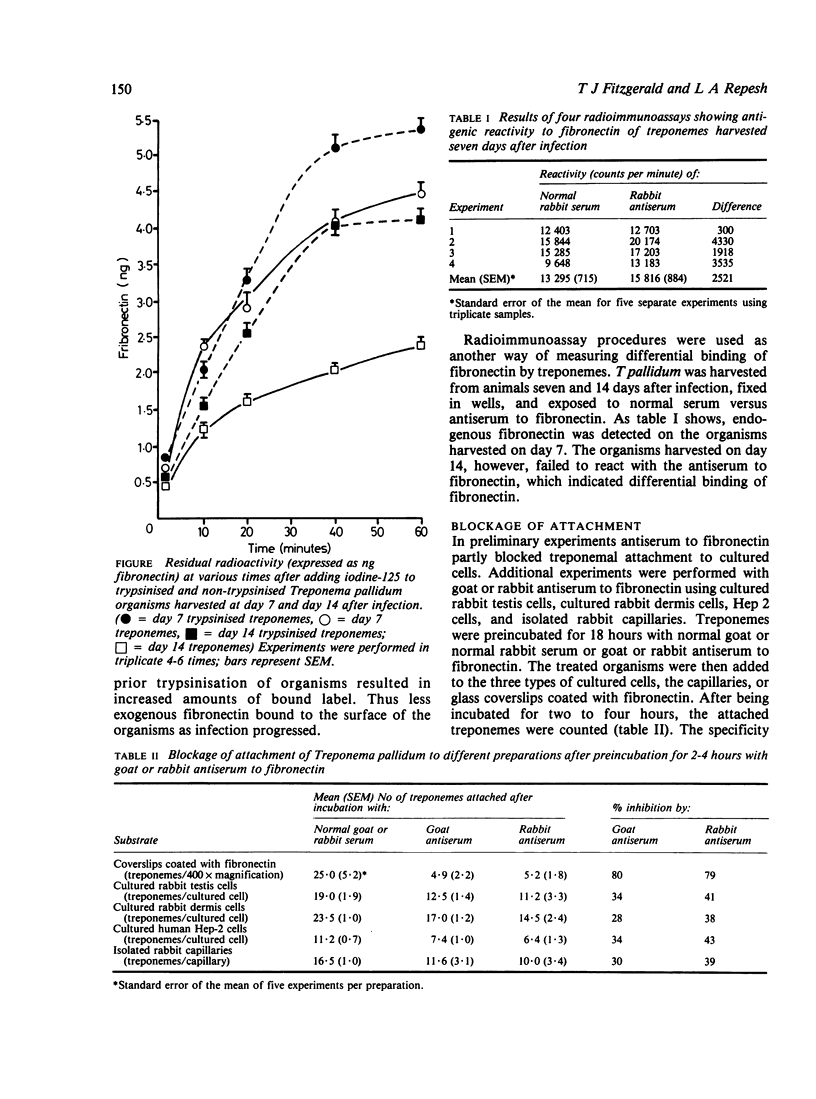
The adhesive or opsonic glycoprotein, fibronectin, is associated with the surface of Treponema pallidum as shown by immunofluorescence. A quantitative assay using iodine-125 (125I) showed that T pallidum harvested seven days after infection bound more fibronectin than T pallidum harvested 14 days after infection. This increased binding by "younger" organisms was confirmed by radioimmunoassay techniques. Fibronectin appears to have a role in treponemal attachment. Preincubation of T pallidum with goat or rabbit antibody to fibronectin blocked treponemal attachment to cultured cells and to isolated capillaries and inhibited treponemal virulence. Treponemes were incubated in glass wool columns pretreated with fibronectin and were then eluted from the columns. This technique yielded a population of T pallidum that failed to bind to fibronectin. Compared with treponemes eluted from control ovalbumin columns, organisms eluted from fibronectin columns attached to cultured cells in larger numbers but did not survive as long and were not as virulent. Findings are discussed in terms of the relevance of interaction between treponemes and fibronectin in the pathogenesis of T pallidum.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. Adherence of streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to fibronectin-coated and uncoated epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1261-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Rieber M. Antibodies to laminin in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.402-406.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu J. P., Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Beachey E. H. Interaction of human plasma fibronectin with cariogenic and non-cariogenic oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.162-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes E. C. Molecular characterization of receptor binding proteins and immunogens of virulent Treponema pallidum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Roccario E., Cho E., Kaplan J. E. Opsonic fibronectin after trauma and particle injection determined by a peritoneal macrophage monolayer assay. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jul;30(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Weber P. An affinity method for the rapid purification of opsonic alpha 2 SB glycoprotein from serum. Adv Shock Res. 1979;2:55–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Clumping of Staphylococcus aureus by human fibronectin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Oct;89(5):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00195_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Repesh L. A., Rice M., Urquhart A. Binding of glycosaminoglycans to the surface of Treponema pallidum and subsequent effects on complement interactions between antigen and antibody. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N. Attachment of Treponema pallidum to fibronectin, laminin, collagen IV, and collagen I, and blockage of attachment by immune rabbit IgG. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Dec;60(6):357–363. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.6.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudewicz P. W., Molnar J., Lai M. Z., Beezhold D. W., Siefring G. E., Jr, Credo R. B., Lorand L. Fibronectin-mediated uptake of gelatin-coated latex particles by peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):427–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., duBuy H. G. Effect of a potent interferon inducer on acute and chronic lactic dehydrogenase virus viremia. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):113–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.113-116.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen I., Hautanen A., Keski-Oja J. Interaction of viral envelope glycoproteins with fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):876–881. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.876-881.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Binding sites for streptococci and staphylococci in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.433-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Furcht L. T. Fibronectin: review of its structure and possible functions. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Aug;77(2):175–180. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12479791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Oberley T. D. Immune-mediated injury to basement membranes in mice immunized with murine laminin. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Apr;31(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Oberley T. D., Mosher D. F. Detection of autoantibodies and glomerular injury in rabbits immunized with denatured human fibronectin monomer. Am J Pathol. 1984 Oct;117(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kuusela P. Binding of human fibronectin to group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.29-34.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepose J. S., Bishop N. H., Feigenbaum S., Miller J. N., Zeltzer P. M. The humoral immune response in rabbits infected with Treponema pallidum: Comparison of antibody levels measured by the staphylococcal protein A-IgG (SPA-TP) microassay with VDRL, FTA-Abs, and TPI antibody responses during the development of acquired resistance to challenge. Sex Transm Dis. 1980 Jul-Sep;7(3):125–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quist E. E., Repesh L. A., Zeleznikar R., Fitzgerald T. J. Interaction of Treponema pallidum with isolated rabbit capillary tissues. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Feb;59(1):11–20. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P. S., Saba T. M. Fibronectin levels during intraperitoneal inflammation. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1411–1418. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1411-1418.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYKES J. A., MOORE E. B. A simple tissue culture chamber. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1960;18:288–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Blumenstock F. A., Weber P., Kaplan J. E. Physiologic role of cold-insoluble globulin in systemic host defense: implications of its characterization as the opsonic alpha 2-surface-binding glycoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Jaffe E. Plasma fibronectin (opsonic glycoprotein): its synthesis by vascular endothelial cells and role in cardiopulmonary integrity after trauma as related to reticuloendothelial function. Am J Med. 1980 Apr;68(4):577–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Mason J. M., Beachey E. H. Fibronectin-mediated binding of group A streptococci to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):805–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.805-810.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeltzer P. M., Pepose J. S., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Microassay for immunoglobulin G antibodies to Treponema pallidum with radioiodinated protein A from staphylococcus aureus: immunoglobulin G response in experimental syphilis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):163–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.163-170.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


