A 6-year-old boy was referred for cardiac evaluation of systemic arterial hypertension associated with occasional abdominal pain and headache crises. On clinical examination, a systolic murmur was heard at the cardiac base, radiating to the back. The arterial blood pressure was well above the 95th percentile for his age, with a pressure gradient between the upper and lower extremities (right arm, 160/105 mmHg; right leg, 80/60 mmHg). Chest radiography did not show any notable anomaly. Electrocardiography recorded left ventricular hypertrophy and nonspecific repolarization abnormalities. Echocardiography confirmed left ventricular hypertrophy, showing a normally functioning bicuspid aortic valve and a severely narrowed aortic isthmus, as well.
In order to better visualize and possibly treat the aortic coarctation, we performed cardiac catheterization. Angiography revealed a severe aortic coarctation (2 mm in diameter) just distal to the left subclavian artery origin, which was causing an ascending-to-descending aortic pressure gradient of 55 mmHg. The coarctation was clearly due to a patent ductus arteriosus closure that had acted as a sling, thus causing the aortic shelf-like deformity to appear (Fig. 1). Due to the discrete narrowing of the aortic isthmus, without hypoplasia of the adjacent aortic segments, a percutaneous balloon-expandable stent (Palmaz-Schatz® P308, Johnson & Johnson; New Brunswick, NJ) was implanted (Fig. 2) and was expanded to 10 mm. The pressure gradient (Fig. 3) disappeared completely.
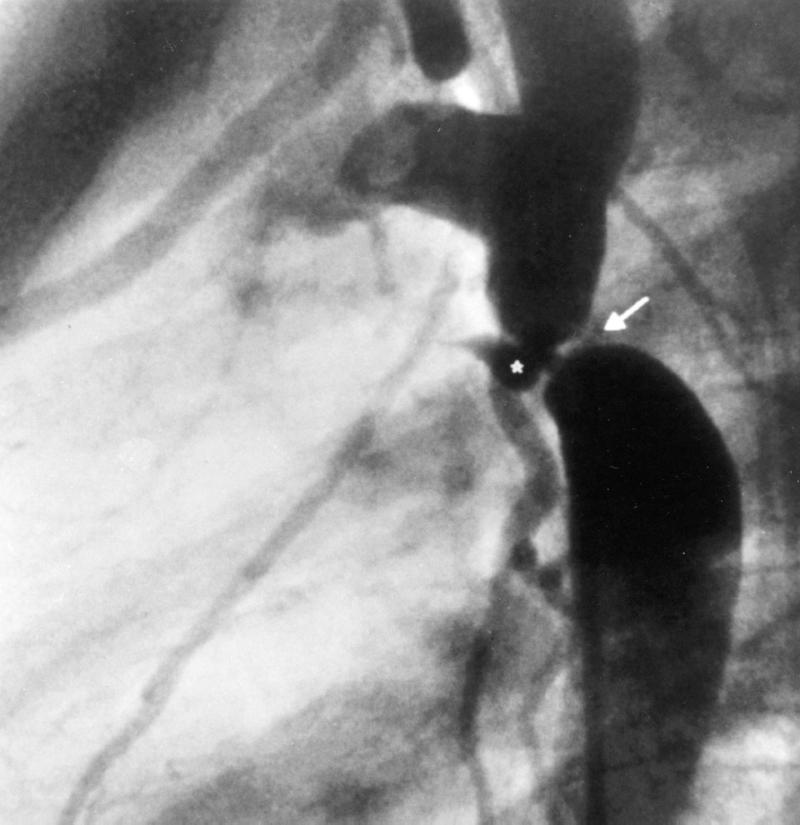
Fig. 1 Aortogram of the coarctation site (lateral view). Note the ligamentum arteriosum (*) that pulls back the aortic wall, producing a shelf-like deformity of the aortic isthmus (arrow).
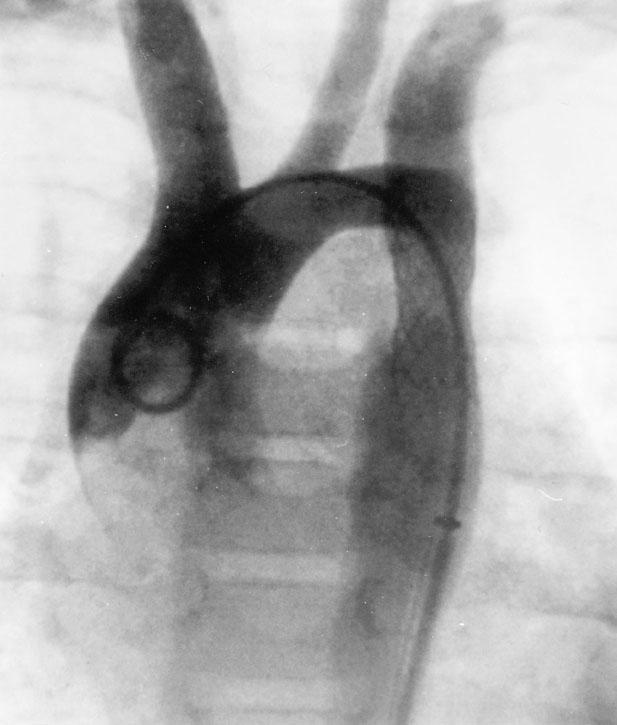
Fig. 2 Aortogram after endovascular stent implantation (postero-anterior view). The aortic coarctation has disappeared, leaving only a slight poststenotic ectasia of the descending aorta.
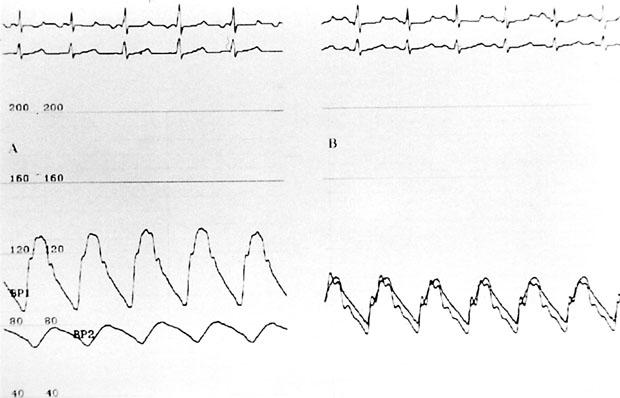
Fig. 3 A) Pressure gradient across the coarcted segment. Note the blood pressure difference between the ascending aorta (upper trace) and the descending aorta (lower trace), which shows a blunted pressure tracing downstream from the stenosed segment. B) The pressure gradient across the aortic isthmus is completely abolished after stent implantation.
Footnotes
Address for reprints: Giuseppe Santoro, MD, Via Vito Lembo, 14, 84131 – Salerno, Italy
This paper has been supported by the Programma Operativo del Piano CCCN-5 B006 of the Ministero dell'Università e Ricerca Scientifica (MURST) and the European Community (no. 711/1998).


