Abstract
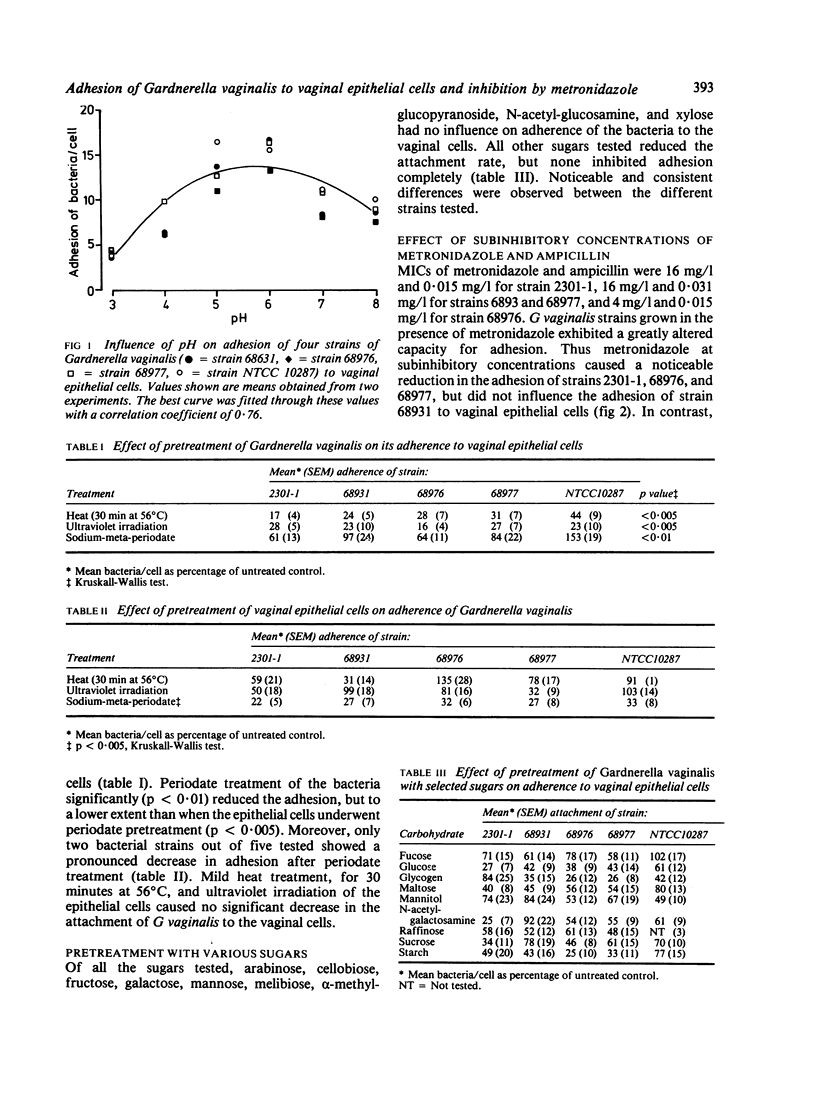
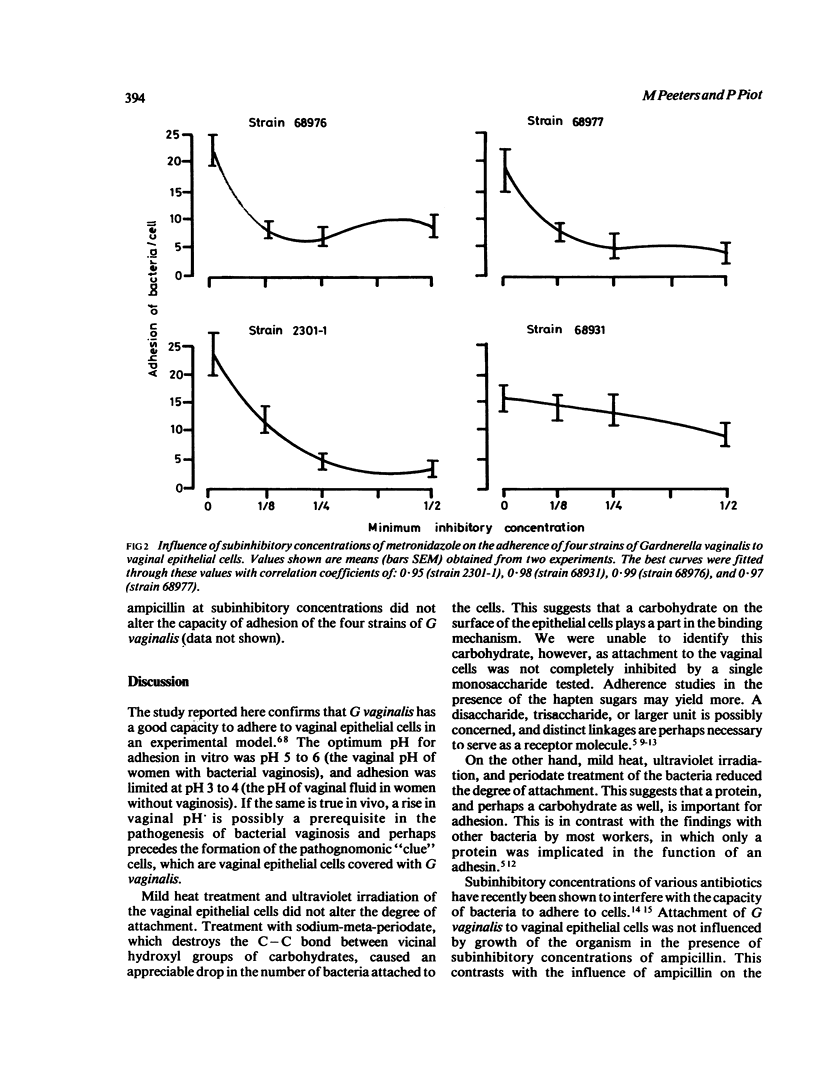
Variables affecting the adherence of Gardnerella vaginalis to human vaginal epithelial cells were examined in vitro. Adherence depended on pH, with maximum attachment occurring between pH 5 and pH 6. Preincubation of the bacteria at 56 degrees C for 30 minutes and ultraviolet irradiation resulted in a noticeable decrease in adherence. In contrast, adherence was not altered by preincubating the epithelial cells under these conditions. Periodate oxidation of the vaginal cells caused an appreciable reduction in subsequent adherence of G vaginalis. None of the 19 single carbohydrates tested inhibited adherence completely. Metronidazole at subinhibitory concentrations for G vaginalis, appreciably reduced the adhesive capacity of G vaginalis, whereas subinhibitory concentrations of ampicillin did not.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. Adherence of streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to fibronectin-coated and uncoated epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1261-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg J., Poxton I. R., Weir D. M., Ross P. W. Binding of type-III group-B streptococci to buccal epithelial cells. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Aug;15(3):363–372. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsdon M. J., Taylor G. E., Pead L., Maskell R. Corynebacterium vaginale and vaginitis: a controlled trial of treatment. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):501–503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Amatnieks Y. E. Relative susceptibilities of Gardnerella vaginalis (Haemophilus vaginalis), Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Bacteroides fragilis to Metronidazole and its two major metabolites. Sex Transm Dis. 1980 Oct-Dec;7(4):157–160. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Austin T. W., Pattison F. L., Schieven B. C. Inhibition of Haemophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginale) by metronidazole, tetracycline, and ampicillin. Sex Transm Dis. 1979 Jul-Sep;6(3):199–202. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197907000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Schneider J., Kaye D., Levison M. E. Adherence of bacteria to vaginal epithelial cells at various times in the menstrual cycle. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):194–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.194-197.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Gillespie R. M., Bhatti A. R., White L. A. Differences in the adhesive properties of Neisseria meningitidis for human buccal epithelial cells and erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.106-113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosbeck K., Mett H., Huber U., Bohn J., Petignat M. Effects of low concentrations of antibiotics on Escherichia coli adhesion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):864–869. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


